- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Why does pain persist after tooth extraction?

If a tooth is severely decayed by caries, improperly positioned in the mouth, or is broken so that it cannot be restored - in this case, it is necessary to resort to its removal. However, this procedure is often associated with psychoemotional trauma of the patient and can cause various complications. Pain is most often observed after tooth extraction. When is it a normal temporary occurrence and when is an alarm?
Why does the gum hurt after tooth extraction?
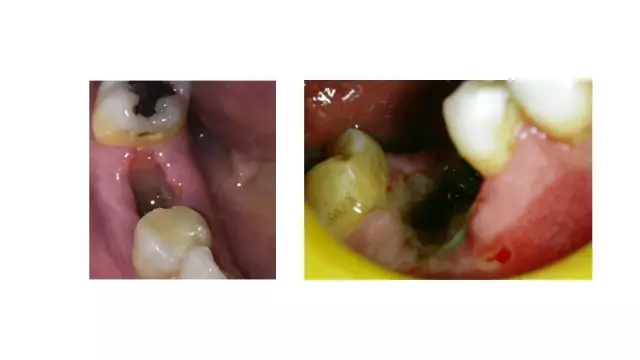
Like any damage in which soft tissue trauma occurs, the tooth extraction procedure cannot do without painful sensations, since this affects the gum tissue, periosteum and nerve endings. And if the gum hurts after tooth extraction, then this is a normal postoperative phenomenon. In normal cases, it goes away in 1-2 days, but if it persists for a long time, this indicates the presence of an infection in the wound.
The degree of injury to bone tissue depends on the complexity of removal, therefore, in especially severe cases, the body's reaction is more significant. Sometimes, before performing a resection, the doctor will first need to make an incision in the gum to allow access to the bone tissue. Usually, such manipulations are carried out with large or uneven roots, the absence of a crown.
Therefore, there is nothing surprising in the fact that after tooth extraction, the jaw hurts, the gums and cheek swell, and discomfort occurs. All these unpleasant symptoms, as a rule, disappear after a couple of days, but sometimes the swelling does not subside, but only increases, which indicates the onset of inflammation of the hole (alveolus) - alveolitis. The main causes of this disease and pain after tooth extraction:
- The ingress of foreign particles into the hole (contents of a carious cavity, dental deposits, fragments of an extracted tooth) quite often leads to inflammation of the hole;
- The destruction of the blood clot that forms in the alveolus and protects the wound from infection, promotes faster healing of the gums. If the hygiene of the hole is not observed, the use of rough or hot food may cause the destruction of the clot and inflammation may begin;
- Removing a tooth in parts sometimes injures the surrounding tissue, the bony walls of the alveoli are partially destroyed, which greatly complicates the healing of the wound and is often accompanied by complications;
- Dry socket - most often contributes to the fact that the jaw hurts after tooth extraction. It is formed if the blood clot did not form for some reason or was accidentally removed. As a result, alveolitis develops or inflammation of the gums occurs, since the wound becomes open and accessible for penetration of various infections. After a while, a purulent plaque forms on top of the hole, which the dentist removes with the help of special disinfectants;
- Osteomyelitis is a more serious alveolitis. It is characterized by decreased immunity, fever, severe pain in the gums and swelling.
Sometimes after removal the adjacent tooth hurts. Such sensations appear as a result of the fact that after the procedure there is pressure on the gums and the newly formed wound. As soon as the adjacent teeth stop moving and bending over, the discomfort immediately disappears. Also, often the adjacent tooth hurts after extraction if a nerve was touched, which is fraught with complications.
Pain after tooth extraction usually occurs after the anesthesia stops acting, and blood may flow from the hole for some time. To stop the bleeding, you need to put a cotton swab on the empty alveolus, bite tightly and hold it for at least half an hour. In order to prevent infection from entering the wound, it is important not to damage the blood clot that forms at the healing site.
Tooth hurts after removing a nerve
Very often, after the depulpation procedure, patients come back to the dentist with complaints that a tooth hurts. In this situation, discomfort and discomfort may be temporary as a result of surgery. But in some cases, pain occurs due to improper tooth treatment.
Pulpitis is an inflammation of the pulp - the fibrous tissue that fills the cavity of the tooth, containing nerve fibers, as well as arterial and venous vessels. Caries often causes damage to the outer membranes of the tooth and penetration of the infection. To eliminate this problem, the doctor performs a depulpation procedure. After removing the nerve, the tooth usually hurts for several days, this is completely normal. However, in some cases, poor quality dentist work can cause pain. The fact is that an inflammatory process develops in a closed tooth cavity.

Most often, pain in a tooth after removal of a nerve occurs if the canals were poorly cleaned, the pulp (nerve tissue of the tooth) was not completely removed, or during the procedure, the doctor did not take into account the degree of sedimentation of the filling material, therefore, a cavity remained unfilled to the end. In all these cases, it is necessary to consult a doctor and re-treat to eliminate the defects.
Also, if a nerve has been removed, and the tooth continues to hurt for more than two days when biting or touching, this is a symptom of trigeminal neuralgia. The disease occurs as a result of damage to the alveolar nerve. At the same time, the patient initially feels numbness, which then turns into constant pain. In the future, it develops into neuralgic attacks, and the discomfort has the character of short bursts.
To avoid the occurrence of various complications and pain after tooth and nerve extraction, you must adhere to simple rules: refrain from eating for 4-5 hours after the operation, do not eat hot, salty or spicy foods, and chew food on the opposite side, where there is no wound … Teeth can only be brushed the next day.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.