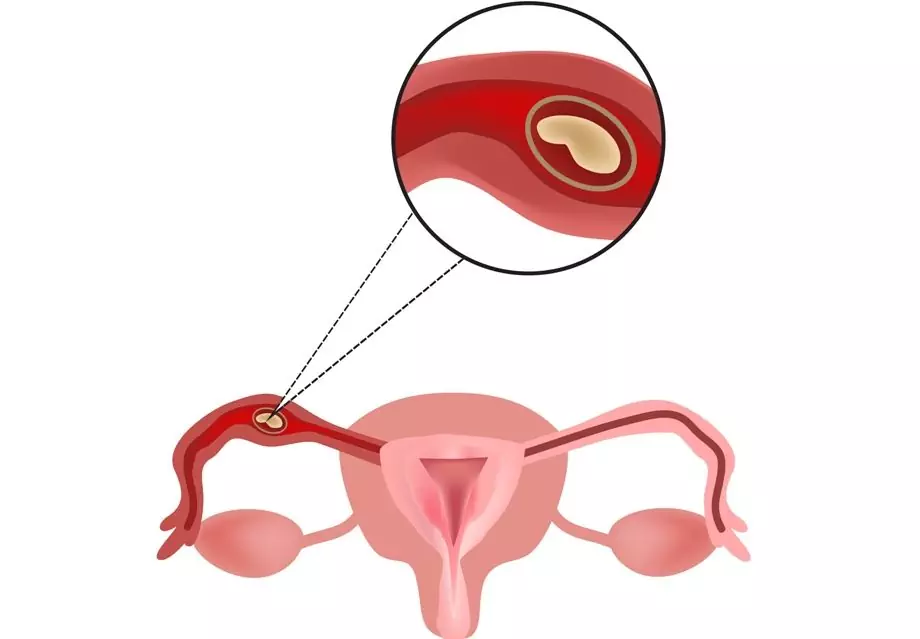
Ectopic pregnancy
The content of the article:
- Causes and risk factors
- Disease types
-
Symptoms
- Tubal pregnancy
- Ovarian pregnancy
- Abdominal pregnancy
- Cervical pregnancy
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Possible complications and consequences
- Forecast
- Prevention
Ectopic pregnancy is a pregnancy in which the attachment and further development of the ovum occurs outside the uterine cavity. This is a dangerous pathology that can lead to serious complications, including life-threatening ones.

Tubal ectopic pregnancy
Causes and risk factors
Ectopic pregnancy is caused by various factors that disrupt the process of moving a fertilized egg into the uterine cavity or implantation. These factors include:
- drug stimulation of ovulation;
- endometriosis;
- hormonal contraception;
- a history of abortion;
- the presence of an intrauterine device;
- delayed sexual development;
- tumors of the internal genital organs;
- previous surgery on the ovaries or fallopian tubes;
- malformations of the genital organs;
- inflammatory diseases of the appendages, in particular sexually transmitted diseases;
- Asherman's syndrome (intrauterine synechiae).
Disease types
Depending on the place of attachment of the ovum, an ectopic pregnancy is:
- pipe;
- ovarian;
- abdominal;
- cervical.
In 99% of all cases of ectopic pregnancy, implantation of the ovum occurs in the fallopian tubes. The most rare form is cervical pregnancy.

Ectopic pregnancy classification
Symptoms
In the early stages, an ectopic pregnancy manifests itself in the same way as a normal one:
- delayed menstruation;
- engorgement of the mammary glands;
- nausea, especially in the morning;
- weakness;
- change in taste preferences.
When conducting a gynecological examination, you can notice that the size of the uterus lags behind the expected duration of pregnancy.

In the early stages, an ectopic pregnancy manifests itself in the same way as a normal one.
As the ovum grows and develops in a place not intended for this, various complications arise that determine the clinical picture of an ectopic pregnancy.
Tubal pregnancy
When the ovum is implanted in the cavity of the fallopian tube, pregnancy usually progresses to 6-7 weeks. Then the ovum dies, and the fallopian tubes begin to contract vigorously, pushing it into the abdominal cavity. This process is accompanied by bleeding. Blood also enters the abdominal cavity. This termination of an ectopic pregnancy is called a tubal abortion.
The clinical picture of tubal abortion is largely determined by the amount of blood poured into the abdominal cavity. With a little bleeding, the woman's condition changes little. She usually complains of cramping pains in the lower abdomen and the appearance of dark spotting bleeding from the genital tract.
A tubal abortion, accompanied by significant bleeding, is characterized by severe pain that can radiate to the anus. In addition, signs of internal bleeding appear and grow:
- general weakness;
- dizziness;
- lowering blood pressure;
- tachycardia.
In some cases, a tubal pregnancy can rupture the fallopian tube. This condition is accompanied by massive internal bleeding and in 10% of cases is complicated by the development of hemorrhagic shock. The clinical picture with a ruptured pipe develops very quickly:
- sharp pain in the lower abdomen, radiating to the anus;
- the appearance of tenesmus (false urge to defecate);
- severe dizziness;
- fainting;
- pallor of the skin and mucous membranes;
- cold clammy sweat;
- lethargy, apathy;
- frequent pulse of weak filling;
- lowering blood pressure;
- dyspnea.

