- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Purulent sore throat
The content of the article:
- Purulent sore throat causes and risk factors
- Forms of the disease
- Symptoms of purulent sore throat
- Features of the course of the disease in children
- Diagnostics
- Treatment of purulent sore throat
- Possible complications of purulent sore throat and consequences
- Forecast
- Prevention of purulent sore throat
Purulent tonsillitis is a name that unites two purulent forms of tonsillitis (acute tonsillitis) - follicular and lacunar. These forms of angina have a similar general and local course; in one patient, signs of both forms of angina may be noted at the same time. Often the pathological process occurs in the palatine tonsils, in more rare cases, the lingual, nasopharyngeal and laryngeal tonsils are affected.
Most often, purulent tonsillitis is diagnosed in children of preschool and primary school age. In children under 5 years of age, as well as in adults, viruses often act as an infectious agent; in the age group 5-15 years, purulent tonsillitis of bacterial etiology is more often observed.
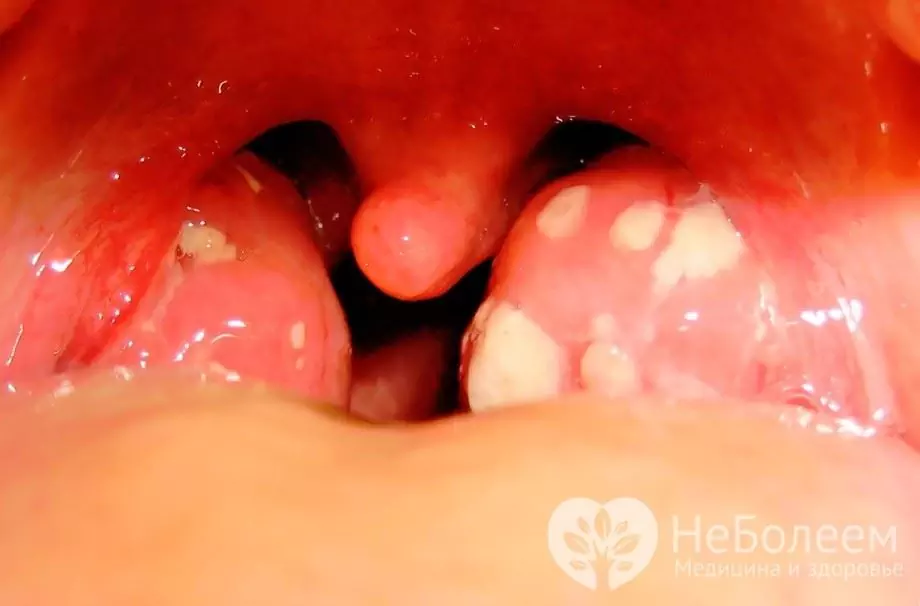
Bubbles of white or yellowish color on the surface of the tonsils - a characteristic sign of purulent tonsillitis
Purulent sore throat causes and risk factors
The cause of purulent sore throat is infectious pathogens. Infectious agents in purulent sore throat are usually bacteria and viruses, in some cases, the disease can be caused by microscopic fungi or parasites. In children, as a rule, the tonsils of the pharyngeal ring are affected by streptococci (85% of all cases). Purulent tonsillitis in adults often occurs against the background of acute respiratory viral infections.
Infectious agents are able to penetrate into the tissue of the tonsils exogenously (from a sick person by airborne, household or alimentary) or endogenous (from carious teeth, with acute respiratory infections, other infectious processes in the body). In people with weakened immunity, the disease can be caused by opportunistic microorganisms that are constantly present on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity or pharynx and do not provoke inflammation under normal conditions.
The risk factors for the development of purulent sore throat include:
- hypothermia of both the body as a whole and the throat (for example, when drinking ice cream, too cold water, etc.);
- infectious processes in the body;
- injury to the tonsils;
- air pollution;
- high humidity in the room;
- change of climatic conditions;
- long-term exposure to the body of solar radiation;
- food and other intoxication;
- poor nutrition;
- bad habits;
- severe overwork;
- stressful situations;
- immunodeficiency.
Forms of the disease
In total, by the nature of the inflammatory process, 4 forms of angina are distinguished, one of which is purulent:
- catarrhal (superficial damage to the tonsils, no purulent plaque);
- herpetic (on the tonsils subepithelial vesicles filled with serous exudate);
- purulent (purulent plaque is characteristic, which is easily removed without damaging the surface under it);
- necrotic (dense green-gray-yellow plaque, after removal of which a bleeding surface is exposed).
