- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2024-01-15 19:51.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Polyps in the gallbladder: symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, consequences
The content of the article:
- Classification
- The reasons
-
Symptoms of polyps in the gallbladder
- Pain sensations
- Dyspeptic symptoms
- Hepatic colic
- Jaundice
- Diagnostics
-
Treatment
- Open cholecystectomy
- Laparoscopic cholecystectomy
- Treatment with folk methods
- Why is a gallbladder polyp dangerous?
- Video
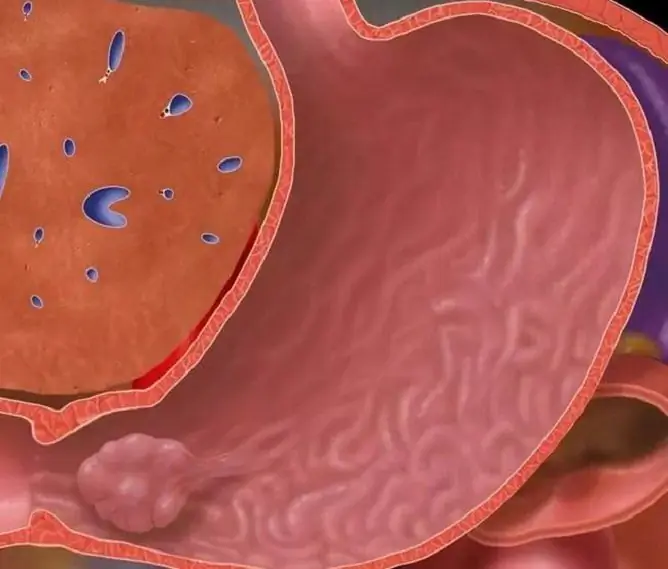
Polyps in the gallbladder are benign neoplasms located on the inner wall of an organ and growing into its lumen. Almost 80% of patients suffering from the disease are women over the age of 35.

The appearance of polyps in the gallbladder can be associated with various reasons.
Often, the signs of the disease are practically absent or very weakly expressed, and the pathology can be detected by chance. The symptoms of the disease depend on the location of the growth.
Classification
In medical practice, the following types of polyps are distinguished:
- true: papillomas of the gallbladder, adenomatous polyps;
- pseudopolyps: cholesterol, inflammatory.

Pseudopolyps can develop due to calcification of cholesterol plaques
Neoplasms are classified as follows:
- adenomatous. They are growths of epithelial tissue covering the walls of the gallbladder. This type of formations more often than others turns into a malignant form;
- cholesterol. They arise as a result of the deposition of cholesterol plaques on the mucous membrane of the organ;
- inflammatory. Pseudotumor resulting from the inflammatory process and proliferation of the epithelium of the mucous membrane.
Papillomas are benign neoplasms that result from infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV). They represent a growth with numerous papillary growths. As well as adenomatous polyps, this type of formation can degenerate into a malignant form.
The reasons
Why do polyps appear in the gallbladder? The causes of the disease include:
| The reasons | Description |
| Inflammatory processes in the liver | Cholecystitis leads to stagnation of bile and the proliferation of granulation tissue on the walls of the bladder, forming inflammatory pseudopolyps |
| Heredity | The disease often develops against the background of a burdened family history, as well as additional factors in the form of stagnation of bile. In most cases, adenomatous polyps and papillomas are inherited |
| Metabolic disorders | This is the most common cause of cholesterol pseudopolyps. As a result of lipid metabolism disorders, the level of cholesterol in the body increases (which is deposited on the walls of the organ in the form of plaques). Polyps form as they calcify. |
Symptoms of polyps in the gallbladder
Pain sensations
Most often, pain occurs when the polyp blocks the outflow of bile, causing the walls of the organ to stretch. Congestion provokes irritation of a large number of nerve receptors located in its walls.

