- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
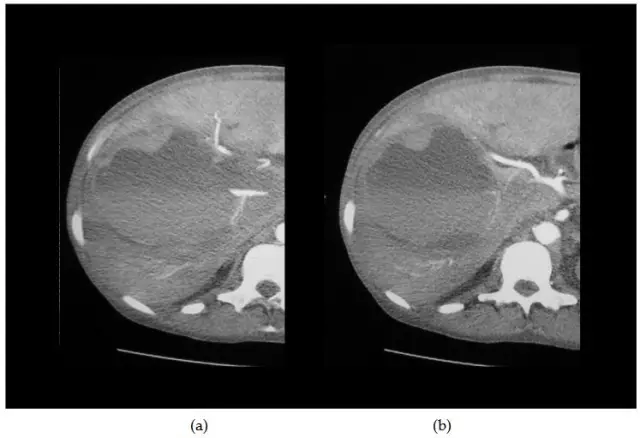
Liver biopsy

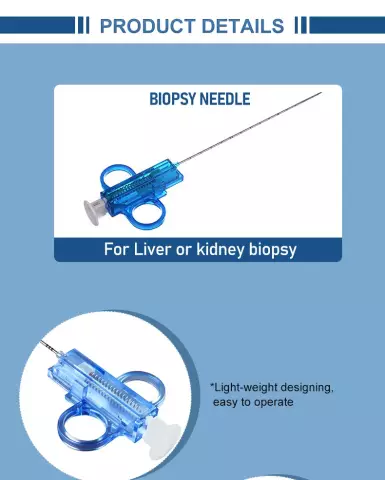
A liver biopsy is performed to determine the condition of an organ that is in the process of inflammation. The procedure consists in the fact that a puncture of the skin, subcutaneous tissues and liver is made with a special needle, material is taken for research - a small piece of an organ (biopsy) about 2 cm long and 1 mm in diameter. The obtained fragment of the liver is transferred to glass and examined under a microscope. Sometimes a larger biopsy is required to make a diagnosis, for which a wedge-shaped biopsy is performed - the wedge-shaped portion of the liver is excised.
Puncture liver biopsy is painful and can cause complications, so it is often not recommended to perform it. For this reason, there is a selective approach to the diagnostic procedure. In some medical institutions, a biopsy is performed for all patients infected with hepatitis C without exception, and in some only for those who have a genotype 1 virus: these patients are only successfully cured with interferons in only 50% of cases (unlike those infected with genotypes 2 and 3), therefore, it is necessary to keep the state of the liver under control and timely adjust the therapeutic regimen.
It is not considered appropriate to prescribe a puncture liver biopsy to those patients who are diagnosed with an advanced form of the disease, because the procedure is traumatic and can worsen the patient's condition. Diagnosis and treatment in this case is carried out according to the results of biochemical, general blood analysis, analysis of the leukocyte formula.
There is also no need for a liver biopsy after hepatitis C is cured.
How is a puncture liver biopsy performed?
Before starting the procedure, the doctor is obliged to inform the patient in detail about how the liver biopsy will take place and what complications may arise. To accurately designate the site for puncture, in some cases, a preliminary ultrasound examination is prescribed.
Take a liver biopsy as follows:
- the patient lies on his back, puts his right hand behind his head. During the biopsy sampling, he needs to remain motionless.
- A mild sedative may be given to provide psychological comfort.
- Before the procedure, the puncture site is disinfected, anesthetized, after which a small incision is made and a biopsy needle is inserted through it, and a small fragment of liver tissue is taken.
After the liver biopsy, the patient should be monitored for another four hours. he may be in discomfort and pain and may need pain relievers. For as long as eight hours after the procedure, the patient is not recommended to get behind the wheel, return to activities related to the control of complex mechanisms. The patient should not play sports for 24 hours after the biopsy. For a week after a liver biopsy, you should not take aspirin and drugs containing acetylsalicylic acid, anti-inflammation agents: Motrin, Advil, Ibuprofen, Naprosyn, Indocin.
Complications after biopsy
Despite the fact that a liver biopsy is regarded as a minor surgical intervention, the likelihood of complications is low - only 1%: during the procedure, an accidental puncture of the gallbladder, lungs, kidney or intestines can be made, an infection can enter the abdominal cavity. There are also cases of discovery of bleeding from the liver. For treatment, an operation or blood transfusion is performed. The probability of death after liver biopsy is 0.1% (one case in a thousand).
If, three days after the procedure, there is an increased temperature, nausea, chills, weakness, breathing problems, acute pain in the chest, liver, shoulder, peritoneum, you should seek medical help.
Biopsy types
In addition to a puncture biopsy of the liver, laparoscopic or transvenous biopsy can be done in some cases.

In a laparoscopic biopsy, an incision is made in the abdominal cavity, a tube with a camera is inserted through it, and the doctor, looking at the image transmitted to the monitor, takes the necessary liver fragments. Laparoscopic diagnostics is used in cases when they want to study a specific fragment from a specific part of the organ.
A transvenous liver biopsy is performed when there is fluid in the abdominal cavity or the patient has poor blood clotting: a catheter with a needle is inserted into a vein in the neck, advanced through the veins to the liver, and material is taken.
Liver biopsy results
There are several ways to evaluate the results of a biopsy. The most common:
- method Metavir. Designed for the interpretation of biopsy results in patients with hepatitis C. During the analysis, the degree and stage of inflammation are established. Depending on the degree, points are indicated - 0-4: "0" - no inflammation, and points "3" and "4" - severe inflammation. The stage of inflammation makes it possible to conclude about scarring and the amount of fibrous tissue in the liver. The stages of fibrosis are also rated on a 0-4 scale: "0" - no scars; "1" - minimal scarring; "2" - there is scarring and it has gone beyond the organ; "3" - spreading bridging fibrosis (areas affected by fibrosis are interconnected); "4" - deep scarring or cirrhosis.
- Knodel method. The biopsy results are assigned four separate points, which are combined into a single index. The first component of the index indicates bridging and periportal necrosis, it is measured on a scale of 0-10. Two more components of the index, reflecting portal inflammation and necrosis of the liver lobes, vary within the range of 0-4. The combination of these indicators reflects the degree of liver inflammation: "0" - no inflammation; "1-4" - minimal inflammation; "5-8" - slight inflammation; "9-12" - moderate inflammation; "13-18" - significant inflammation. The fourth last component reflects the degree of organ scarring in the range of 0-4 ("0" no scars - "4" cirrhosis and extensive scarring).
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.