Hemorrhoids in children: why hemorrhoids develop in a child, how to treat it, preventive measures
The content of the article:
- Causes of the appearance of hemorrhoids in childhood
- How does hemorrhoids manifest in a child
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- How to treat hemorrhoids in children
- Complications
- Course and forecast
- Prevention
- Hemorrhoids: ICD-10 code
Hemorrhoids in children are very rare. It is considered a disease of middle-aged and older people. And if in adults the causes of this disease often lie in their own carelessness, then in children it develops due to the carelessness of their parents or caregivers. At the same time, pathology in children has a course different from that of adults and requires slightly different approaches to treatment.
Causes of the appearance of hemorrhoids in childhood
The reasons for children of younger and older age groups are different. In young children, the development of the disease is most often caused by constipation, improper planting on a pot and strong crying.

One of the reasons for the development of hemorrhoids in children is prolonged sitting on the potty
Constipation can occur in a child of any age and even in a baby. With a rare emptying of the intestine, the feces become denser. They injure the rectal mucosa, causing inflammation. During defecation, the child is forced to push hard, which leads to increased blood flow to the corpora cavernosa of the rectum. In addition, against the background of constipation, children often have a crack in the anus (anal fissure).
Some parents go out of their way to potty train their child. They plant a baby on it not when he has a physiological need for it, but according to a schedule they have invented themselves. As a result, children sit for a long time, but to no avail. In this case, there is an overflow of blood in the veins of the rectum, which creates the prerequisites for the formation of hemorrhoids. Prolonged potty sitting, especially in combination with constipation, is the main cause of another proctological disease - rectal prolapse. Therefore, even a child at 2 years old should not be forcibly placed on a potty, and even more so should not be done with older children.
Long and strong crying is a common cause of hemorrhoids in young children. At the time of crying, there is a significant increase in intra-abdominal pressure, which, in turn, causes blood to overflow the veins of the pelvic organs. If hemorrhoids are diagnosed in a frequently crying child for 3 years, then for its effective treatment it is necessary to identify and eliminate the cause of crying.
Congenital enlargement of hemorrhoidal veins is the most rare cause of the disease. In this case, the pathology begins to manifest itself from the first days of the baby's life.
In children over 5 years of age, the causes of hemorrhoids, in addition to the above, can be:
- a sedentary lifestyle, leading to the onset of congestion in the pelvic organs;
- improper nutrition - insufficient content in the diet of fresh vegetables, fruits, the predominance of fast food in it, the so-called junk food, sugary carbonated drinks;
- weightlifting - with an incorrectly drawn up training plan that does not take into account the characteristics of a developing child's body, conditions are created for the formation of hemorrhoids.
Older schoolchildren sometimes start to taste alcohol. Alcohol irritates the rectal mucosa, increases blood flow to it, which eventually leads to hemorrhoids.
How does hemorrhoids manifest in a child
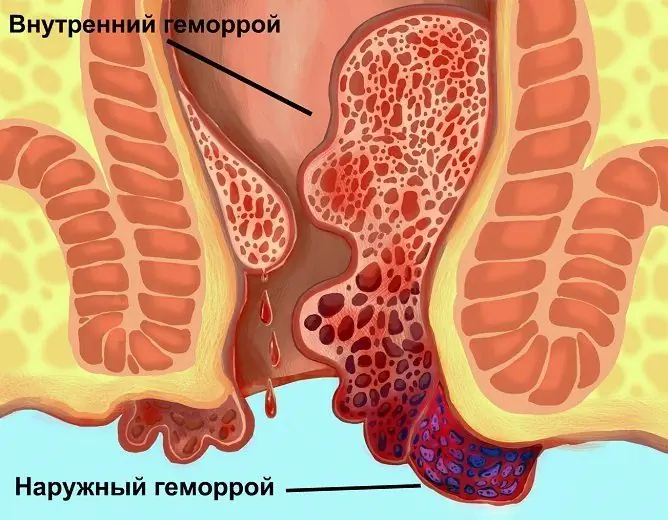
The essence of this disease in children and adults is the same. Pathology consists in the expansion and hyperplasia of the cavernous bodies of the distal rectum, which form hemorrhoids. They can be located both inside the rectum (internal hemorrhoids) and outside (external hemorrhoids). The external manifestations of the disease are the same in people of any age, hemorrhoids in a child in the photo looks the same as in an adult.
Symptoms
The initial stage of the disease in children is almost asymptomatic. Signs of hemorrhoids begin to appear only as it progresses. These include:
- itching, burning and / or pain in the anal area;
- feeling of incomplete emptying of the rectum;
- spotting during or immediately after a bowel movement;
- the appearance of small protrusions around the anus.
Infection of hemorrhoids is accompanied by an increase in their soreness, a rapid increase in body temperature to febrile values, the appearance of symptoms of intoxication (head and muscle pain, lack of appetite, weakness).
Usually, only children aged 4 years and older can correctly and accurately formulate complaints. Young children inform others about their ailments with whims, crying. Therefore, in this case, the observation of parents, their ability to understand their baby, is of great importance for making the correct diagnosis.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the disease in children is carried out in the same way as in adult patients. The diagnosis is made on the basis of a characteristic clinical picture, the results of a medical examination (including examination in rectal mirrors), sigmoidoscopy and sphincterometry.
Differential diagnosis is carried out with the following diseases:
- anal fissure;
- hypertrophied anal papilla;
- polyp;
- paraproctitis;
- prolapse of the rectum;
- prolapse of the rectal mucosa.
How to treat hemorrhoids in children
Treatment of hemorrhoids in children is usually conservative. It is aimed at arresting the inflammatory process, regulating the stool and normalizing venous blood flow in the rectal area and includes:
- sessile baths with infusions of medicinal herbs (oak bark, pharmacy chamomile) or a pale pink solution of potassium permanganate;
- ointment or suppositories with heparin;
- microclysters with Vishnevsky ointment, rosehip oil or sea buckthorn oil;
- physiotherapy procedures (ultraviolet irradiation of the perineum with a quartz lamp, UHF);
- laxatives - if indicated and only if it is not possible to normalize the stool with the help of a diet;
- ointment or suppositories with anesthesin - with severe pain;
- hydrocortisone ointment - for severe itching.
With frequent bleeding of hemorrhoids or the occurrence of profuse bleeding from them, hemostatic therapy is prescribed (Vikasol, Ditsinon).
Conservative therapy in children is carried out at home, but always by appointment and under the supervision of a doctor.
The need for surgery in children is extremely rare. The indications for surgery are:
- prolapse and infringement of hemorrhoids;
- bleeding;
- hemorrhoidal necrosis.
Complications
In children, a complicated course of hemorrhoids is extremely rare. More often complications develop in children from disadvantaged families, in the absence of proper treatment and care. These include:
- thrombosis of hemorrhoids;
- irreducibility or infringement of the prolapsed hemorrhoid;
- necrosis of hemorrhoids;
- paraproctitis;
- phlegmon;
- anal itching;
- Iron-deficiency anemia;
- incontinence of gases and feces;
- sepsis.
Course and forecast
With timely initiation of treatment and elimination of the factor that caused the course of hemorrhoids in children, in most cases, favorable. The disease enters the stage of long-term remission, and often complete recovery occurs.