Purulent tonsillitis, in turn, can be follicular (mainly the follicles of the tonsils are affected, purulent islets are found on the tonsils, as well as purulent plaque on the mucous membrane of the tonsils, which is released from the follicles) and lacunar (characterized by the accumulation of pus in the lacunae of the tonsils).
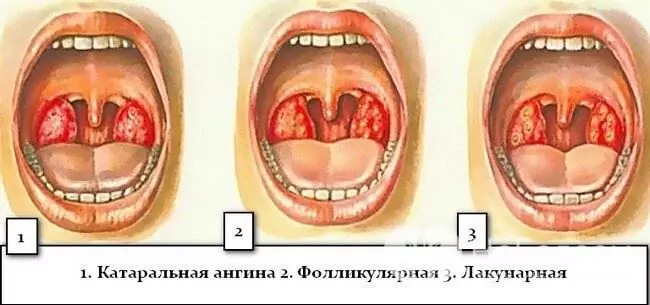
Types of purulent sore throat
Depending on the localization of the pathological process, angina can be unilateral (rarely, usually only at the beginning of the disease, in the future the process extends to both sides) and bilateral.
Symptoms of purulent sore throat
The incubation period lasts from 12 hours to three days. The disease makes its debut acutely, with an increase in temperature to febrile values - 39-40 ˚С, chills, headache, weakness, aching muscles and joints appear. There is a sharp pain in the throat, aggravated by swallowing and during a conversation, the cervical lymph nodes are enlarged, painful on palpation. The palatine tonsils and adjacent tissues are hyperemic and edematous, in some cases the edema is so significant that it makes breathing difficult.
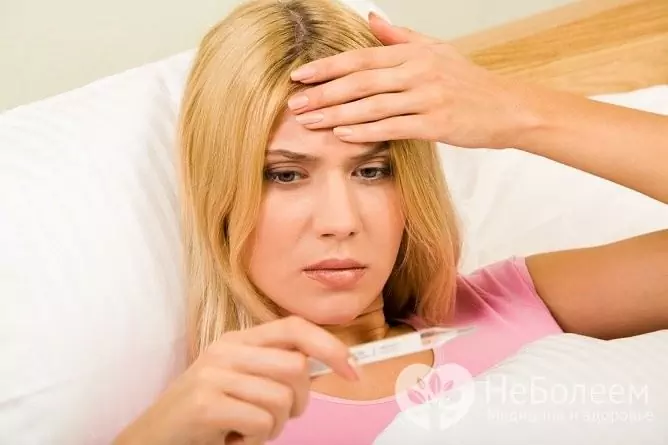

Purulent angina debuts acutely, with an increase in temperature to critical values
A common sign of purulent sore throat in the follicular form are areas of purulent fusion on the surface of the tonsils, which have the appearance of white or yellowish bubbles, which, in combination with a hyperemic tonsil, provides a characteristic symptom of the "starry sky". With the lacunar form, pus is located in the mouths of the lacunae of the palatine tonsils, having the appearance of whitish-yellow films or stripes that can go beyond the lacuna. In both lacunar and follicular forms, plaque is easily removed, without the appearance of a bleeding surface under it - this symptom distinguishes purulent sore throat from other forms of the disease similar to it.
Features of the course of the disease in children
Purulent tonsillitis in children has a violent course. The disease begins with a sharp increase in temperature (up to 40 ˚С), the child becomes moody and drowsy, refuses to eat and drink due to perspiration and severe sore throat. Regional lymph nodes increase, tachycardia often develops. In some cases, with purulent tonsillitis in children, there is such a pronounced swelling of the tonsils that they begin to put pressure on the Eustachian tubes, causing congestion and noise in the ears, and sometimes the spread of the infectious process to the ear.
Diagnostics
To diagnose purulent tonsillitis, anamnesis and patient complaints are collected, as well as pharyngoscopy. This is usually sufficient to make a diagnosis. If necessary, clarification is carried out by a general analysis of blood and urine, as well as a bacteriological study with an antibioticogram of a smear from the throat. In the general analysis of blood, there is an increase in the number of leukocytes with a shift of the leukocyte formula to the left. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate increases, reaching 40-50 mm / h (the norm is 1-15 mm / h). In some cases, to identify an infectious agent, a serological blood test, determination of the pathogen's DNA by polymerase chain reaction is necessary.
