- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Increased cortisol: symptoms, signs, causes of increased cortisol in women
The content of the article:
- Causes of high cortisol levels
- Signs of high cortisol
- Blood test for cortisol: how to donate correctly
- How to lower blood cortisol levels
Cortisol (hydrocortisone) is a steroid hormone secreted by the cells of the cortex, that is, the outer layer of the adrenal glands under the influence of adrenocorticotropic hormone produced by the pituitary gland. He takes an active part in the regulation of many biological processes in the body:
- regulation of carbohydrate, protein, fat metabolism;
- contraction of muscle fibers;
- decreased activity of inflammatory processes;
- suppression of histamine activity and, due to this, a decrease in the severity of allergic reactions;
- the formation of stress reactions (therefore, it is sometimes called the fear hormone or death hormone).
In those cases when the level of cortisol is increased, not only endocrine, but also systemic disorders develop.
Causes of high cortisol levels
The level of cortisol in the blood is not constant; it changes throughout the day. It is highest in the morning hours, gradually decreases during the day and reaches its minimum by 22-23 hours. In women, the level of the hormone in the blood depends on the phase of the menstrual cycle. In pregnant women, cortisol is doubled or more (maybe a fivefold increase), but this is not a pathology. In addition, physiological increases in hydrocortisone occur during lactation.

Normal cortisol levels rise during pregnancy and lactation
In women, cortisol is elevated in the presence of polycystic ovary disease. Polycystic ovary syndrome is manifested by the presence in the ovaries of many cystic formations, the occurrence of which is associated with a whole complex of endocrine disorders (dysfunctions of the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, adrenal cortex, pancreas and thyroid glands, ovaries).
Certain medications can provoke an increase in cortisol in both men and women:
- amphetamines;
- oral contraceptives, estrogens;
- corticotropin;
- methoxamine;
- vasopressin;
- interferon;
- naloxone;
- metoclopramide.
An excess of the hormone in the blood can be caused by smoking, drinking alcohol and drugs.
An increase in the level of hydrocortisone is observed with the following pathologies:
- hyperplasia of the adrenal cortex;
- benign (adenoma) and malignant (carcinoma) tumors of the adrenal cortex;
- dysfunction of the pituitary gland;
- Itsenko-Cushing's disease;
- mental disorders (depression, stressful conditions);
- liver disease (chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis, chronic liver failure);
- some systemic diseases;
- chronic alcoholism;
- obesity or anorexia.
Signs of high cortisol
When cortisol is elevated, symptoms are as follows:
- increased appetite (and the desire to eat something high-calorie or sweet);
- increased sleepiness;
- decreased concentration, memory impairment;
- obesity - in the case when cortisol is increased, the secretion of estrogen is suppressed and the prerequisites are created for the deposition of adipose tissue;
- depressed mood, depressive states - high levels of cortisol suppress the activity of dopamine and serotonin (the so-called hormones of pleasure);
- poor wound healing;
- joint pain.
In women, it can be suspected that cortisol is elevated, with the appearance of hirsutism, edema, menstrual irregularities, as well as recurrent, treatment-resistant thrush (vaginal candidiasis).
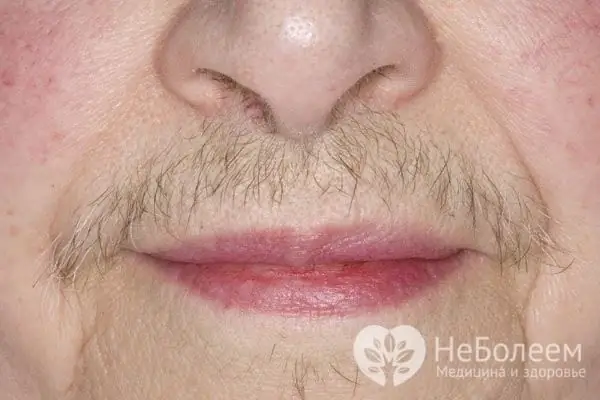
Hirsutism may be a symptom of high cortisol in women.
Increased cortisol in children is manifested by premature puberty, both in girls and boys.
