- Author Rachel Wainwright [email protected].
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Uveitis
General characteristics of the disease

Uveitis is an inflammatory process in the area of the choroid. Depending on the localization of inflammation, several types of uveitis are distinguished.
Anterior uveitis develops with inflammation of the ciliary body and the iris of the eye. This type of disease is otherwise called iridocyclitis.
Peripheral uveitis affects not only the ciliary (aka ciliary), but also the vitreous body of the eye, as well as the retina and choroid - the posterior part of the choroid.
With chorioditis or chorioretinitis, a type of posterior uveitis of the eyes, the choroid, retina and optic nerve are affected.
Uveitis can be acute or chronic. The disease progresses to the chronic stage if the patient's symptoms of uveitis last 6 or more weeks.
Without timely treatment, uveitis can lead to an accretion of the lens to the pupil, to cataracts, secondary glaucoma, edema or detachment of the retina, clouding of the vitreous humor of the eye.
Causes of eye uveitis
The causes of recurrent uveitis are often allergic. Moreover, with inflammation of the anterior choroid, the cause of uveitis is most often an allergen of streptococcal etiology. And inflammatory processes in the area of the posterior membrane usually cause toxoplasmins.
The cause of uveitis of tuberculous etiology is the infection of the eye with the mycobacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Uveitis of syphilitic, cytomegalovirus, herpeutic nature is also possible.
In children, the cause of uveitis is often all sorts of trauma to the choroid. Among the possible causes of uveitis are also called systemic inflammatory processes in the body with rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, sarcoidosis, Reiter's syndrome, etc.
Eye uveitis symptoms
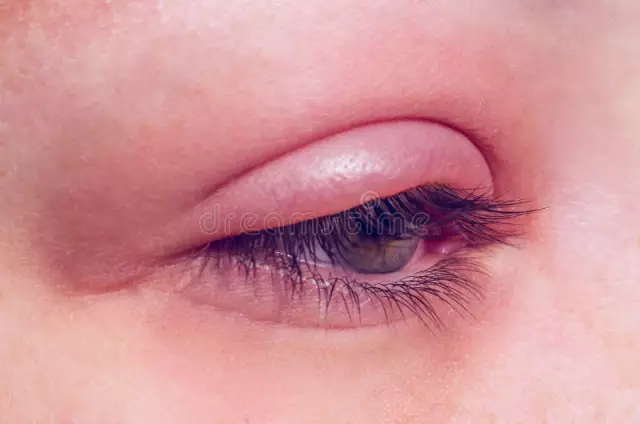
Uveitis symptoms differ depending on the type of disease. Typical symptoms of anterior uveitis are:
- photophobia,
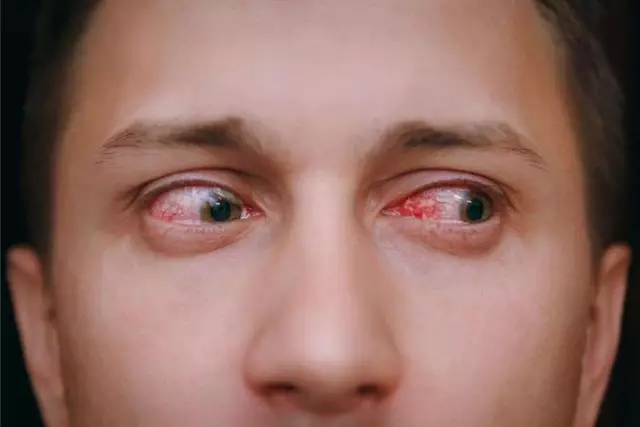
- redness and soreness of the eyes
- significant decrease in visual acuity,
- chronic lacrimation,
- constriction of the pupil,
- increased intraocular pressure.
Among the characteristic symptoms of peripheral uveitis are called:
- symmetrical damage to both eyes,
- the appearance of spots (flies) before the eyes,
- decreased visual acuity.
The symptoms of posterior uveitis appear late enough. This type of inflammation of the choroid is not characterized by pain or redness. Most often, posterior uveitis is manifested by a gradual decrease in vision, distortion of objects and the formation of a veil in front of the eyes.
Diagnostics of the eye uveitis
In the diagnosis of uveitis, the patient's history and information about his immunological status play an important role. With the help of an ophthalmological examination, the localization of inflammation in the choroid is clarified.
The etiology of eye uveitis is determined by skin tests for bacterial allergens (streptococcus, staphylococcus or toxoplasmin). In the diagnosis of a disease of tuberculous etiology, the decisive symptom of uveitis is the combined lesion of the conjunctiva of the eyes and the appearance on the patient's skin of specific acne - flikten.
Systemic inflammatory processes in the body, as well as the presence of infections in the diagnosis of eye uveitis, is confirmed by tests of the patient's blood serum.
Treatment of eye uveitis

The treatment regimen for uveitis depends on the etiology and type of disease. However, in any form of inflammation, symptomatic treatment of uveitis involves the prevention of destruction of the structure of the vitreous body of the eye and lens. For this purpose, the patient is prescribed solutions of Atropine, Scopolamine, Adrenaline, etc.
In the drug treatment of streptococcal uveitis, broad-spectrum antibiotics, corticosteroids and vitamin therapy are used. The extinction of the inflammatory process occurs approximately 3-5 days of treatment of eye uveitis.
With uveitis of the eyes against the background of toxoplasmosis, therapy with Sulfadimezin and Chloridine is performed. Treatment of this form of uveitis lasts at least 2 weeks with constant monitoring of the patient's kidneys and blood.
Uveitis of tuberculous etiology is arrested with anti-tuberculosis chemotherapy. In especially severe cases, with significant destruction of the vitreous body of the eye, surgical treatment of uveitis is sometimes required.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!