- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Neurobion
Neurobion: instructions for use and reviews
- 1. Release form and composition
- 2. Pharmacological properties
- 3. Indications for use
- 4. Contraindications
- 5. Method of application and dosage
- 6. Side effects
- 7. Overdose
- 8. Special instructions
- 9. Application during pregnancy and lactation
- 10. Use in childhood
- 11. Drug interactions
- 12. Analogs
- 13. Terms and conditions of storage
- 14. Terms of dispensing from pharmacies
- 15. Reviews
- 16. Price in pharmacies
Latin name: Neurobion
ATX code: A11DB
Active ingredient: Pyridoxine + Thiamin + Cyanocobalamin (Pyridoxine + Thiamine + Cyanocobalamin)
Manufacturer: Merck KGaA, Germany; Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited, Japan.
Description and photo update: 2019-12-08
Prices in pharmacies: from 220 rubles.
Buy
Neurobion is a complex of B vitamins.
Release form and composition
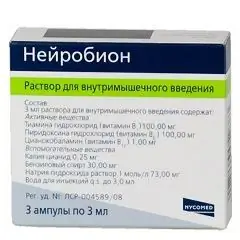
- Solution for intramuscular injection: transparent, red (3 ml each in dark glass ampoules, 3 ampoules in blisters, 1 pack in a cardboard box);
- Film-coated tablets: round, convex on both sides, almost white, shiny (10 pcs. In blisters, 2 blisters in a cardboard box).
Active ingredients and their content in 1 ampoule and 1 tablet:
- Thiamine hydrochloride (vitamin B1): 100 mg each;
- Pyridoxine hydrochloride (vitamin B6): 100 mg and 200 mg (respectively);
- Cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12) (respectively): 1 mg and 0.24 mg (including 20% excess).
Solution excipients: sodium hydroxide solution, benzyl alcohol, potassium cyanide, water for injection.
Excipients of tablets: methylcellulose, gelatin, corn starch, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, talc.
Composition of the tablet shell: methylcellulose, glycerol 85%, acacia, colloidal silicon dioxide, povidone 25, titanium dioxide, kaolin, calcium carbonate, gelatin, wax, sucrose, talc.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Neurobion contains a complex of B vitamins, which are neurotropic active substances. These vitamins (pyridoxine, thiamine, and cyanocobalamin) play an important role in intermediate metabolism in the peripheral and central nervous system. They act as coenzymes.
The combined use of vitamins B 1, B 6 and B 12 is due to the fact that in the complex their action is more effective than for each component separately. The combination of B vitamins accelerates the regeneration processes in damaged nerve fibers.
Like other vitamins, pyridoxine, thiamine, and cyanocobalamin are essential nutrients that cannot be synthesized in the body on their own. With the therapeutic administration of B vitamins, the deficiency of vitamins from food is replenished.
The use of Neurobion in diseases of the nervous system, on the one hand, compensates for the existing deficit, which often arises due to the increased needs of the body due to the disease, and on the other hand, it stimulates natural mechanisms that are aimed at restoring the function of nerve tissues. The indirect analgesic effect of the drug has a beneficial effect on the therapeutic result.
Pharmacokinetics
After taking Neurobion inside, thiamine undergoes dose-dependent transport in the body. Its mechanism has a dual nature: at a substance concentration of up to 2 μmol / L, active absorption occurs, at concentrations above 2 μmol / L, passive diffusion is observed. Thiamine metabolism occurs in the liver by phosphorylation. The half-life is 4 hours. The tissues of the body contain about 30 mg of thiamine, with a rapid metabolism, it is excreted after 4-10 days.
The absorption of pyridoxine is very rapid and occurs mainly in the upper intestine. The half-life is 2-5 hours. To act as a coenzyme, pyridoxine is phosphorylated to pyridoxal phosphate. In phosphorylated form, it binds almost 80% to plasma proteins. In the body, the content of pyridoxine is 40-150 mg. It is excreted in the urine. From 1.7 to 3.6 mg of pyridoxine is excreted per day.
The absorption of cyanocobalamin from the digestive tract is carried out by two mechanisms: the first is the release under the influence of gastric juice and further rapid binding with an internal factor; the second is passive diffusion in the intestine, independent of the intrinsic factor. The second mechanism is more often observed at doses of cyanocobalamin more than 0.0015 mg. In patients with megaloblastic anemia (B 12 -deficient), the reabsorption of cyanocobalamin after oral administration is about 1% of a dose of 0.1 mg or more. An excess amount of cyanocobalamin accumulates in the liver, from where it is excreted with bile into the intestine, and then is reabsorbed during further intestinal-hepatic circulation. Its metabolic rate is 0.0025 mg per day.
Indications for use
Complex therapy of diseases of the nervous system:
- Paresis of the facial nerve;
- Trigeminal neuralgia;
- Sciatica, lumbago;
- Herpes zoster;
- Pain syndrome caused by diseases of the spine, such as cervical syndrome, lumbar syndrome, intercostal neuralgia, shoulder-hand syndrome, and radicular syndrome caused by degenerative changes in the spine.
Contraindications
The main contraindication to the use of Neurobion is hypersensitivity to its components.
The drug is not used in pediatrics.
In the form of tablets, the drug is contraindicated in case of hereditary intolerance to galactose or fructose, lactase deficiency, sucrose-isomaltase deficiency, glucose-galactose malabsorption (because the composition includes sucrose and lactose).
Due to the high content of vitamins, Neurobion is not recommended for use during pregnancy and lactation.
Instructions for the use of Neurobion: method and dosage
Injection
The solution is injected deep into the gluteus muscle.
