- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Wisdom tooth hurts - treat or remove

Of the thirty-two teeth, four complete both rows located on the upper and lower jaws. According to the anatomical formula adopted by doctors all over the world, the last molars are numbered "eight". Accordingly, the teeth located in front of the last, "seven". Teeth with serial numbers: six and seven are exposed to the greatest load during chewing. The latter cut through much later than the rest. Some people still have twenty-eight teeth until old age. That is, not all of them have root "eights". These people do not understand how a wisdom tooth hurts, since it is absent. It often happens like this: the upper "eights" cut through, and the lower ones remain inside the jawbone, in a state of reserve.
When dentists find that a wisdom tooth is hurting, rather than the nearby 7s, many dentists suggest removal. For some reason, it is believed that a person does not need the last teeth at all. The diet changed, and the need for powerful chewing teeth disappeared. Since the "eights" are considered rudiments, their removal is considered quite normal manipulation. In Germany, for example, if a person does not even have a wisdom tooth hurting, doctors still insist on removing it, since the G8 is much more troublesome than practical. In the recent past, doctors in East Germany did the same with the appendix. Considering it an unnecessary rudiment, it was removed during the neonatal period. A minor scar remained, but the person was protected from unforeseen life situations in which acute appendicitis may develop. However, the same German histologists came to the conclusion that the removal of a powerful lymphoid organ is not at all as harmless as it seems at first glance. The situation is approximately the same with the number eight molar teeth. It seems to be rudiments, but for some reason they appear in people, regardless of changes in nutrition over several centuries.
Why does a wisdom tooth hurt
Wisdom teeth erupt at that age when the growth processes are completely completed in the human body. The appearance of "eights" indicates the completion of the formation of tissues and organs. Due to the phenomenon of acceleration, wisdom teeth appear much earlier, therefore, at a younger age, young people may complain that a wisdom tooth hurts.
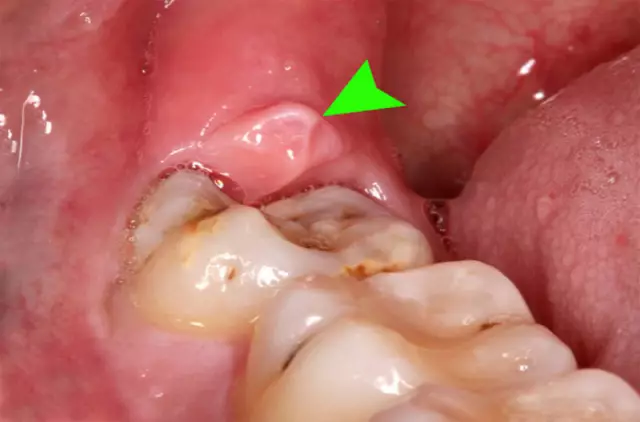
Teething in humans at the age of 20-25 or a little later is painful. By this age, the jaw is fully formed, the mucous membrane of the oral cavity becomes hard. Dental sprouts hardly break it, therefore, when teething, a wisdom tooth hurts, not yet having time to appear. When one or more cusps erupt, the rest of the tooth remains beneath a thick layer of oral mucosa. This forms a hood that inhibits further tooth growth. Pericorneitis develops, in which surgery is indispensable. It is important not to allow a situation when the wisdom tooth hurts, the gum swells with the capture of the cheek. With the resulting flux, a surgical dissection of the hood surface, not only is very painful, but also fraught with infectious complications.
A different situation in which a wisdom tooth hurts occurs when the direction of growth is wrong. When the dentition is already formed, there is not enough space for the newly erupting tooth. "Eight" begins to grow towards the dentition, pressing the tip to the seventh tooth. As a result, a domino effect occurs: under pressure, one tooth deflects forward, and the next one behind it. As a result, the so-called crowding of teeth is formed, in which not only the wisdom tooth hurts, the jaw is taken away from the pain. Such clinical cases are always interpreted unambiguously - the wisdom tooth must be removed.
