- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Symptoms and treatment of acute laryngitis in children
The content of the article:
- The reasons for the development of pathology
- Symptoms of acute laryngitis in children
- Urgent care
-
Treatment of acute laryngitis in children
Drug treatment
- Video
Acute laryngitis in children is quite common. In most cases, it accompanies bronchitis and tracheitis. Usually the disease occurs in preschool age. Treatment should be comprehensive and timely, since pathology can cause respiratory failure and often leads to the development of serious complications.

If signs of illness appear, you must seek qualified help.
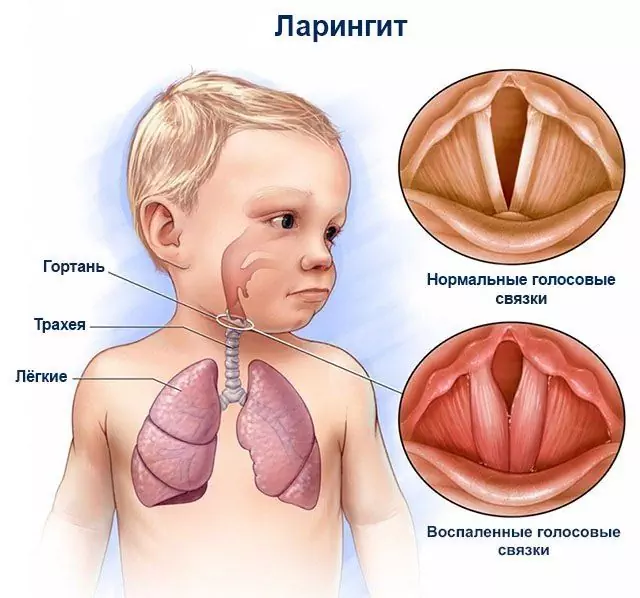
Laryngitis is a disease in which inflammation affects the lining of the larynx. ICD-10 code - J04 (acute laryngitis and tracheitis).
Laryngitis is considered a seasonal illness and usually peaks during the colder months of the year. The disease can be complicated by a pharyngeal abscess and acute obstruction of the upper respiratory tract, which is especially dangerous in children under one year old.
Depending on the localization of inflammation, laryngitis is divided into diffuse, subglottic and laryngotracheobronchitis. By the nature of the course, the disease can proceed in a catarrhal, edematous or phlegmonous form.
The reasons for the development of pathology
The acute form of the disease in childhood can occur in the following cases:
- viral infection. It is the most common cause of laryngitis in children. The disease occurs against the background of colds, measles, whooping cough or scarlet fever and can be triggered by the influenza virus, adenoviruses, herpes simplex virus;
- bacterial infection. Staphylococcus bacteria, streptococcus, or Haemophilus influenzae lead to the development of an inflammatory process in the larynx less often than viruses;
- fungal infection or chlamydia. In children, the disease for these reasons occurs very rarely, usually against the background of general disorders of the immune system;
- allergic reaction. Allergies to dust, food, wool, chemicals, or plant pollen can cause laryngitis symptoms;
- hypothermia and the use of cold food and drinks.
The following factors can influence the development of the disease:
- immunodeficiency states;
- metabolic disorders in diseases of the thyroid gland or diabetes mellitus;
- laryngeal injury;
- prolonged crying or screaming;
- unbalanced diet;
- regular hypothermia;
- violation of nasal breathing with adenoids;
- living in ecologically unfavorable areas;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Symptoms of acute laryngitis in children
In most cases, the first symptoms of laryngitis are similar to ARVI (acute respiratory viral infection) or develop against the background of this disease. The child has weakness, fatigue, nasal discharge appears. The body temperature rises slightly. The kid becomes restless, refuses to eat and does not sleep well. Acute laryngitis, which has arisen due to hypothermia, trauma to the larynx or overexertion of the voice, usually proceeds without deterioration of the general condition.

The initial symptoms of laryngitis are similar to those with ARVI
In the future, a sore throat appears, which may be accompanied by pain when swallowing or during inhalation or exhalation. As a result of edema of the mucous membrane of the larynx, the child's voice changes, it becomes hoarse, hoarse, deaf and loses its sonority. In some cases, aphonia (complete loss of voice) occurs.
In young children, laryngitis is almost always accompanied by respiratory failure. When air passes through the narrowed larynx, noise and whistling are noted. Breathing becomes rapid, in some cases, as a result of hypoxia, the nasolabial triangle is blue.
Acute laryngitis is characterized by the appearance of a cough. At the initial stage, it is dry without phlegm, like a dog barking. A cough attack can begin at any time, but most often it bothers at night.
After the end of the acute period of the disease, the cough becomes moist. In this case, a large amount of light translucent mucus is released. If the causative agent of the disease is a bacterial infection, the sputum may acquire a yellowish or greenish tint.
When signs of respiratory distress appear, parents should be very careful, as stenosis of the larynx (stenosing or obstructive laryngitis) may occur at any time.
In most cases, asthma attacks occur at night. At the same time, noisy rapid breathing is observed, against the background of which the skin turns pale and becomes covered with sweat. The child throws his head back, his heartbeat becomes more frequent, and blood vessels pulsate on his neck. Temporary respiratory arrest may occur.
If at this stage the child is not provided with medical assistance, convulsions, frothy discharge from the nose and mouth may appear. The baby's skin becomes cold, he loses consciousness. A severe attack can result in cardiac arrest and death.
Urgent care
If a child develops stenosis of the larynx, an emergency should be called immediately. Before her arrival, you need to provide the baby with fresh and moist air. To do this, you can bring it to an open window, turn on a humidifier in the room, or create steam by turning on hot water in the bathroom.

