- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Polyps in the stomach: causes, symptoms, treatment, prevention
The content of the article:
- Classification
- The reasons
- Symptoms
-
Diagnostics
- Fibrogastroduodenoscopy
- Other diagnostic methods
-
Treatment
- Polypectomy
- Stomach resection
- Complications
- Prevention
- Forecast
- Video
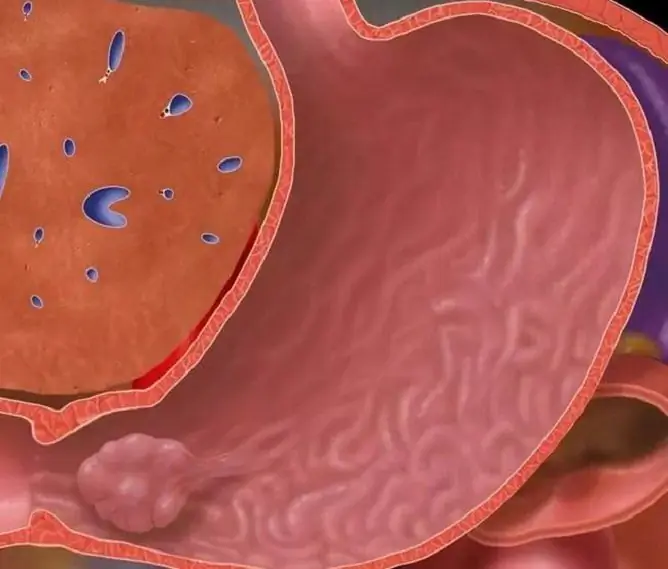
Polyps in the stomach are benign, tumor-like epithelial formations that rise above the mucous membrane and grow into the cavity of the organ. At the beginning of their formation, they do not cause any symptoms, sometimes they are accidentally discovered during an examination prescribed for another disease.

Polyps grow in the stomach cavity, towering over the mucous membrane
Pathology usually occurs in middle-aged people (45-55 years), however, there are cases of its detection at a younger age and in children. In male patients, it is found twice as often. The most common localization is the pylorus (sphincter, which is located between the stomach and duodenum).
The disease is dangerous in the event of complications, in particular, during the transformation of the growth into a malignant neoplasm.
Depending on the clinical course and structure of the polyps, the patient's treatment tactics can be expectant, in which the underlying disease that provoked the polyposis is treated, or active surgical.
Classification
Polyps by their morphological characteristics can be glandular (adenomatous) or hyperplastic.

Most often, the development of hyperplastic formations occurs.
Hyperplastic neoplasms are the most common type found in the stomach. They are found 16 times more often than other formations. It has an extremely low probability of transformation into a malignant tumor.
According to the histological structure, adenomas are classified as follows:
| View | Description |
| Tubular | With a predominance of tubular glandular cells |
| Papillary | With a predominance of papillary formations |
| Papillotubular | Mixed - papillary and tubular structures are equally represented |
Depending on the number of formations in the wall of the organ, there are single, multiple polyps and diffuse family polyposis (genetically determined disease).
The reasons
One of the common theories of the appearance of neoplasms in the mucous membrane of an organ is inflammatory. According to this theory, long-term persistence of an infectious agent in the organ wall causes a disturbance in local regulatory mechanisms, provoking excessive proliferation of the epithelium, respectively, the appearance of polyps.

The presence of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori is one of the trigger factors for the appearance of polyps in the stomach
Factors that increase the risk of neoplasm formation:
- age over 40, male;
- hereditary predisposition (hereditary colon cancer syndrome: familial intestinal adenomatosis - a disease in which the risk of developing not only colon cancer, but also stomach formations increases);
- Helicobacter pylori infection (the bacterium Helicobacter pylori is found in most of the world's population, it has been proven that it can be the etiological factor of gastritis);
- taking certain medications (for example, the use of proton pump inhibitors in the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease can cause the appearance of polyps of the fundic glands);
- smoking, alcoholism.
Symptoms
For a long time, the disease can be asymptomatic. The presence of symptoms from the digestive system is possible, however, with small uncomplicated polyps, it often testifies in favor of gastritis.

One of the symptoms of the pathology is intense cramping pain in the abdomen.
Since gastritis can cause the appearance of formations, it should be noted the characteristic symptoms of inflammatory processes in the mucous membrane. Patients may complain of dyspeptic symptoms: heartburn, nausea, epigastric pain, vomiting, stool disturbances, etc.
Symptoms indicating the presence of a polyp are nonspecific. They can appear in case of malnutrition or the integrity of the neoplasm, reaching large sizes, etc. In this case, the following symptoms are observed:
- signs of gastric bleeding: melena (tarry stools, indicating bleeding in the stomach), vomiting of coffee grounds, vomiting mixed with blood;
- obstructive syndrome: large growths can prevent the passage of chyme into the duodenum, blocking the sphincter. As a result, food lingers in the stomach for a long time, provoking bad breath, fetid vomiting;
- intense cramping pains with irradiation throughout the abdomen, under the sternum: associated with infringement of the neoplasm by the gatekeeper
- anemic syndrome: occurs due to gastric bleeding.
Diagnostics
To suspect the presence of a neoplasm in the organ, even after questioning the patient with details of his complaints, collecting anamnesis of life and disease, most often fails, due to the non-specificity of the clinical picture. Usually, the preliminary diagnosis is gastritis or a stomach ulcer. Then the patient is sent to confirm the diagnosis for additional studies.
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS) is a modern and most informative diagnostic method that allows visualizing the gastric mucosa, neoplasms and other pathological processes.

