- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Pain when urinating in men

Painful urination is an abnormal process and indicates a pathology of the genitourinary system. The male genital organs are closely interconnected with the urinary system, so diseases of both internal organs and genitals can be the cause of pain. Anatomically, the vas deferens and urethra are one curved tube formation that starts from the bladder and ends with an outlet at the head of the male member. The vas deferens joins the duct in the area of the prostate - so important that it is considered the "second heart of a man."
The sensation of pain when urinating in men depends on the organs that carry out the functions of forming urine, concentrating it and, finally, excreting it.
The following organs represent the urinary system in sequential order:
- Kidneys;
- Ureters;
- Bladder;
- Urethra and vas deferens.
In the renal tubules, water is reabsorbed, as a result of which urine is concentrated and excreted from the kidneys. If the absorption of electrolytes is impaired, they are deposited on the renal papillae and tubular walls. This is how small stones are formed, up to 0.5-0.8 cm in diameter. They remain attached to the walls of the urinary tract for a long time, and then are separated from them and enter the urinary tract. With the discharge of small calculi, acute pain during urination in men is felt in the head of the penis and spreads to the lower abdomen and lumbar region. The so-called birth of a stone provokes a clinic of renal colic, the pain in which is relieved only by potent drugs.
The migration of a stone through the ureter irritates the receptors of the mucous membrane, which, in the places of contact with calculi, is destroyed with the formation of wounds. Therefore, during the discharge of the stone, the pain is accompanied by the staining of urine in red due to red blood cells.
The bladder is a powerful muscular organ, the thickness of its walls reaches 3-4 cm, and the cavity is an extensive receptor field that immediately responds to irritation. Whether it is a "foreign body" in the form of a stone or inflammatory edema of the mucous membrane caused by an infectious agent.
The male urethra is a convoluted S-shaped canal up to 18-20 cm long, with three narrowings in the following anatomical areas:
- Prostatic;
- Membranous;
- Openings of the urethra.
It is here that pain appears when urinating in men, regardless of the cause that caused it.
In the male urethra, there are two anatomical extensions located between the constrictions. Bacteria accumulate in these cavities, causing inflammation.
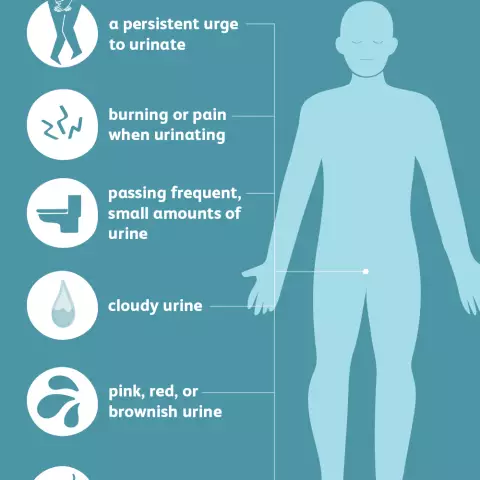
Clinical manifestations of pain during urination allow to determine the source of damage to the urinary system of a man.
Pain before urination in men
With renal pathology, pain appears in the lumbar region, then they spread to the entire urinary tract. As a rule, renal pathology is accompanied by a violation of urination, but in the absence of stones (sand), it is painless. When the process of excretion of a stone occurs, the act of urination provokes a painful attack. The following urges are usually accompanied by painful sensations.
Most often, pain before urinating in men is provoked by a pathological process in the bladder area - inflammation or cancer. Excretion of urine dulls pain, but does not relieve them completely.
A similar clinical picture is observed with inflammation of the external opening of the urethra. The onset of urination is accompanied by pain and is fixed reflexively. Painful sensations begin immediately before urinating, so patients through the central nervous system interrupt the urge, which becomes even more painful.
Pain at the beginning of urination
The beginning of the process of urine excretion is accompanied by painful sensations in inflammatory lesions of the urethra, including in sexually transmitted infections. Pus accumulated in the wide cavities of the urethra flows out with the release of urine, increasing pain. The feeling of itching is replaced by pain when urinating in men, and when the sticking lips of the urethra open under the pressure of urine, the pain stops.
The following diseases lead to a similar feeling:
- Gonorrhea (gonorrhea);
- Chlamydiasis;
- Mycoplasmosis;
- Candidiasis.
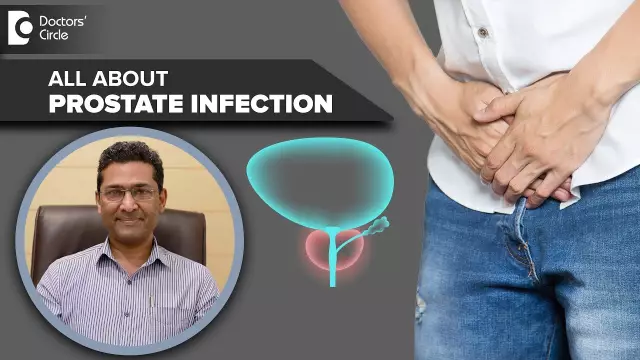
With bacterial prostatitis, pain spreads along the urethra immediately after the beginning of urine excretion. Then relief is felt, but there is no sensation of complete emptying of the bladder. With tumor processes of the prostate, pain becomes constant.
Pain after urination in men
As a separate sensation after urination, pain appears when the mucous membrane of the urethra is affected. Urine is a biologically compatible fluid for the body, so while it passes through the canal, the receptors "calm down". As soon as the lining of the urethra is emptied of urine, the wounds are exposed.
By a similar mechanism, pain appears after urination in men with cystitis. Emptying the bladder exposes mucosal wounds. Most often, they are formed as a result of friction of small stones during their discharge. First of all, the area of the isthmus suffers, that is, the place behind which the urethra begins. With urolithiasis cystitis, a feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen is accompanied by pain during urination and its intensification after urination.
Pain when urinating in men associated with genital involvement

The male sex glands are the most sensitive, therefore, with vesiculitis, pain is noted both during urination and during ejaculation. The patient's sperm turns brownish because erythrocytes are mixed with the semen. Pain with vesiculitis extends to the lower back and perineum. The intensity of pain reaches such a value that it necessitates a novocaine blockade of the spermatic cord. Eases the condition of wearing the suspensor. However, every act associated with the excretion of urine or ejaculation is accompanied by acute pain.
The most common cause of urinary pain in men is damage to the foreskin of the penis. Phimosis and paraphimosis lead to compression of the urethra. In this regard, the process of urination becomes painful.
The appearance of pain during urination in men is associated with the pathology of both urinary and sexual function. The anatomical structure of the urethra and vas deferens and the close relationship of the reproductive and excretory systems determine the symptoms of their lesions. Therefore, at first glance, diseases that have nothing in common turn out to be interrelated. For example, painful urination and male infertility.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.