- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Treatment of laryngitis in children at home
The content of the article:
- Causes and mechanism of laryngitis development
- Classification
- Diagnostics
- Laryngitis treatment in children
- Video
Treatment of laryngitis in children at home should certainly take place under the supervision of a doctor. As a rule, the district pediatrician visits a sick child at regular intervals and monitors the condition over time.

Treatment of laryngitis at home should be carried out in consultation with the doctor and under his supervision
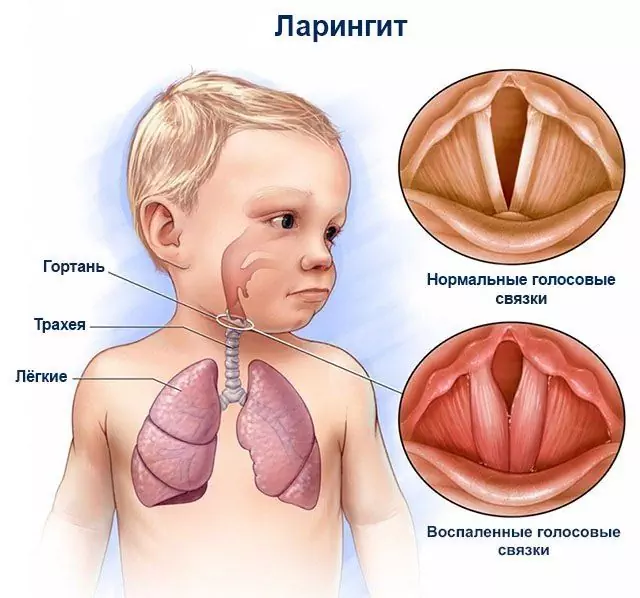
Laryngitis is quite often diagnosed in children and is an inflammatory disease that affects the lining of the larynx.
Acute laryngitis is more common in older childhood. Symptoms can develop either gradually or rapidly progress, causing a rapid deterioration in general condition. Depending on the severity of the disease, the body temperature may not rise, or vice versa, reach febrile numbers (38.1-39 ° C).

Larynx with indirect laryngoscopy
Acute laryngitis is characterized by hypersensitivity of the larynx. Children may complain of dry, sore, and burning throats. There is a hoarseness of the voice, a dry, painful convulsive cough. Pain may occur when swallowing. A dry cough can be replaced by a wet cough with the separation of mucous or mucopurulent sputum.
Causes and mechanism of laryngitis development
When studying the causes and mechanism of laryngitis development, it is necessary to take into account the age-related anatomical and physiological features of the development of the larynx in children:
- the larynx in young children is located high, in boys and girls under 3 years old it has the same length;
- intensive growth of the larynx, vocal and vestibular folds, epiglottis begins at the age of 4;
- the funnel-shaped shape of the larynx begins to change to cylindrical from the age of 5;
- an abundance of lymphatic gaps and blood vessels in the larynx, a large number of thin-walled blood vessels, mucous glands, an extensive accumulation of lymphoid tissue is characteristic of children of all ages;
- the tendency of the larynx to convulsions and spasms during irritation is explained by the lability of the nervous system in children, mainly of young age;
- the inflammatory process in the nasopharynx in young children very quickly spreads to the larynx, which is associated with the small distance from the oral cavity to the glottis with a high larynx;
- the lumen of the larynx in children is narrow, and the vocal folds are short, so even a slight inflammation of the mucous membrane can lead to stenosis, significantly aggravating the child's condition;
- the vocal folds in children under one year old are more susceptible to inflammatory and traumatic lesions due to anatomical and physiological immaturity.

The development of pathology is facilitated by a prolonged cry or cry
The cause of the development of inflammation of the larynx can be:
- viral, bacterial, or fungal infection;
- acute and chronic inflammatory diseases of the upper and lower respiratory tract;
- household injuries;
- the presence of a foreign body;
- surgical interventions;
- burns: chemical, thermal, electrical, radiation;
- allergy;
- inhalation of cold air;
- overstrain of the vocal apparatus;
- Difficulty nasal breathing, in which the child begins to breathe through the mouth;
- drinking cold drinks;
- metabolic disease;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- vegetative neuroses.
Under the influence of an exogenous or endogenous stimulus, inflammation of the laryngeal mucosa occurs: hyperemia, small-point infiltration, serous tissue permeation appears. The increased penetration of leukocytes through the interepithelial spaces and the increased work of the mucous glands contribute to rupture, desquamation and partial rejection of the columnar epithelium of the larynx.
Classification
Depending on the course of inflammation, acute and chronic laryngitis is distinguished.
According to the prevalence of the inflammatory process, acute laryngitis can be:
- diffuse, or spilled;
- limited.
Forms of pathology by the nature of the course:
- catarrhal;
- stenosing;
- hyperplastic, or hypertrophic;
- atrophic;
- hemorrhagic;
- phlegmonous;
- diphtheria.
Depending on the etiology, laryngitis can be:
- viral;
- bacterial;
- fungal, or laryngomycosis;
- traumatic;
- allergic.
Infection of the larynx most often occurs downward by inhalation of polluted air, inflammation of the nasopharynx, sinuses or tonsils. An ascending path is also possible - with tracheitis, bronchitis, pneumonia, tuberculosis.
Acute laryngitis can be a manifestation of many infectious diseases (flu, measles, scarlet fever, etc.).
In case of untimely or inadequate treatment, the development of a chronic form of the disease is possible.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is established by a doctor based on examination data, complaints of the child and parents, test results and instrumental research.