In order to prevent hemorrhoids, the child should move more and sit less
Prevention
Could it be that the child will have hemorrhoids again after recovery? This is quite possible if prevention is not carried out, which is built in the following areas:
- Fight against hypodynamia. Parents should ensure that their children spend sufficient time outdoors playing active games. Sports, dancing are welcome. The time you sit at the computer or in front of the TV should be limited.
- Proper nutrition. Products that contribute to constipation (sweets, white bread, fast food) and irritating the intestinal mucosa (coffee, cola, lemonade) should be excluded from the child's diet. The menu should meet the needs of the child's body for basic nutrients and be sure to contain a sufficient amount of greens, fresh vegetables and fruits.
- Instilling the right hygiene habits. From an early age, the baby should be taught not to sit on a potty or toilet for a long time. After defecation, the genitals and perineum must be washed with soap under running water.
Hemorrhoids: ICD-10 code
The International Classification of Diseases, Revision 10 (ICD-10) is a generally accepted system for coding medical diagnoses developed by WHO. Based on the changes made to it in January 2013, the following codes are assigned to hemorrhoids:
- K64.0 - stage I hemorrhoids, without loss of nodes from the anal canal;
- K64.1 - stage II hemorrhoids (hemorrhoids under the influence of increased pressure in the abdominal cavity go beyond the anal canal, after which they spontaneously are drawn into it);
- K64.2 - stage III hemorrhoids (hemorrhoids that have fallen out at the moment of tension require manual reduction);
- K64.3 - stage IV hemorrhoids (manual reduction of fallen hemorrhoids is impossible);
- K64.4 - residual hemorrhoidal skin marks of the anus;
- K64.5 - perianal venous thrombosis;
- K64.8 - specified other hemorrhoids;
- K64.9, unspecified hemorrhoids.
YouTube video related to the article:

Elena Minkina Doctor anesthesiologist-resuscitator About the author
Education: graduated from the Tashkent State Medical Institute, specializing in general medicine in 1991. Repeatedly passed refresher courses.
Work experience: anesthesiologist-resuscitator of the city maternity complex, resuscitator of the hemodialysis department.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.