- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
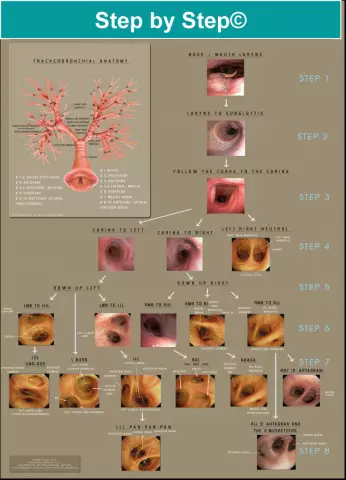
Bronchoscopy

Bronchoscopy is a shorter name for an endoscopic method for assessing the lumen of the trachea, bronchi and assessing the mucous membrane - tracheobronchoscopy.
Indications for bronchoscopy
Bronchoscopy of the lungs is used for both diagnosis and treatment.
Bronchoscopy is recommended for diagnosis with the following symptoms:
- traces of blood in sputum;
- persistent cough without obvious reasons;
- suspected pulmonary infections;
- violation of the breathing process;
- pathological changes as a result of X-ray examination - nodules, seals, inflammatory processes.
In addition, the indications for bronchoscopy are:
- long experience of smoking for the purpose of preventive examination;
- chronic bronchitis, obstructive pulmonary disease;
- tuberculosis;
- suspected lung cancer;
- atelectasis of the lung (i.e. the condition of the lung tissue when the alveoli lose their airiness).
To make a bronchoscopy of the lungs for therapeutic purposes is recommended for:
- removal of foreign bodies from the respiratory tract;
- removal of a neoplasm that blocks the airways;
- placing a stent in one of the airways if, for example, it is compressed by a tumor.
You need to do a bronchoscopy in order to:
- remove a benign or malignant tumor, foreign body, bronchial secretions and mucous plug from the bronchial tree;
- study the features of the tumor;
- to find out the intensity of bleeding, the degree of obstruction of the lumen of the bronchus, the localization and nature of the foreign body;
- by obtaining a piece of tissue for cytological and microbiological research, obtain additional information for the diagnosis of tuberculosis, bronchogenic cancer, fungal infection, interstitial pneumonia, parasitic invasion of the lungs.
Contraindications
Absolute:
- myocardial infarction, transferred less than six months ago;
- intolerance to drugs that are used for local anesthesia;
- violation of the heart rhythm;
- acute stroke;
- stenosis of the larynx and / or trachea;
- hypertonic disease;
- exacerbation of bronchial asthma;
- cardiovascular or pulmonary heart failure;
- pain syndrome in the abdominal cavity;
- neuropsychiatric diseases (schizophrenia, epilepsy, etc.);
- condition after traumatic brain injury;
- the serious condition of the patient in the case when the clarification of the diagnosis will no longer affect the treatment.
Relative contraindications for lung bronchoscopy:
- period of the menstrual cycle;
- second half of pregnancy;
- cardiac ischemia;
- ARI of the upper respiratory tract;
- chronic alcoholism;
- severe diabetes mellitus;
- enlargement of the thyroid gland (III degree).
How is bronchoscopy performed
During bronchoscopy, the patient is connected to a monitor so that the doctor can monitor blood pressure, oxygen levels in the body and pulse. The examined person is given general anesthesia or a sedative is injected intravenously. Supplemental oxygen is injected through the nose or mouth.

Lidocaine, a local anesthetic, is applied to the back of the larynx or into the nasal cavity, then a brochofibroscope is inserted. The study lasts 20 - 60 minutes, if necessary, the doctor records the resulting image, performs a biopsy or performs medical manipulations.
Possible complications after bronchoscopy
Each procedure must be carried out taking into account the indications for bronchoscopy and the contraindications of each patient, therefore, complications after it are quite rare. However, in some cases it may be:
- damage to the vocal cords;
- nose bleed;
- irregular heart rate;
- bleeding at the biopsy site;
- insufficient oxygen supply to tissues;
- puncture of the lung;
- complications associated with the use of anesthetics and sedatives.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.