- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Blood sugar: permissible fasting rate, measurement methods
The content of the article:
- Blood sugar rate
- What determines the sugar level
- Methods for measuring blood sugar
- How is a blood sugar test done?
- Measuring blood sugar at home
The blood sugar rate is the same for both men and women. Various factors affect the level of glucose uptake. A deviation from the norm up or down can have negative consequences and requires correction.
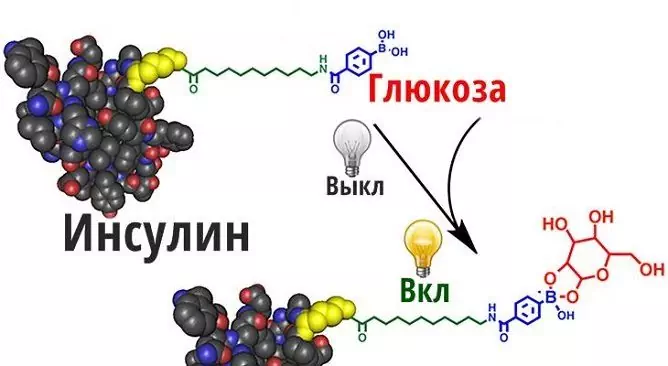
One of the main physiological processes in the body is glucose uptake. In everyday life, they use the phrase "blood sugar", in fact, blood contains dissolved glucose - simple sugar, the main carbohydrate in blood. Glucose plays a central role in metabolic processes, being the most versatile energy resource. Getting into the blood from the liver and intestines, it is carried with the bloodstream to all cells of the body and supplies energy to the tissue. When the level of glucose in the blood rises, the production of insulin, a hormone of the pancreas, increases. The action of insulin is the process of glucose transfer from the intercellular fluid into the cell and its utilization. The mechanism of glucose transport into the cell is associated with the effect of insulin on the permeability of cell membranes.

Insulin helps glucose to enter the cell, where glucose serves as an energy source
The unused portion of glucose is converted into glycogen, which reserves it to create an energy store in liver and muscle cells. The process of synthesizing glucose from non-carbohydrate compounds is called gluconeogenesis. The breakdown of accumulated glycogen to glucose is by glycogenolysis. Maintaining blood sugar levels is one of the main mechanisms of homeostasis, in which the liver, extrahepatic tissues and a number of hormones (insulin, glucocorticoids, glucagon, steroids, adrenaline) are involved.
In a healthy body, the amount of glucose supplied and the response fraction of insulin always correspond to each other.
The consequence of absolute or relative insulin deficiency is the development of diabetes mellitus.
Blood sugar rate
The glucose content in the blood is called glycemia. The glycemic level can be normal, low, or high. The unit of measure for glucose is millimole per liter (mmol / L). Under the normal state of the body, the norm of blood sugar in adults ranges from 3.3-5.5 mmol / l.
A blood sugar level of 7.8-11.0 is characteristic of prediabetes, an increase in glucose over 11 mmol / l indicates diabetes mellitus.
Fasting blood sugar is the same for both men and women. Meanwhile, indicators of the permissible norm of sugar in the blood may differ depending on age: after 50 and 60 years, a violation of homeostasis is often observed. If we talk about pregnant women, then their blood sugar level may deviate slightly after eating, while on an empty stomach it remains normal. An elevated blood sugar level during pregnancy indicates the development of gestational diabetes.
Blood sugar levels in children differ from those of adults. So, in a child under two years of age, the blood sugar rate ranges from 2.8 to 4.4 mmol / l, from two to six years - from 3.3 to 5 mmol / l, in children of the older age group it is 3, 3-5.5 mmol / l.
What determines the sugar level
Several factors can affect the change in sugar level:
- diet;
- physical exercise;
- increased body temperature;
- the intensity of the production of hormones that neutralize insulin;
- the ability of the pancreas to produce insulin.
Sources of blood glucose are carbohydrates in the diet. After a meal, when easily digestible carbohydrates are absorbed and broken down, glucose levels increase, but after a few hours they usually return to normal. During fasting, the concentration of sugar in the blood decreases. If the glucose level in the blood decreases too much, the pancreas hormone glucagon is released, under the action of which the liver cells convert glycogen into glucose, and its amount in the blood increases.
With a reduced amount of glucose (below 3.0 mmol / l), hypoglycemia is diagnosed, with an increased amount (more than 7 mmol / l) - hyperglycemia.
Hypoglycemia entails energy starvation of cells, including brain cells, the normal functioning of the body is disrupted. A symptom complex is formed, which is called hypoglycemic syndrome:
- headache;
- sudden weakness;
- feeling of hunger, increased appetite;
- tachycardia;
- hyperhidrosis;
- trembling in the limbs or throughout the body;
- diplopia (double vision);
- behavior disorders;
- convulsions;
- loss of consciousness.