If necessary, a video endostroboscopic examination of the larynx using a rigid endoscope is prescribed
The main diagnostic method is laryngoscopy. In young children, the study may be complicated by the narrow grooved shape of the epiglottis. Modern fibrolaryngoscopes allow you to display an image on the screen and record a video.
In the diffuse form of acute laryngitis, diffuse hyperemia and edema of the laryngeal mucosa are determined. With a limited form of the disease, there is hyperemia and edema of the vocal folds, intercranial and sub-vocal spaces. Dilated blood vessels are visible on the surface of the mucous membrane. In the lumen of the larynx, a viscous mucopurulent secret is determined. During phonation, the vocal folds do not close completely, and the glottis is oval.
To identify the causative agent of an infectious lesion, discharge from the laryngeal mucosa is taken. Bacteriological culture allows you to determine the sensitivity to the action of antibiotics.
In order to exclude bronchopneumonia, a chest x-ray may be prescribed.
Laryngitis treatment in children
How to treat laryngitis in a child 2 years old and younger? How to effectively and safely cure laryngitis in a child 3 years of age and older? In order to disassemble these questions, it is necessary to take into account not only age characteristics, but also the form of laryngitis, the general condition of the body, the presence of concomitant somatic pathology.
General recommendations for home treatment, regardless of the child's age:
- bed rest;
- voice peace;
- elimination of irritating drinks and food;
- plentiful warm drink;
- alkaline mineral waters.
Distracting procedures are used: hot foot baths or mustard plasters for calves.

When coughing, the use of marshmallow root is effective
To relieve cough, expectorant drugs (marshmallow root, Herbion, Lazolvan) are prescribed. It is unacceptable to take simultaneously expectorant and antitussive drugs.
Among herbal remedies, it is recommended to use Tonsilgon N, containing expectorant fees (marshmallow root, chamomile flowers, dandelion, pine buds). The drug has anti-inflammatory properties, reduces swelling of the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract. By normalizing the work of lymphocytes, it has an immunostimulating effect.
When a bacterial infection is suspected, etiotropic treatment plays an important role. Given the global spread of antibiotic resistance in infectious agents, the use of antibiotics must be taken seriously.

Antibiotics are prescribed only if bacteria are the causative agent of the pathology
Before you start taking any medications, especially antibacterial ones, you need to consult a doctor and choose a therapy regimen depending on the etiological agent that caused the inflammation.
The duration of antibacterial treatment is on average 7-10 days. Depending on the suspected pathogen, protected penicillins, cephalosporins, macrolides are prescribed.
To reduce tissue edema, antihistamines are used (Suprastin, Tavegil).
Ascorbic acid is indicated to strengthen the vascular wall, and B vitamins - to improve the state of the nervous system.
According to the indications, the doctor may prescribe glucocorticoid drugs (Dexamethasone).
In a hospital setting, local treatment is carried out, including infusion of an emulsion of peach oil, hydrocortisone and an antibacterial drug into the larynx.
Among physiotherapy procedures, a positive effect is provided by:
- inhalation of humidified oxygen;
- infusion of trypsin and chymotrypsin into the larynx;
- electrophoresis of hyaluronidase or 1% potassium iodide;
- the effect of a therapeutic laser on the larynx region.
With inflammation of the tissues of the larynx, stenosis is possible, accompanied by difficulty or even inability to breathe. It occurs due to edema and infiltration of the mucous membrane of the larynx and trachea, muscle spasm and hypersecretion of glands with accumulation of mucopurulent discharge in the lumen of the larynx.
The child develops a barking cough, shortness of breath on inspiration, the skin and visible mucous membranes turn pale, the cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle and fingers is noted.
What to do with the development of an emergency with specific and nonspecific laryngitis?
Providing first aid for laryngitis in children at home in case of laryngeal stenosis includes the following points:
- call an ambulance;
- ensure maximum air flow into the room;
- help the child to take a sitting position (for the participation of the auxiliary muscles in the act of breathing);
- free from embarrassing clothing.

In case of emergency, parents must provide first aid before the arrival of doctors
For mild seizures, a warm alkaline drink is often given, for fever, paracetamol or ibuprofen (by mouth or rectally).
Inhalation of a suspension of budesonide through a compressor nebulizer helps well.
Judging by the positive reviews and recommendations of doctors, one of the effective drugs is Berodual. It has anti-inflammatory and antispasmodic effect, normalizes the secretion of mucous glands. It is recommended to use a nebulizer for inhalation. As a result of the procedure, the child's cough decreases, breathing is easier.
Dr. Komarovsky and many other pediatricians recommend using folk remedies only in addition to the main therapy, having previously coordinated them with your doctor. The anti-inflammatory effect is exerted by:
- chamomile extract;
- Oak bark;
- walnut leaves;
- yarrow herb.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Alina Ervasova Obstetrician-gynecologist, consultant About the author
Education: First Moscow State Medical University. THEM. Sechenov.
Work experience: 4 years of work in private practice.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.