Fibrogastroduodenoscopy is highly informative for the diagnosis.
Fibrogastroduodenoscope is a special flexible optical device that is introduced to the patient through the oral cavity. It allows you to examine the inner wall of the esophagus, stomach and duodenal bulb.
During the EGD, when a pathological formation is detected, a biopsy of the damaged tissue is usually taken and sent to the laboratory for cytological and histological examination.
Other diagnostic methods
Also, pH-metry is performed - determining the level of the acid-base state of the contents of the organ. Normal pH of the stomach is acidic, on average - 1.5-2.

In some cases, an X-ray examination with contrast is prescribed
Another method is X-ray examination using a contrast agent. In this case, the patient drinks a special solution and after a certain time X-rays are taken. If the polyp has reached a large size, the configuration of the organ wall and its relief change; with the introduction of contrast, the changed zone is clearly visible in the picture.
If there are no obvious signs of gastric bleeding, it is possible to assign a fecal occult blood test.
To detect Helicobacter pylori infection, the following are prescribed:
- PCR (polymerase chain reaction): to detect the DNA of a pathogen;
- ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay): to detect antibodies to the pathogen.
Treatment
There is no conservative treatment for stomach polyps. However, with small uncomplicated hyperplastic formations, the doctor may recommend a wait-and-see tactic, in which the patient is prescribed a special diet, therapy for other gastroenterological diseases or diseases of a different profile is carried out.

The choice of treatment method is determined individually, depending on the type of education, its size and other factors.
The use of traditional medicine methods, including decoctions / infusions of celandine, in the treatment of stomach polyps has no evidence base and is not recommended.
With expectant tactics, the patient needs dispensary observation with regular (at least 1-2 times a year) EGD examination. The doctor notes the dynamics of growth, the nature of the surface (the presence of ulceration, bleeding, irregularities, erosion), the appearance of new formations.
If one or more signs change, complications appear, or the risk of malignancy increases, surgical treatment is recommended.
Polypectomy
Surgery to remove a polyp (polypectomy) is the most optimal treatment, the basis for which is gastric adenomas exceeding 10 mm.
Polypectomy can be performed endoscopically - without making incisions, access is through the oral cavity. This method is less traumatic, with a minimal risk of side effects. However, it is shown only for small single build-ups. Removal is carried out using an electric loop by electro excision or by electrocoagulation.
Healing of mucosal defects occurs within two to nine weeks. After endoscopic removal, dispensary observation with control endoscopy in 10-12 weeks is necessary.
Stomach resection
With multiple, large neoplasms, gastric resection is possible.
Attention! Photo of shocking content.
Click on the link to view.
Gastric resection is an operation with direct access, in which part of an organ is removed with further restoration of the continuity of the gastrointestinal tract.
Resection is an extreme measure, it is justified only in case of life-threatening complications or malignant processes in the organ wall.
Complications
With a timely undetected and untreated polyposis, the following complications may occur:
- gastric bleeding;
- anemia;
- pinching;
- obstruction of the stomach;
- polyp necrosis;
- malignancy (malignancy of the neoplasm).
Prevention
There are no specific preventive measures to prevent the formation of polyps. In view of the fact that the main etiological factor of this process is an inflammatory lesion of the inner wall of the organ - gastritis, the main measures should be aimed at preventing its occurrence.

Fractional nutrition is the prevention of the development of pathology
Preventive measures include:
- compliance with the rules of a balanced diet and food intake: frequent, fractional 4-5 meals a day in small portions with the correct ratio of proteins, fats and carbohydrates is recommended;
- getting rid of bad habits: smoking, drinking alcohol;
- a cautious approach to drug therapy: it is necessary to exclude or minimize the use of drugs that have a gastrotoxic effect, including nonselective non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (diclofenac, ibuprofen, indomethacin).
You should completely give up alcohol and cigarettes. Alcohol has a destructive effect on the gastric mucosa, which can lead to ulceration of the polyp, the appearance of erosions, bleeding. Smoking reduces the protective properties of the inner wall of the organ and increases the production of gastric juice.
Non-selective non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are contraindicated in patients with gastric polyposis.
Forecast
With timely removal of the neoplasm, the prognosis is favorable. However, surgical treatment does not exclude the possibility of relapse, therefore, regular dispensary observation is a necessity, since it will allow early diagnosis and the necessary therapy for repeated processes. Disability recovery usually occurs in full.
In order to find out why there are symptoms from the digestive system and how dangerous it is, you need to contact a therapist or gastroenterologist. A long course of the disease without adequate therapy can lead to the development of stomach cancer.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.