If cortisol levels remain high for long periods of time, the consequences can be serious, including:
- arterial hypertension;
- decrease in muscle tissue volume;
- increased deposition of visceral fat;
- decreased general immunity;
- atherosclerosis;
- diabetes;
- ischemic heart disease, myocardial infarction;
- stroke;
- infertility.
Therefore, this condition should be promptly identified and actively treated.
Blood test for cortisol: how to donate correctly
To determine the level of hydrocortisone, in addition to actually detecting it in the blood, a general and biochemical blood test is performed, a study of urine collected in 24 hours (daily urine), in some cases (rarely) - a saliva test.
In an adult, the concentration of hydrocortisone in the blood is 138-165 nmol / l. In different laboratories, the indicators of the norm may differ, therefore, when a result is obtained, it is evaluated based on the reference values given by the laboratory that conducted the study.
When referred to a laboratory for cortisol testing, patients are given the following recommendations:
- follow a diet with a low salt content (no more than 2-3 g per day) for three days before blood sampling;
- limit physical activity at least 12 hours before taking the test.
48 hours before the upcoming study, all drugs that can affect the level of cortisol (phenytoin, androgens, estrogens) are canceled. If this is not possible, then in the referral form indicate the drug taken and its dosage.
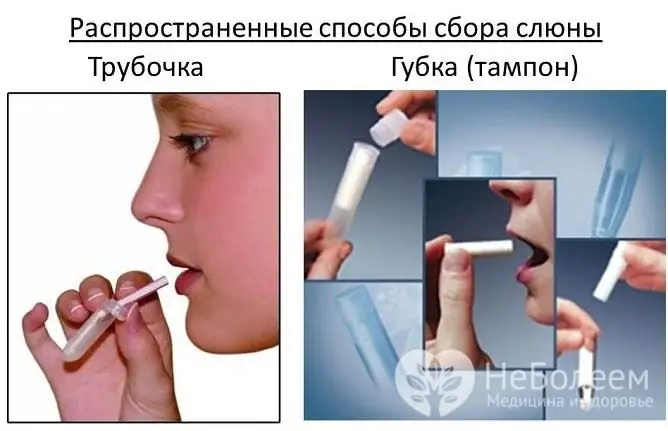
In some cases, a cortisol test is done by examining saliva.
Blood sampling is performed between 6 and 9 am. Before blood sampling, patients are placed on a couch in a quiet room and allowed to rest for at least 30 minutes, after which blood is taken from a vein. If it is necessary to determine the daily dynamics of cortisol, a second blood sampling is prescribed in the period from 16 to 18 hours.
How to lower blood cortisol levels
In cases where the hypersecretion of cortisol is associated with one or another disease, it is actively treated by a doctor of the appropriate profile (endocrinologist, gynecologist, hepatologist, narcologist).
If the increase in cortisol is due to functional reasons, modification of lifestyle and diet is recommended to reduce it.
- Adhere to the daily routine, taking sufficient time for adequate rest and night sleep.
- Go to bed no later than 22 hours, the duration of sleep should be 8-9 hours. If you have difficulty falling asleep, you should consult a doctor for the selection of a sleeping pill.
- Introduce as many positive emotions into your life as possible.
- Learn relaxation techniques, develop stress resistance.
- Drink enough water (1.5-2 liters) throughout the day.
- Refuse caffeine-rich drinks (coffee, strong tea, cola, energy), give preference to water instead.
- Regularly include fish dishes, especially seafood in the diet. If this is not possible for one reason or another, you can take fish oil in capsules.
- Exclude refined foods (white rice, pasta, pastries, white bread) from the diet.
- Avoid physical activity that causes a significant increase in heart rate (such as running or cycling), as they increase cortisol levels. Instead, it is recommended to practice Pilates, yoga, swimming.
YouTube video related to the article:

Elena Minkina Doctor anesthesiologist-resuscitator About the author
Education: graduated from the Tashkent State Medical Institute, specializing in general medicine in 1991. Repeatedly passed refresher courses.
Work experience: anesthesiologist-resuscitator of the city maternity complex, resuscitator of the hemodialysis department.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.