Wisdom tooth hurts, what to do
When a tooth hurts, it does not matter "wisdom" or "eye", you need to see a doctor. The dentist will always suggest possible options. The "eight" is subject to unconditional removal in the following situations:
- The eighth tooth is in a horizontal position relative to the jaw. Its further growth leads to the destruction of the seventh tooth and the displacement of the entire dentition. The eruption of a wisdom tooth in this position is impossible;
- The growth of the tooth is directed towards the cheek. In such cases, the wisdom tooth grows incorrectly, the gums and cheek hurt. With each chewing movement, the mucous membrane of the cheek "bites", constant irritation of the wound leads to the development of stomatitis;
- Initially fragile eighth molar. Immediately after eruption, or long before it, pulpitis develops - an acute inflammation of soft tissues ("nerve"). The wisdom tooth is destroyed, the gums hurt, migraine develops.
The rest of the indications for G8 extraction are exactly the same as for other teeth, including the incisors:
- Complete destruction of enamel due to periodontitis - diffuse inflammation of the hard shell of the tooth;
- Dental canal obstruction;
- Lack of effect from therapeutic treatment: filling, implantation.
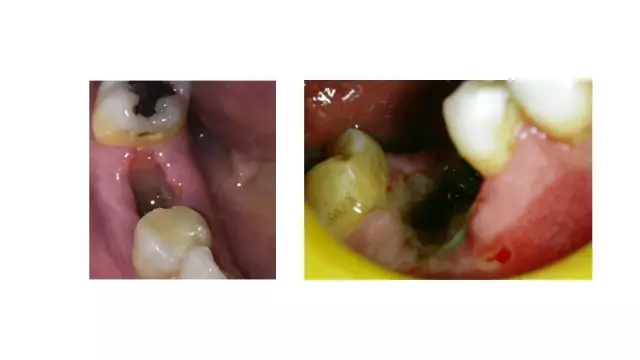
The formation of a cyst, as a rule, leads to the development of purulent inflammation of the bone tissue. In advanced cases, the wisdom tooth hurts, the jaw is destroyed due to osteomyelitis. So the defeat of one single tooth can lead to the loss of the jaw with the entire dentition.
Pain after removing a wisdom tooth
After the removal of the figure eight, especially from the lower jaw, the problems with the rest of the teeth are solved by orthodontists. They place braces to correct the bite.
Patients are often worried about pain after wisdom tooth extraction, which does not go away for a long time. This happens because the extraction of the eighth painter is a technically very difficult operation with limited access. As a rule, the roots of a wisdom tooth are twisted and multidirectional, similar to a "tee" fish hook. Removing the figure eight leads to injury to the soft tissues of the gums and jaw bone. Even after the operation, the patient feels as if a wisdom tooth hurts, as pains of the same intensity are felt. This indicates an inflammatory process, the cause of which (a bad tooth) has been eliminated, but the consequences remain.

Usually, prescribing antimicrobial drugs will resolve the problem within a few days.
If the extraction of the tooth was difficult with cutting the gums and then suturing the wound, a hematoma may form. It either dissolves or is opened under local anesthesia.
How best to resolve the issue if a wisdom tooth hurts
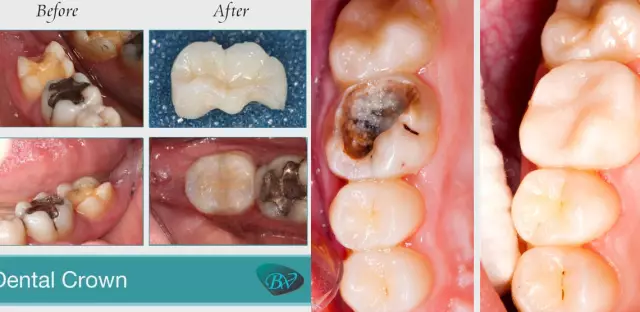
In each case, the issue is resolved individually. When a wisdom tooth hurts, what to do is decided by the dentist, based on the clinical picture of the disease. Wisdom teeth are subject to conservative treatment. In addition, the saved "eights" allow the installation of fixed prostheses (bridges). Most often, the sixth and seventh molars are destroyed, therefore, the installation of a bridge between the eighth and fifth painter solves the problem of chewing and the normal position of the remaining teeth.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.