The rupture of the fallopian tube threatens massive internal bleeding, which threatens the woman's life
Ovarian pregnancy
Ovarian pregnancy can progress up to 16-20 weeks, which is associated with the high elasticity of the ovarian tissue. However, at a certain point in time, they cease to have time to stretch following the growth of the embryo. The onset of the limit is characterized by abdominal pain, painful bowel movements. Then the ovary ruptures with the development of massive bleeding into the abdominal cavity. The clinical picture is similar to the clinical picture of rupture of the fallopian tube.
Abdominal pregnancy
In an abdominal pregnancy, the fetus is implanted between the intestinal loops. As it grows, irritation of the nerve endings of the peritoneum occurs, manifested by intense pain in the abdomen.
In the overwhelming majority of cases, during abdominal pregnancy, the death of the fetus occurs, which is further macerated or saturated with calcium salts, turning into a fossilized fetus.
With an abdominal pregnancy, there is always a high risk of rupture of the fetus with the development of pronounced internal bleeding, accompanied by symptoms traditional for such a condition - weakness, hypotension, tachycardia, pallor of the skin, cold sweat.
In very rare (literally isolated) cases, an abdominal pregnancy develops before the end of the term and ends with the birth of a child by cesarean section.
Cervical pregnancy
With this type of ectopic pregnancy, the ovum is implanted in the cervical canal of the cervix. In the early stages, the disease is asymptomatic or with signs characteristic of a normal uterine pregnancy. Then, at a period of 8-12 weeks, bloody discharge from the genital tract appears. There is no pain. Bleeding during cervical pregnancy can be of varying intensity: from minor spotting to profuse, life-threatening.
During a gynecological examination, it is noted that the cervix is much larger in size than the body.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of an ectopic pregnancy before termination is often difficult. Its presence can be assumed based on the following signs:
- discrepancy between the size of the uterus and the expected gestational age;
- inconsistency of the hCG content in the blood with the expected gestational age.
In these cases, an ultrasound examination of the uterus is performed using the transvaginal method, determining the presence of an ovum in the uterus.
When an ectopic pregnancy is interrupted, in most cases, the diagnosis is straightforward. It is based on a characteristic clinical picture, anamnesis, examination result, ultrasound data (fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity, absence of an ovum in the uterus are detected).

Ultrasound shows the absence of the ovum in the uterus and the accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity during an ectopic pregnancy
In doubtful cases, a diagnostic puncture of the posterior vaginal fornix is performed. The presence of dark blood in the punctate, which does not form clots, confirms a disturbed ectopic pregnancy.
Treatment
Treatment of an ectopic pregnancy is surgical, regardless of the place of implantation of the ovum.
In a tubal pregnancy, laparoscopic surgery is usually performed, during which the affected fallopian tube and blood that has poured into the abdominal cavity are removed. When a pregnancy is terminated by the type of tubal abortion, it is possible to carry out an organ-preserving operation - tubotomy.

Operation to retrieve the ovum
In an ovarian pregnancy, an oophorectomy (removal of the ovary) is performed.
The choice of the method of surgical intervention for abdominal pregnancy is determined by several factors - first of all, the place of implantation of the ovum and the gestational age.
With cervical pregnancy, extirpation of the uterus (removal of the body and cervix) is indicated. The medical literature describes the successful removal of the ovum from the cervical canal with subsequent suturing of the fetal bed. However, such operations have a high risk of developing profuse bleeding, therefore, they are allowed to be performed only in a hospital, in an expanded operating room.
Possible complications and consequences
The main complications of an ectopic pregnancy:
- hemorrhagic shock;
- posthemorrhagic iron deficiency anemia;
- adhesive process in the small pelvis;
- secondary infertility.
Forecast
With timely diagnosis and treatment, the prognosis is favorable for life.
Patients who have once had an ectopic pregnancy have a 10 times higher risk of developing it than healthy women.
Prevention
Ectopic pregnancy prevention consists of the following measures:
- avoidance of casual sex and related sexually transmitted diseases;
- timely detection and treatment of inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system;
- medical examination at the stage of pregnancy planning;
- prevention of abortion (use of contraception);
- after an ectopic pregnancy - a long course of rehabilitation with planning a new pregnancy no earlier than 6, and better - 12 months.
YouTube video related to the article:

Elena Minkina Doctor anesthesiologist-resuscitator About the author
Education: graduated from the Tashkent State Medical Institute, specializing in general medicine in 1991. Repeatedly passed refresher courses.
Work experience: anesthesiologist-resuscitator of the city maternity complex, resuscitator of the hemodialysis department.
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!