- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Polyps in the nose: causes, symptoms, treatment, complications
The content of the article:
- Causes of polyps in the nose
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
-
How to treat pathology
-
Conservative therapy
Complementary treatment
-
Surgery
- Removal with a polyp loop
- Surgical removal with a scalpel
- Laser removal
- Functional endoscopic endonasal surgery of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses
- Features of surgery
-
- Why are polyps in the nose dangerous?
- Prevention
- Video
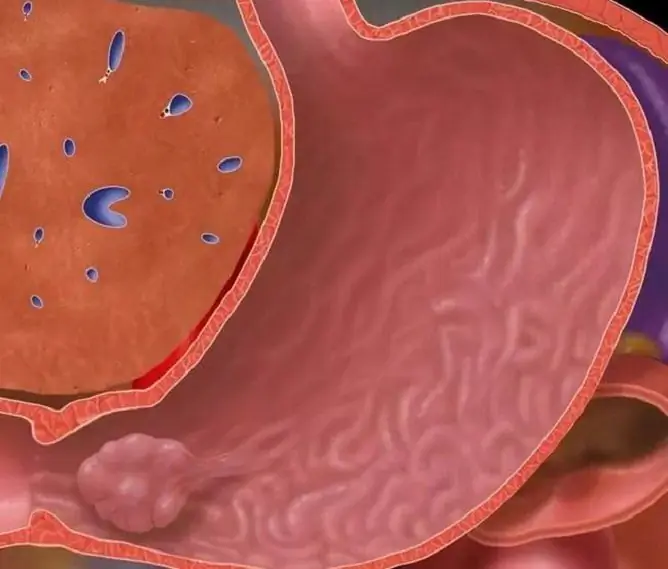
Polyps in the nose are soft, painless, benign growths localized on the mucous membrane of the nasal passages or sinuses. Outwardly, they resemble bunches of grapes. Found in 4% of the world's population.

If symptoms of polyps appear, you should consult an otolaryngologist
Having reached a sufficiently large size, the growths can block the airways, causing their obstruction.
With early detection, the disease is treated conservatively, with later treatment, the development of obstructive syndrome, they resort to surgical treatment - polypectomy.
Causes of polyps in the nose
Why does tissue proliferation occur? There are many reasons for the appearance of pathology: the growth of formations can provoke sensitization to various allergens, inflammatory diseases of the sinuses, drug intolerance, etc.

Formations can have different shapes and sizes, which is determined by the reason for their development
Polyps can be primary or secondary.
In primary nasal polyposis, there are no previous, damaging factors. The disease develops against the background of the normal state of the mucous membrane of the nasal passages and sinuses. The reason for the development of primary nasal polyposis is not fully understood.
Secondary nasal polyps form as a result of chronic local inflammation.
With a long-term inflammatory process in the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract, local immune factors compensate for it for a long time, but at a certain moment compensatory mechanisms break down, the mucous membrane, hypertrophing, increases its volume to stop the inflammatory process. As a result, polyps grow.
Risk factors:
- allergic diseases: bronchial asthma, allergic fungal sinusitis, allergic rhinitis, hay fever, etc.;
- chronic inflammatory process of the paranasal sinuses: sinusitis, frontal sinusitis, ethmoiditis;
- congenital or acquired disorders of the anatomical structure of the upper respiratory tract: curvature of the nasal septum, hypertrophic rhinitis, etc.;
- genetic diseases: cystic fibrosis, Churge-Strauss syndrome, etc.;
- hypersensitivity to aspirin.
Symptoms
Basically, the symptoms are associated with the presence of a mass in the nasal cavity, which makes breathing difficult and is a provoking factor for infection.

Polyps in the nose can manifest as nasal congestion, runny nose
The main symptoms of nasal polyps in adults and children:
- nasal congestion, sneezing, rhinorrhea (runny nose);
- impossible or difficult nasal breathing, prevalence of oral breathing;
- anosmia: decreased sense of smell, often to a complete loss;
- foreign body sensation, discomfort;
- postnasal syndrome: constant excess production of mucus, which is felt by the patient, and upon visual examination, is visible on the back of the pharynx;
- a feeling of pressure in the forehead, face, the development of a headache or pain at the point of projection of the sinuses of the nose, upper jaw (as a result of infection);
- mucous or mucopurulent nasal discharge: evidence of polyposis, complicated by infection;
- snore.
Diagnostics
Before prescribing additional research methods, the doctor clarifies complaints, medical history, life history, including concomitant diseases, and clarifies hereditary predisposition.
The next stage is an examination, in which the doctor examines the oral cavity, nose, reveals the characteristic signs, the presence and nature of the discharge. For this, a special instrument equipped with lighting is used - a nasoscope.
With a deeply located polyp and its small size, nasal endoscopy may be prescribed. A nasal endoscope is an apparatus equipped with an optical fiber, a camera and a thin flexible tube, which is inserted into the nasal cavity and allows a more detailed assessment of the nature of the mucous membrane, revealing the localization of the neoplasm.