If necessary, do inhalation with Pulmicort, Hydrocortisone or alkaline mineral water
You can give your child a warm foot bath. Inhalation with Pulmicort, Hydrocortisone or alkaline mineral water (Borjomi, Essentuki) using a nebulizer is effective.
In order to relieve a spasm of the larynx, it is necessary to press with a spoon on the root of the tongue.
If the child often has severe seizures, you need to have Prednisolone, Suprastin or Tavegil in the medicine cabinet and, if necessary, give an injection.
When breathing stops, artificial respiration and chest compressions are performed. For this, the baby is laid on a flat, hard surface. A roller is placed under the neck so that the head is thrown back. The oral cavity is freed from mucus and saliva.

Parents should be able to perform chest compressions
Two fingers are placed in the middle of the chest and pressed twice in one second. If all actions are performed correctly, the chest rises.
After thirty clicks, mouth-to-mouth artificial respiration is performed. The child's nose is pinched, and the adult blows in air for a second, after which the baby exhales on its own. Then again press on the chest five times. Pulse and breathing are checked every minute. Resuscitation continues until an emergency arrives or until breathing and heartbeat are restored.
During the procedure, it is necessary to concentrate as much as possible and not to panic, since excessive pressing force can lead to a bruise or fracture of the chest.
Treatment of acute laryngitis in children
With a mild course of the disease in children over a year old, treatment is carried out at home.

In the room where the child is located, it is necessary to maintain an optimal temperature and humidity.
First of all, it is necessary to create optimal conditions for the child. The air temperature in the apartment where the baby is located should not exceed 22 ° C. At the same time, it is important to maintain the humidity at the level of 40-60%, which is especially important in winter when the central heating is on. It is recommended to regularly ventilate the room where the child sleeps and, if he feels well, walk with him in the fresh air.
The kid needs enough liquid. Drink should be warm, without harsh tastes. You can give tea, dried fruit compote or still water.
With food, the child needs to receive a sufficient amount of vitamins and minerals, so the diet should be balanced. If it hurts to swallow, the food is crushed to a puree state.

During treatment, calm games are preferable to active ones.
Laughing or screaming can trigger a coughing fit, so it is recommended that you choose quiet games.
Children under one year old with severe symptoms of acute laryngitis are shown hospitalization. Also, hospital treatment is necessary in the presence of attacks of laryngeal stenosis.
Drug treatment
If the cause of the disease is a viral infection, antiviral drugs are prescribed (Viferon, Anaferon, Arbidol, Groprinosin). They can shorten the period of the disease, reduce its manifestations and improve the functioning of the immune system.

With viral etiology of laryngitis, antiviral agents are prescribed
In the complex therapy of acute laryngitis, antihistamines are used (Fenistil, Suprastin, Diazolin, Erespal). They reduce swelling of the mucous membrane, suppress dry cough and prevent the development of stenosis of the larynx. Drugs in this group are used for both allergic and infectious forms of the disease.
To suppress coughing attacks at night, centrally acting antitussive drugs (Sinekod) are used. It is very important to follow the dosage regimen, as overdose can lead to respiratory failure.
When the cough becomes wet, mucolytics are used. They thin phlegm, promoting its excretion, and have an anti-inflammatory effect (Ambroxol, Lazolvan). It must be remembered that such medicines are not prescribed for dry barking coughs.
Often, antitussives of herbal origin based on ivy, licorice, and marshmallow are used to treat cough in children. They can also help reduce inflammation and coughing fits.

In the treatment of cough in children, herbal preparations based on ivy, licorice, marshmallow are effective
If the cause of the disease is a bacterial infection, then antibiotics are prescribed. Most often, drugs from the group of penicillins, macrolides or cephalosporins (Augmentin, Aziklar, Cefodox) are used. For children, such drugs are prescribed in the form of a suspension or injection.
If symptoms of a disease in a child are detected, treatment should not be started on their own; it is necessary to seek medical advice and further follow all clinical recommendations.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.