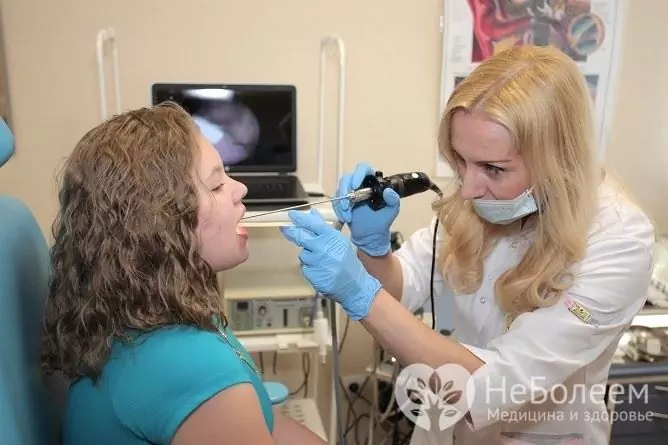
Pharyngoscopy allows in most cases to reliably diagnose purulent sore throat
Differential diagnosis with diphtheria, infectious mononucleosis is required.
Treatment of purulent sore throat
Treatment of purulent sore throat is usually carried out at home, hospitalization is indicated only in severe cases and for children under 3 years of age. The main method of treatment is antibacterial therapy, with the correct selection of the drug and dosage, the patient's condition improves already on the second day from the start of admission, however, the course of antibiotic therapy must be completely completed in order to avoid the development of antibiotic-resistant forms of microflora, as well as the appearance of complications. Since there is a need for an urgent start of treatment, as a rule, broad-spectrum antibiotics are used.
With a significant increase in temperature, antipyretics are used (the need for them, as a rule, arises only in the first 1-3 days). General therapy is complemented by frequent rinsing of the throat with antiseptic solutions and decoctions of medicinal herbs, which make it possible to remove pus from the mucous membrane of the oral cavity and pharynx. In addition to rinsing, topical medications can be prescribed in the form of sprays (irrigation with sprays in the treatment of purulent sore throat replaced the lubricants used earlier, since they are more convenient and less painful).

Strict bed rest, a sparing diet and plenty of drinking are indispensable components of the treatment of purulent sore throat.
As long as the body temperature remains elevated, patients require strict bed rest. A sparing diet and plenty of drink are shown. In the period of the most acute manifestations, refusal to eat is permissible, but an intensive drinking regimen is required.
Sometimes abundant liquid pus, localized in the mouths of the lacunae of the tonsils, is poorly removed by rinsing. In this case, a positive effect can be provided by washing the tonsils, which is performed by an otorhinolaryngologist.
Possible complications of purulent sore throat and consequences
Against the background of purulent sore throat, early and / or late complications may develop. Early complications are caused by the spread of the infectious and inflammatory process to nearby organs and tissues: sinusitis, otitis media, purulent inflammation of the lymph nodes, inflammation of the mediastinal tissue (mediastinitis), paratonsillar abscess. A rare, but dangerous complication of purulent tonsillitis can be severe swelling of the tonsils, up to the development of suffocation (including in a dream).
Late complications develop 3-4 weeks after the onset of the disease. These include glomerulonephritis, renal failure, myocarditis, septic arthritis, acute rheumatic fever, rheumatic joint disease, sepsis.
In the case of frequent relapses of purulent tonsillitis, the inflammation becomes chronic, chronic tonsillitis develops. The constant presence of an infectious agent in the tonsils leads to it entering the bloodstream, and with the blood stream it spreads to other organs and systems. To prevent the development of complications, as well as in the absence of a positive effect from conservative therapy, it is recommended to remove the pathologically altered glands. Surgical treatment is not indicated for patients with heart defects (2 and 3 degrees of severity), severe forms of diabetes mellitus, hemophilia.
Forecast
With timely diagnosis and adequate treatment, the prognosis is favorable. In the case of complications, as well as with frequently recurring purulent tonsillitis, the prognosis worsens.
Prevention of purulent sore throat
In order to prevent the development of purulent tonsillitis, it is recommended:
- timely diagnosis and treatment of helminthic invasions;
- regular, at least twice a year, preventive examinations at the dentist;
- strengthening general and local immunity (hardening the body, rational nutrition, avoiding hypothermia, etc.);
- rejection of bad habits;
- compliance with the rules of personal hygiene;
- avoiding contact with patients with infectious diseases of the respiratory tract.
YouTube video related to the article:

Anna Aksenova Medical journalist About the author
Education: 2004-2007 "First Kiev Medical College" specialty "Laboratory Diagnostics".
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!