With severe pain syndrome, treatment begins with a dose of 3 ml (1 ampoule) once a day. After the removal of acute symptoms, as well as in the case of moderate pain syndrome, the drug is administered 3 ml 2-3 times a week for a course of 2-3 weeks.
For prophylaxis, maintenance therapy and, if necessary, to continue the ongoing therapeutic course, the drug is prescribed in the form of tablets.
Film-coated tablets
The tablets are taken orally, swallowed whole and washed down with water, with or after meals. Usually, 1 tablet is prescribed 3 times a day, the duration of treatment is 1-1.5 months. In the case of therapy for more than 4 weeks, dose adjustment is recommended.
Side effects
In tablets Neurobion is generally well tolerated, in rare cases, side effects are noted:
- Immune system: hypersensitivity reactions (excessive sweating, tachycardia);
- Digestive system: diarrhea, nausea, abdominal pain, vomiting;
- Allergic reactions: urticaria and itching.
Possible side effects with parenteral administration of the drug:
- Due to vitamin B1: very rarely - sweating, allergic reactions in the form of rash and itching, tachycardia, hypersensitivity reactions (shortness of breath, exanthema, anaphylactic shock);
- Due to vitamin B12: in some cases - urticaria, eczema, acne.
Overdose
B vitamins have a wide range of effective concentrations. When using Neurobion in compliance with the recommended dosage regimens, overdose symptoms are not observed.
Vitamin B 1 in high doses exceeding the recommended 100 times or more (over 10 g) exhibits a curariform ganglion blocking effect, suppressing the transmission of impulses in nerve cells (muscle relaxant effect).
Peripheral sensory neuropathy may occur after taking vitamin B 6 in a daily dose of more than 50 mg for 6-12 months. Prolonged intake (more than 2 months) of pyridoxine in doses exceeding 1 g per day can cause neurotoxic effects. Daily doses of more than 2 g led to the appearance of neuropathy with ataxia, cerebral convulsions with changes in the electroencephalogram, sensory disorders, hypochromic anemia and seborrheic dermatitis.
After parenteral administration of high doses of cyanocobalamin and in rare cases after its ingestion, symptoms of overdose such as benign acne and eczematous skin disorders were observed.
Treatment consists in discontinuation of the drug, gastric lavage and intake of activated charcoal. If necessary, symptomatic, including desensitizing, therapy is carried out.
special instructions
Neurobion solution is not allowed to be administered intravenously.
Vitamin B12 can affect the clinical picture and laboratory tests in pernicious anemia and funicular myelosis.
Vitamin B1 can inactivate other vitamins, especially cyanocobalamin.
If long-term treatment is necessary, the patient's condition should be monitored regularly, because long-term use (more than 6 months) of vitamin B6 in a daily dose of 50 mg can lead to the development of peripheral sensory neuropathy.
Neurobion does not have a negative effect on the speed of reactions and the ability to concentrate.
Application during pregnancy and lactation
Neurobion is not recommended for use during pregnancy and breastfeeding due to its high vitamin content.
B vitamins are secreted in breast milk, but the risk of overdose in infants has not been established. In some cases, taking high doses of pyridoxine (more than 600 mg per day) can lead to suppression of lactation.
If the use of the drug during lactation is necessary according to indications, breastfeeding should be discontinued.
Pediatric use
According to the instructions, Neurobion is contraindicated in children and adolescents under the age of 18 (due to the high content of active ingredients).
Drug interactions
- Antacids: decreased absorption of thiamine;
- Fluorouracil: inactivation of thiamine;
- Levodopa: a decrease in its antiparkinsonian action;
- "Loop" diuretics (for example, furosemide): increased excretion of thiamine with prolonged use and, as a result, a decrease in its concentration in the blood;
- Pyridoxine antagonists (eg, penicillamine, hydralazine, cycloserine, isoniazid): increased need for pyridoxine;
- Ethanol and black tea: decreased absorption of thiamine;
- Sulphite-containing drinks (including wine): enhances the breakdown of thiamine.
In the form of a solution, Neurobion cannot be mixed with other drugs in the same syringe.
Analogs
Analogs of Neurobion are: Vitaxon, Complex B1, B6, B12, Neuromultivit, Neurobion, Nerviplex, Neurobeks, Unigamma.
Terms and conditions of storage
Store in a dark place out of reach of children. Do not exceed a temperature of 20 ° C.
The shelf life is 3 years.
Terms of dispensing from pharmacies
Dispensed by prescription.
Reviews about Neurobion
The drug is an effective remedy for diseases of the nervous system, including for their prevention. According to reviews, Neurobion has several advantages over non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, also used for neurological diseases. First, it rarely causes side effects, and if they occur, they are mild. Secondly, Neurobion has low toxicity.
The disadvantages of the drug are the price (it is more expensive than some analogues) and availability (it is often not available in the range of a number of pharmacies).
Price for Neurobion in pharmacies
Prices for Neurobion depend on the form of release of the drug and a specific pharmacy:
- film-coated tablets (20 pcs. in a package) - 270-330 rubles;
- solution for intramuscular injection (3 ampoules per package) - 275-310 rubles.
Neurobion: prices in online pharmacies
|
Drug name Price Pharmacy |
|
Neurobion (for injection) solution for intramuscular injection 3 ml 3 pcs. 220 RUB Buy |
|
Neurobion coated tablets 20 pcs. RUB 300 Buy |
|
Neurobion tablets p.p. 20 pcs. RUB 318 Buy |
|
Neurobion solution for intramuscular injection 3ml 3 pcs. RUB 614 Buy |

Maria Kulkes Medical journalist About the author
Education: First Moscow State Medical University named after I. M. Sechenov, specialty "General Medicine".
Information about the drug is generalized, provided for informational purposes only and does not replace the official instructions. Self-medication is hazardous to health!