Hypoglycemia leads to cell starvation, and, accordingly, a deterioration in well-being
Factors provoking hypoglycemia in a healthy person:
- inappropriate nutrition, diets leading to severe nutritional deficiency;
- insufficient drinking regime;
- stress;
- the predominance of refined carbohydrates in the diet;
- intense physical activity;
- alcohol abuse;
- intravenous administration of a large volume of saline.
Hyperglycemia is a symptom of metabolic disorders and indicates the development of diabetes mellitus or other diseases of the endocrine system. Early symptoms of hyperglycemia:
- headaches;
- increased thirst;
- dry mouth;
- increased urination;
- the smell of acetone from the mouth;
- itching of the skin and mucous membranes;
- progressive decrease in visual acuity, flashes before the eyes, loss of visual fields;
- weakness, increased fatigue, decreased endurance;
- trouble concentrating;
- rapid weight loss;
- increased frequency of respiratory movements;
- slow healing of wounds and scratches;
- deterioration in the sensitivity of the legs;
- tendency to infectious diseases.
Prolonged hyperglycemia leads to severe damage to organs and systems as a result of metabolic disorders and blood supply, as well as a significant decrease in immunity.
Analyzing the above symptoms, the doctor prescribes a blood sugar test.
Methods for measuring blood sugar
A blood test allows you to accurately determine the blood sugar index. The indications for the appointment of a blood sugar test are the following diseases and conditions:
- symptoms of hypo- or hyperglycemia;
- obesity;
- visual disturbances;
- cardiac ischemia;
- early (in men - up to 40 years, in women - up to 50 years) the development of arterial hypertension, angina pectoris, atherosclerosis;
- diseases of the thyroid gland, liver, adrenal glands, pituitary gland;
- elderly age;
- signs of diabetes or a pre-diabetic condition;
- burdened family history of diabetes mellitus;
- suspicion of developing gestational diabetes. Pregnant women are tested for gestational diabetes between the 24th and 28th weeks of pregnancy.
Also, the analysis for sugar is carried out during preventive medical examinations, including in children.
The main laboratory methods for determining blood sugar levels are:
- fasting blood sugar measurement - the total blood sugar level is determined;
- glucose tolerance test - allows you to identify hidden disorders of carbohydrate metabolism. The test is a three-fold measurement of glucose concentration at intervals after carbohydrate load. Normally, blood sugar values should decrease in accordance with the time interval after taking the glucose solution. When a sugar concentration of 8 to 11 mmol / l is detected, a violation of tissue glucose tolerance is diagnosed in the second analysis. This condition is a harbinger of diabetes (prediabetes);
- determination of glycated hemoglobin (connection of a hemoglobin molecule with a glucose molecule) - reflects the duration and degree of glycemia, allows you to detect diabetes at an early stage. The average blood sugar is assessed over a long period of time (2-3 months).
Additional tests to determine blood sugar levels:
- concentration of fructosamine (a combination of glucose and albumin) - allows you to determine the degree of glycemia over the previous 14-20 days. An increase in fructosamine levels may also indicate the development of hypothyroidism, renal failure, or polycystic ovary disease;
- blood test for c-peptide (the protein part of the proinsulin molecule) - used to clarify the cause of hypoglycemia or assess the effectiveness of insulin therapy. This indicator allows you to assess the secretion of your own insulin in diabetes mellitus;
- the level of lactate (lactic acid) in the blood - shows how much the tissues are saturated with oxygen;
- a blood test for antibodies to insulin - allows you to distinguish between type 1 and type 2 diabetes in patients who have not received insulin treatment. Autoantibodies produced by the body against its own insulin are a marker of type 1 diabetes. The results of the analysis are used to draw up a treatment plan, as well as to predict the development of the disease in patients with a burdened hereditary history of type 1 diabetes mellitus, especially in children.
How is a blood sugar test done?
The analysis is carried out in the morning, after an 8-14 hour fast. Before the procedure, it is allowed to drink only plain or mineral water. Before the study, the intake of certain medications is excluded, treatment procedures are stopped. A few hours before the test, it is forbidden to smoke, two days - to drink alcohol. It is not recommended to conduct an analysis after operations, childbirth, infectious diseases, gastrointestinal diseases with impaired glucose absorption, hepatitis, alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver, stress, hypothermia, during menstrual bleeding.
Measuring blood sugar at home
Blood sugar levels can be measured at home using an electrochemical device called a home glucometer. Special test strips are used, on which a drop of blood taken from a finger is applied. Modern glucometers automatically conduct electronic quality control of the measurement procedure, count down the measurement time, and warn of errors during the procedure.

It is convenient to measure sugar level with a glucometer, it can be done at home
Regular self-monitoring of blood sugar helps to maintain normal blood sugar levels, detect early signs of an increase in blood glucose in time and prevent the development of complications.
Patients with diabetes are advised to keep a control diary, which can be used to track changes in blood sugar levels over a certain period, see the body's response to insulin administration, fix the relationship between blood glucose levels and food intake, exercise and other factors.
YouTube video related to the article:

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.