If it is necessary to clarify the size and localization of the formation, computed or magnetic resonance imaging is used
Computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging can also be used to visualize the polyps in the sinuses, to determine their exact size and location. The method allows:
- detect defects in the bone skeleton of the area under study;
- to carry out (indirectly) differential diagnosis with other, more dangerous diseases, such as cancer.
In young children, it is necessary to exclude hereditary diseases such as cystic fibrosis, Kartagener's syndrome, etc.
How to treat pathology
Depending on the nature of the course of the disease, the complications that have developed, the size of the formation, the individual characteristics of the patient, the doctor chooses the tactics of therapeutic measures.
Therapy for nasal polyposis can be conservative and operative.
It should be noted that primary polyposis is rarely treatable and is characterized by frequent relapses. However, therapy in this case is not aimed at eliminating the disease, but at controlling it and improving the patient's quality of life.
With secondary polyposis, the prognosis is more favorable, since adequate and complete treatment of provoking diseases leads to complete recovery.
Conservative therapy
Small uncomplicated growths can only be treated conservatively with topical glucocorticosteroids.
Topical glucocorticosteroids (GCS) are hormonal drugs produced as an intranasal spray or drops and used topically. The drugs are prescribed for anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic, anti-edema purposes. They rarely cause adverse reactions and are well tolerated by patients.

Before using GCS, it is necessary to clear the nasal mucosa from crusts and mucus
To increase the availability of GCS, it is necessary to prepare the nasal cavity before using them. Preparation consists in cleansing the mucous membrane of crusts, mucus and other secretions. For this purpose, isotonic sea salt solutions are used in the form of intranasal sprays or drops.
After cleaning with a solution of sea water, it is necessary to improve the patency of the nasal passages by introducing local vasoconstrictor drugs. Only after cleaning and providing access can the GCS be introduced. This will improve their bioavailability, and, accordingly, the effect of the prescribed therapy.
Complementary treatment
If an allergic component is detected in the formation of polyposis, it is possible to use antihistamines of the latest generation.
Treatment of sinusitis, sinusitis, rhinitis is an integral part of the treatment of nasal polyps.
With stagnant purulent processes in the sinuses, it is possible to puncture them with aspiration of purulent contents and subsequent antibiotic therapy.
Surgery
There are several types of surgical treatment of growths, the essence of all methods is polypectomy (excision and removal of neoplasms with the least traumatization of unaffected tissues).

The method of removing neoplasms is determined by the doctor
Removal with a polyp loop
The loop captures the formation and mechanically cuts it off.
Cons of this method:
- soreness;
- the possibility of severe bleeding;
- incomplete polypectomy: only those formations that are visible to the doctor in the nasal cavity are removed; when the growth is localized in the sinus, this method is ineffective.
Surgical removal with a scalpel
The use of this method is possible with the localization of polyps in the maxillary sinus (anthrochoanal growths). In this case, an incision is made under the lip, the front wall of the maxillary sinuses is opened. Formations are mechanically cleaned out.
Minuses:
- high invasiveness;
- the possibility of scarring on the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinuses;
- the possibility of postoperative sinus infection;
- soreness.
Laser removal
The method consists in laser evaporation of liquid from neoplasms, which leads to adhesion of the walls of the polyp and a significant reduction in its size.
Minuses:
- limited use only with single formations, with multiple polyposis, the method is ineffective;
- incomplete removal with possible relapses.
Functional endoscopic endonasal surgery of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses
The operation is less traumatic, since the endoscope is inserted through the nose, and no incisions are made.
Removal is performed with a special instrument - a shaver or microdebrider, which allows to separate the affected tissue with high precision, minimizing trauma to the healthy one.
Another advantage is the possibility of performing the operation under local anesthesia. The likelihood of bleeding is minimal.
Features of surgery
Surgical treatment is carried out in a hospital and requires further observation of the patient for 3-7 days.
Intranasal glucocorticoids may also be prescribed for at least 3-6 months after surgical treatment. Additionally, antihistamines are used.
The swelling of the nasal mucosa can persist for 1-3 months after the operation, therefore it is recommended that regular observation in the clinic by a family doctor or otolaryngologist is recommended.
Why are polyps in the nose dangerous?
Polyps are dangerous because they can block nasal breathing, impair mucus drainage and cause chronic inflammation of the upper respiratory tract.

One of the possible complications of the pathology is obstructive sleep apnea syndrome
Potential complications include:
| Complications | Description |
| Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome | Symptom complex, which is characterized by a short-term cessation of breathing, alternating with a compensatory increase in breathing rate during sleep. As a result, normal sleep is disrupted, the patient feels tired, exhausted, scattered |
| Exacerbation of asthma | Appears as a consequence of chronic rhinosinusitis |
| Sinus infections | Etmoiditis, sinusitis, frontal sinusitis, etc. A growing polyp violates local defense mechanisms, is the soil and the cause of the development of local inflammatory processes of infectious origin and prevents their timely sanitation with the development of chronicity |
Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome can be recognized by its characteristic symptoms: snoring and daytime sleepiness. The syndrome can lead to disorders of the cardiovascular system: ischemia, arterial hypertension, heart rhythm disturbances, etc.
Prevention
To reduce the risk of nasal polyps developing or recurring after treatment, it is recommended:
- control the symptoms of allergies and asthma through regular examinations and correct treatment;
- regularly ventilate and clean the premises, use a humidifier, especially in the winter season;
- avoid strong olfactory irritants (tobacco smoke, dust, chemical vapors, allergens, etc.);
- regularly clean the nasal cavity: for this purpose, it is recommended to use isotonic saline solutions or filtered boiled chilled water.
Usually, with adequate and complete therapy, the prognosis is favorable, with careful adherence to preventive measures, the risk of relapse is significantly reduced, and complete recovery occurs.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.