- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Leather
The skin plays a very important role in the body. It not only covers the entire body, protecting it from adverse conditions, but is also a powerful organ of touch, temperature and pain sensitivity, participates in thermoregulation of the body, in the release of metabolic products, in the formation of some biologically important substances.

Skin structure
In the structure of the skin, the upper section is distinguished - the epidermis, and the lower - the dermis, or the skin itself. On the surface of the dermis, there are many dermal papillae in the form of outgrowths, which give the border between the epidermis and the dermis a wavy appearance in cross section.
The epidermis protects the skin from adverse effects. It consists of several layers. The lowest layer of epithelial cells adjacent to the dermis is called the basal layer. Its cells are constantly multiplying, renewing the overlying layers, they also contain the pigment melanin, which determines the color of the skin.
The second bottom layer of the epithelium is called the styloid; its irregularly shaped cells are separated by styloid tubules. The next layer is granular; in the cells of the epithelium of this layer, the process of formation of the skin horny substance begins. The fourth layer is shiny, it has this name because of the gloss that keratin gives the cells. The uppermost layer is the stratum corneum, its cells are flattened, loosely adjacent to each other and constantly slough off.
The dermis, or skin itself, consists of two layers. The lower papillary layer contains connective tissue fibers - elastic, collagen and reticulin. Collagen fibers pass into subcutaneous fatty tissue. The top layer of the dermis is called mesh. It is dominated by elastic fibers that give the skin firmness and elasticity. The dermis contains hair follicles, temperature, pain and tactile receptors, sweat and sebaceous glands.
Skin diseases
The health of the whole organism affects the condition of the skin. The condition of the skin suffers with concomitant diseases of the digestive, endocrine and hematopoietic systems, with insufficient intake of some important substances, with an unfavorable environmental situation.
The group of skin diseases themselves is quite extensive, among them are:
- Hereditary and congenital diseases;
- Allergodermatosis;
- Infectious and parasitic lesions;
- Tumors;
- Pigmentation disorders;
- Damage - mechanical, chemical, thermal, etc.
Skin diseases can occur at any age.
With a congenital genetic disease ichthyosis, excessively dry skin is subject to the process of excessive keratinization. It constantly cracks, which causes severe pain.
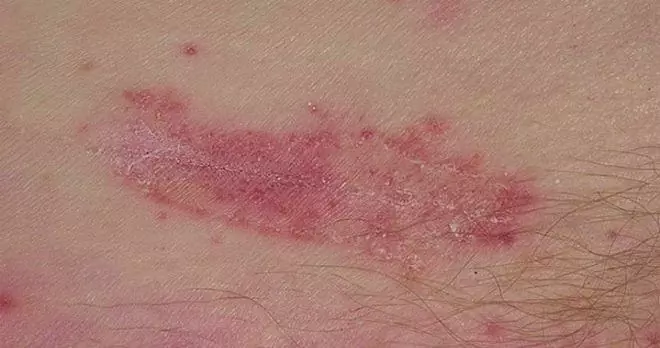
With dermatitis, inflammation develops in the skin. Contact dermatitis occurs when damaging agents - chemical, physical, biological - are exposed directly to the skin. Such dermatitis develops at the site of contact, and the area of the lesion is proportional to the site of contact. This category includes dermatitis with hogweed burns, contact with detergents, etc.
Allergic dermatitis develops upon repeated contact with the allergen, the inflammation in it is due to the effects of histamine in the skin. In this case, the reaction is usually disproportionate to the strength of the stimulus, and even small amounts of the allergen can cause significant damage in area and intensity. An allergen can either come in direct contact with the skin or come from the digestive tract. Children are characterized by such an allergic skin disease as atopic dermatitis. In adulthood, it manifests itself in the form of neurodermatitis. These conditions are characterized by dry skin, flaking, redness and itching.
Hyperkeratosis is manifested by excessive keratinization of the outer layer of the epidermis. It is a non-inflammatory skin disorder. Normally, excessive keratinization of the skin occurs during post-traumatic healing. In this case, the upper layers of cells excessively protect the lower layers, which are restored at this time. The phenomena of hyperkeratosis are also detected with prolonged solar irradiation. Symptoms that indicate hyperkeratosis are a thick, dense layer of keratinized skin, its tuberosity and peeling, painful thickening on the palms and soles, keratinization of hair follicles.
Calluses on hands and feet during physical work are a particular case of hyperkeratosis. They protect the skin from excess pressure. Pronounced manifestations of corns can be the cause of flat feet, deformities of the feet.
Impetigo is more common in children. It is an acute infectious skin disease caused by staphylococci and streptococci. It is highly contagious, especially when immunity is low. The symptoms of impetigo are:
- Focal redness of the skin;
- Small and large vesicles with purulent contents in them on a reddened surface;
- The bubbles break open from damage;
- A golden-yellow crust forms at the opening site.
The danger of impetigo is that it can spread significantly and lead to inflammatory lesions of other organs and tissues, and subsequently rheumatism.
Skin care
The skin requires regular care. In modern conditions of life, she is under severe stress, and it is important to help her withstand adverse environmental factors.
Skin care should start with general activities that will be beneficial for the whole body as well:
- Get regular and adequate sleep;
- Compliance with the work and rest regime;
- Healthy and proper nutrition.
It is important to cleanse the skin daily from sweat and sebaceous secretions, dust, dead epidermis. A daily shower will help to keep it clean, and if you also alternate between hot and cold water, you will get a workout for the blood vessels, as well as a general hardening of the body.
Facial skin care requires a more subtle approach. The skin of the face is thin and delicate, and with improper cleansing it can sag, become flabby.
With dry skin, it is advisable to wash your face with cool water using cleansers that do not contain soap, which dries the skin very much, washing away the protective lipid layer from it. Movement when washing or cleansing with cosmetic milk should be in the direction of the so-called massage lines. After washing, the skin is toned using special tonics. At night, excessively dry skin is moistened with a cream, it is better to remove the excess with a cotton swab after 15 - 20 minutes.
For oily skin, it is better to use warm water for washing, since hot water enhances the secretion of sebum by the glands, and cold water does not sufficiently cleanse the skin. Oily skin must be cleansed at least 2 times a day.
For oily skin, it is especially helpful to use facial toners. To regulate the work of the sebaceous glands, dermatologists recommend making therapeutic masks for oily skin 1 - 2 times a week.
A differentiated approach to cleansing and moisturizing the skin will make it beautiful and healthy, prolonging its youthfulness.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.