Polyps in the gallbladder are manifested by pain in the right hypochondrium
Aching dull pain with neoplasms in the gallbladder is localized in the right hypochondrium. It occurs if a person overeats, consumes fatty and spicy foods or alcoholic beverages. In some cases, stressful situations become the cause of pain.
Dyspeptic symptoms
Signs of pathology include dyspeptic symptoms, namely:
- nausea (especially in the morning);
- bitterness in the mouth;
- vomiting after overeating.
These symptoms indicate a violation of the outflow of bile and its stagnation. The absence of bile acids in the intestine leads to the fact that food (especially fatty and abundant) is poorly digested and practically not absorbed.
As a result, the person loses weight quickly. The throwing of bile from the duodenum into the stomach causes a bitter taste in the mouth, which is difficult to get rid of.
Hepatic colic
This symptom is observed quite rarely, usually in cases where the polyp is located in the neck of the organ and it has a very long and thin leg, which can be twisted and pinched. When contracted, the build-up is clamped, as a result of which the patient experiences sharp, intense, paroxysmal pain.
The painful sensations are so strong that the patient cannot stay in one place, he rushes about and cannot find a suitable position to relieve pain. His pulse quickens and blood pressure rises, the skin becomes pale and covered with sweat.
Jaundice
The cause of jaundice is an increase in the level of bilirubin in the blood (above 14 mmol / l). Pathology occurs as a result of stagnation of bile, when its components begin to seep into the blood. In some cases, this phenomenon can provoke a polyp located in the gallbladder duct or in the neck.

One of the manifestations of pathology is an increase in the level of bilirubin in the blood, which leads to the development of jaundice.
First of all, the color of the sclera changes in the patient, they become yellow. Subsequently, the skin tone changes - to bright yellow (in people with fair skin) or dark orange (in dark-skinned people). The yellowness is so intense that it can be seen even in the photo.
Jaundice is accompanied by itching of the skin, which occurs as a result of bile acids entering the bloodstream. Moving along the bloodstream, they irritate the nerve endings, causing an irresistible urge to scratch. Often, patients experience scratching in different places, since itching does not have a clear localization. The skin becomes dry and tight.
In addition, the patient's urine color changes, it becomes dark. Jaundice may be accompanied by nausea, vomiting, joint and muscle pain, or fever.
Diagnostics
In order to identify the disease, the following methods are used:
- ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the liver and gallbladder. The gallbladder on ultrasound is an oval dark formation of a uniform color. The growth looks like a light, non-uniform spot growing from the wall against a dark background. A cholesterol or inflammatory polyp on ultrasound looks like a completely white formation;
- endoscopic ultrasonography. An endoscope with a miniature camera at the end is inserted through the mouth into the duodenal cavity, from where tissue is scanned at a distance of 12 cm. This method allows you to study in detail the polyps located on the walls of the organ;
- computed tomography. With this method, you can see even the smallest polyps, determine their structure, and also identify abnormalities in the structure or work of the organ.

To detect small polyps and other organ diseases, computed tomography is prescribed
Treatment
No medication is given because it is not effective. Medicines are prescribed to treat the underlying disease that could cause the development of the tumor.
In complex therapy, choleretic agents are used: Holiver, Allohol, Hepabene. In order to remove pain in the gallbladder, antispasmodics are used: No-shpa, Riabal.
During surgery, not only polyps are removed, but also the entire gallbladder. This type of surgery is called cholecystectomy. There are the following indications for its implementation:
- multiple neoplasms;
- the size of the polyp is more than 1 cm;
- rapid growth of the polyp;
- the presence of stones in the gallbladder;
- suspicion of malignancy of education;
- cholecystitis;
- burdened family history.
Open cholecystectomy
During the operation, the gallbladder is removed through an oblique incision, which is made along the edge of the costal arch. Surgery is performed under general anesthesia.

