- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Hyperplasia
Hyperplasia (hyperplasia; Greek hyper- - excessive, over, over + plasis - formation, formation) - an increase in the number of intracellular structures, cells, intercellular fibrous formations as a result of intense organ function or due to pathological tissue neoplasm.
Types of hyperplasia:
- glandular (glandularis): hyperplasia of the glandular epithelium, for example, in the lining of the uterus, mammary gland, stomach;
- glandular cystic (glandulocystica): glandular hyperplasia, accompanied by a racemose expansion of the lumens of the newly formed glands / hyperplasia of the endometrial glands, noted against the background of ovarian dysfunction;
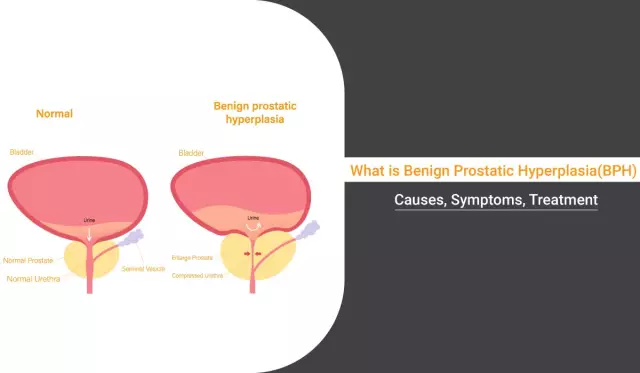
- glandular muscle (glandulomuscularis): glandular hyperplasia, accompanied by increased development of smooth muscles in the stroma of the gland, for example, the prostate;
- pseudoepitheliomatous skin (cutis pseudoepitheliomatosa; synonym: pseudocarcinomatous skin hyperplasia): epidermal hyperplasia, characterized by its uneven growth and thickening;
- renal artery fibromuscular (arteriae renalis fibromuscularis): hyperplasia of the wall of the renal artery due to its muscle and connective tissue elements; causes narrowing of the lumen of the artery and vasorenal hypertension.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.