- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Swelling after wisdom tooth extraction
The content of the article:
- The reasons
-
Manifestations of edema after wisdom tooth extraction
- The normal course of the postoperative period
- What complications can occur after removing a wisdom tooth
-
How to relieve swelling after removing a wisdom tooth on the lower jaw and upper
Prevention of complications
- Video
Edema after the removal of a wisdom tooth (tooth extraction) is almost always formed, but normally it does not last long and goes away on its own. Given the localization, the invasiveness of the procedure, and sometimes the need for additional incisions, the gums and cheeks can swell for a period of 1 to 5 days. Puffiness may be accompanied by the release of a small amount of blood, soreness of the gums. We can talk about a pathological condition when, after the extraction of a tooth, the body temperature rises, the edema does not subside, but on the contrary, it increases, the pain sensations increase.

Normally, edema after the removal of a wisdom tooth disappears without treatment in 1-5 days
The reasons
The pathological process can develop with alveolitis, incision of the gums during surgery (for example, with an abscess), removal of impacted or dystopic teeth, the presence of pathologies of blood vessels in the patient, arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus, reduced immunity.
Risk factors for the development of swelling of the soft tissues of the gums are:
- absence of a blood clot in the hole after the operation;
- an allergic reaction to the analgesic and / or antiseptic drugs used during the procedure;
- poor-quality processing of the hole after tooth extraction;
- incomplete tooth extraction;
- the presence of a cyst.
Manifestations of edema after wisdom tooth extraction
How long the swelling lasts after the removal of a wisdom tooth in the lower or upper jaw depends on the qualifications of the dentist, the type of pain relief, the quality of the antiseptic, and also on how difficult the intervention was.
In case of alveolitis (inflammation of the socket of the extracted tooth), in addition to swelling, the patient may have bad breath, severe pain, which, after the cessation of the action of analgesics, does not calm down gradually, but increases.
The sudden development in a patient of a tumor, shortness of breath, a state of panic may indicate the occurrence of anaphylactic shock.
After a difficult, traumatic removal of a wisdom tooth (for example, with its dystopia), discomfort can bother a person for one to two weeks.
The normal course of the postoperative period
The normal course of the period after the extraction of the wisdom tooth is characterized by the following features:
- A satisfactory general condition.
- The body temperature does not rise; if it was increased before tooth extraction, then it gradually normalizes.
- Puffiness is limited to the tissues surrounding the extracted tooth, does not extend to the patient's face, and is not significant.
- The pain is tolerable, if necessary, it is easily stopped by analgesics, lasts no more than three to four days, all this time gradually subsiding.
- There is no hyperemia of the skin and mucous membranes.
- There is no unpleasant smell or taste in the mouth.
What complications can occur after removing a wisdom tooth
The table shows some of the most common complications after wisdom tooth extraction:
| Complication | Clinical signs |
| Damage to the gums and mucous membranes of the mouth | Discharge of large amounts of blood, pain, hematoma |
| Trauma to the seventh tooth | Visible damage to tooth tissue, pain when biting |
| Nerve injury (lingual and / or mandibular) | Numbness of the tongue and / or lower lip |
| Damage to the lower jaw (fracture, dislocation) | Severe pain in the lower jaw, difficulty speaking or chewing food |
The development of complications can also be indicated by the presence of shortness of breath, tachycardia, an increase in body temperature above 38 ° C, deterioration of the general condition, difficulty in swallowing, pain when moving the jaw.
The following phenomena also indicate the appearance of adverse effects of removal:
- sharp pain in the gums and / or cheek;
- discharge of pus from the hole;
- severe bleeding from the hole;
- discoloration of the gums;
- an increase in edema in comparison with the first days after surgery.
If one or more of these symptoms are found, you should immediately consult a doctor.
How to relieve swelling after removing a wisdom tooth on the lower jaw and upper
Immediately after the extraction of the tooth, the patient is advised to sit quietly for 15-30 minutes, the tampon left by the doctor should be kept in the mouth for 30-40 minutes. After the procedure, you must follow all the instructions of the dentist.
If the swelling is significant (for example, it interferes with opening your mouth wide, taking solid food), in the first one or two days after tooth extraction, you can do cold compresses, that is, apply cold to the cheek. Sleeping on a high pillow can contribute to the early removal of puffiness.
If necessary, the dentist can prescribe to the patient:
- analgesics;
- antibiotics;
- anti-inflammatory drugs.
A few days after the extraction of the tooth, you can start rinsing the mouth with solutions of medicinal plants (chamomile, oak bark, sage, calendula) or antiseptic preparations, but you should not do this too intensively so as not to disrupt the healing process. It is best to simply draw up and keep the solution in your mouth for a while. Rinsing is carried out 3-4 times a day on the recommendation of a doctor.
Helps relieve puffiness by rinsing the mouth with a salt solution. To prepare it, take 1 teaspoon of table salt in 1 glass of water at room temperature. To prepare an alkaline solution, 0.5 teaspoon of soda is added to 1 glass of water. Sometimes rinse your mouth with a solution of propolis (5 drops of the substance per 1 glass of water).
In a severe course of the pathology, repeated surgical intervention may be required. With the development of suppuration, the patient will undergo wound sanitation (opening of the abscess). It may be necessary to rinse the well with an antiseptic solution, the use of anti-infectious drugs.
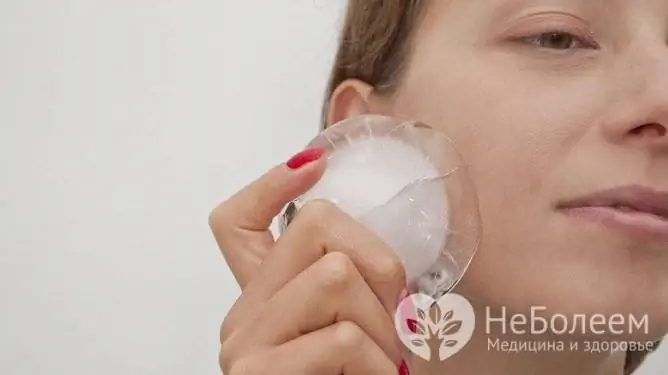
Apply cold to the cheek to reduce swelling.
Prevention of complications
To prevent the development of excessive swelling and other complications, a number of recommendations should be followed:
- refuse to eat within 3 hours after tooth extraction to form a clot and fix it in the hole;
- do not rinse the mouth at first after the operation (the attending physician will indicate the exact dates);
- for a week after the procedure, avoid chewing food in the area of the extracted tooth;
- brush your teeth in the area of the hole carefully so as not to damage it; it is recommended to use a soft toothbrush until complete healing;
- avoid eating too hot, cold, solid foods, spicy, spicy foods, carbonated drinks;
- do not touch the wound with your hands or any objects;
- refuse to visit the bath and sauna until the gums are healed;
- refuse to drink alcohol (may provoke bleeding);
- avoid excessive physical and psycho-emotional stress.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Aksenova Medical journalist About the author
Education: 2004-2007 "First Kiev Medical College" specialty "Laboratory Diagnostics".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.