In some cases, open cholecystectomy is performed
The area of the preliminary incision is treated with an antiseptic. The tissue is cut with a scalpel. The gallbladder is removed from the bed, tied up and removed. At the next stage, the incision is sutured.
Open cholecystectomy is performed if neoplasms become large and there is a suspicion of malignancy. Therefore, at the same time, regional lymph nodes are removed, and part of the liver is also resected. The stitches are removed after the operation on the 6-7th day.
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy
In laparoscopic cholecystectomy, removal of the gallbladder is performed by the endoscopic method. The operation is performed under general anesthesia. Four small incisions are made in the abdominal wall through which trocars (hollow tubes with valve devices at the ends) are inserted. With their help, tissues are moved apart.
An eyepiece with a video camera and a laparoscope are inserted through the trocars into the abdominal cavity. On examination, the hepato-duodenal ligament is revealed, the cystic duct and artery are isolated from it (they are ligated and crossed). Using an electrocoagulator, the gallbladder is removed from the liver bed. Through the passages, it is removed from the abdominal cavity. Then the incisions are sutured.
The advantage of this operation is a short postoperative period (up to 5 days). At the same time, the patient experiences not too intense pain and can take care of himself. After laparoscopic cholecystectomy, complications such as hernias and adhesions are very rare.

After the operation, it is necessary to revise the diet, excluding fatty, salty, spicy and fried foods from it
After removal of the gallbladder, it is necessary to follow a strict diet for 2-3 months. In the future, you need to revise the diet and remove fatty, salty, fried and spicy foods, as well as smoked meats and alcohol from it.
Treatment with folk methods
For the treatment of polyps in the gallbladder without surgery, as well as in order to prevent the growth of education and avoid its degeneration into a malignant tumor, the following folk remedies are used:
- recipe number 1: 200 ml of boiling water is poured over one tablespoon of dried viburnum berries and insisted for three hours. Strain, add a teaspoon of honey and drink 100 ml each morning and evening. Treatment is continued for 2 weeks, then a break is taken. After 14 days, the reception is resumed. The infusion is taken for 3 months;
- recipe number 2: 300 g of fresh celandine herb together with the roots are thoroughly crushed and 200 g of may honey is added. The tool is insisted for a week in a dark, cool place. Then it must be filtered, placed in a dark glass container and stored on the door in the refrigerator. 5 drops of the infusion are dissolved in one tablespoon of water and taken once a day half an hour before meals. Reception continues for 20 days, then a ten-day break is made. Treatment should be continued until the remedy is completely over;
- recipe number 3: 100 g of natural butter is dissolved in a water bath, 10 g of propolis powder is added and kept on fire for 10 minutes. Then it is filtered and stored in the refrigerator. A teaspoon of the product is dissolved in a glass of warm milk and taken once a day before meals. They use the remedy for 2 weeks, then take a week break and continue the treatment.
Why is a gallbladder polyp dangerous?
If polyps of the gallbladder are detected, timely treatment is necessary, since they can cause the following complications:
| Complication | Description |
| Malignant polyp (degeneration into a malignant tumor) | If the size of the neoplasm is more than 20 mm, then it becomes malignant in about 50% of patients. In other cases, the chances of a polyp becoming cancerous is 35%. The prognosis for gallbladder cancer is poor, no more than 15% of patients survive to a year |
| Hepatic colic | The patient has regular, excruciating severe pain in the right hypochondrium, which can radiate to the back, neck or shoulder blade. Attacks appear more often at night and last from one to several hours |
| Purulent cholecystitis | A serious pathology that can lead to the development of gangrenous cholecystitis, cholangitis, liver abscess or peritonitis. These complications threaten not only the health, but also the patient's life. |
| Cholestasis | Chronic disturbance of the outflow and stagnation of bile become the cause of the development of jaundice and dyspeptic symptoms. In severe cases, this can lead to liver cirrhosis or liver failure. |
In order to prevent the appearance of polyposis, it is necessary to eat right, stop drinking alcohol, and also treat inflammatory processes of the gastrointestinal tract in time. People whose parents suffered from this disease should be examined regularly.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.