- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Erythema nodosum

Erythema nodosum is a disease in which inflammation of the subcutaneous fat and blood vessels of the skin occurs. It is very common, especially erythema nodosum occurs during pregnancy.
Symptoms of erythema nodosum
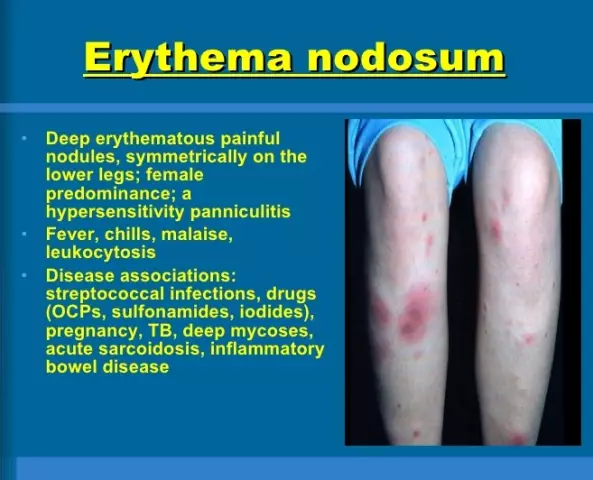
The symptom of erythema nodosum is the appearance of nodules with a diameter of 1 to 3 cm. Often they occur on the legs, but can also appear in the thighs, buttocks and arms. Typically, the appearance of nodules is symmetrical on both limbs. The nodules are shiny, thin and hot, are just above the surface of the skin, and are painful to pressure.
The harbingers of the appearance of a rash with erythema nodosum are painful sensations in the joints, states of general malaise and fever, similar to those of the flu.
Causes of erythema nodosum
There are many reasons for erythema nodosum and they are quite different. The most common are tuberculosis, streptococcal infections, and sarcoidosis. Other major causes of erythema nodosum are:
Infectious:
- Trichophytosis;
- Inguinal lymphogranulomatosis;
- Cat scratch disease;
- Leprosy;
- Blastomycosis;
- Histoplasmosis;
- Coccidioidomycosis;
- Yersiniosis;
- Psittacosis.
Non-infectious:
- Pregnancy;
- Vaccines;
- Medicines;
- Hodgkin's disease;
- Leukemia;
- Tumors;
- Regional enteritis;
- Ulcerative colitis;
- Inflammatory bowel disease;
- Behcet's syndrome.
Erythema nodosum can occur from the use of salicylates, iodides, bromides, sulfonamides, antibiotics, and other drugs, especially from the use of contraceptives and contraceptives. Also affected are those people who have varicose veins and thrombophlebitis. These factors explain why pregnant women are highly susceptible to erythema nodosum.
Often, erythema nodosum can be an independent disease. In such cases, it is impossible to establish the cause.
Forms of the disease
Distinguish between acute and chronic erythema nodosum.
The acute form is characterized by an increase in body temperature up to 39 ° C, the appearance of chills, pain in joints, neck, hips and shoulders. Seals appear under the skin that do not have clear boundaries. The bright red spots that appear at the beginning disappear within a month.
The subtypes of the chronic form are allergic vasculitis and Beverstedt's erythema vagus. Allergic vasculitis is characterized by a small number of nodules that do not go away and, accordingly, do not change their color. It lasts a very long time, relapses often occur. With wandering erythema of Beverstedt, nodules appear and fade, and new foci appear along the perimeter that do not change their color.
Treatment of erythema nodosum
In order to determine the causes and prescribe treatment for erythema nodosum, you must consult a dermatologist. The doctor will make the diagnosis during a visual examination. At the initial treatment, a throat swab is taken to identify streptococcus and feces for Yersinia, an X-ray of the lungs is taken to exclude sarcoidosis and tuberculosis.
Erythema nodosum rash is usually treated with corticosteroids. But they are not used if there are infectious diseases.

Basically, erythema nodosum is treated with salicylates and a wide range of antihistamines: diazolin, suprastin, zirtek, tavegil, telfast, claritin. Antibiotics are sometimes given as well. Self-medication or self-administration of antibiotics is strictly prohibited, as this can cause allergic manifestations and complications in the gastrointestinal tract.
Bed rest is necessarily shown. Physiotherapy is also used for treatment - warming ichthyol compresses, phonophoresis, UHF, warm compresses on the lower leg, diathermy. After the local symptoms are cured, immuno-strengthening therapy is performed.
A dairy-plant diet is recommended. It is advisable to exclude spicy, fried and fatty foods, preservatives from the diet.
Erythema nodosum during pregnancy
When a pregnant woman develops erythema nodosum, doctors immediately diagnose the cause. This is very important because if the cause is a serious illness such as tuberculosis, Behcet's disease or gastrointestinal tract diseases, treatment will be much more difficult.
Erythema nodosum practically does not affect the child in the womb. It is more harmful to the mother herself, as it can cause heart complications. There are also cases when the disease goes away on its own by the end of the II-III trimester.
In the absence of complications, local treatment is carried out: indovazin is used to lubricate the lesions, courantil and small amounts of paracetamol are prescribed orally. Inflammation is removed with aspirin in small doses, diclofenac is injected.
During the treatment of erythema nodosum during pregnancy, it is important to adhere to the correct rest and sleep regimen. It is also important to determine the load on the vessels in the lower extremities: it should be minimal, but at the same time, it should keep the vessels in good shape. The doctor, depending on the severity of the disease, will prescribe either the alternation of motor loads with rest, or bed rest. It is very important to choose the right treatment, otherwise, even after childbirth, erythema nodosum may not go away, but take on a chronic form, in which it will constantly worsen in spring and autumn, as well as during adverse conditions (stress, climate change, infectious diseases) or the next pregnancy.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!