- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
First aid for bruises

A bruise is a closed injury to tissues without violating their integrity. Contusion refers to injuries of minor and moderate severity and, as a rule, in such cases, first aid is sufficient, although there may be exceptions. Thus, severe injuries to the head (brain), internal organs, eyes, spine, chest and abdomen can pose a health hazard.
There is one difficulty - immediately after a bruise, especially a severe one, it is not always possible to quickly and correctly determine the severity of the injury. What at first seemed like a bruise may be a fracture or fracture of a bone, or a rupture of internal organs, or a concussion. That is why first aid for bruises must be provided correctly, and in any doubtful cases it is necessary to seek medical help at the emergency room or trauma department of the nearest hospital.
Signs of injury
The first and main signs of a bruise are pain and swelling in the injured area. The pain is intense, but short-term, however, as the edema increases, the painful sensations resume and intensify, which is explained by the compression of the nerve endings. The pain from a bruise can be very long - we are talking about weeks, and sometimes months, depending on the anatomical location of the injured area of the body.
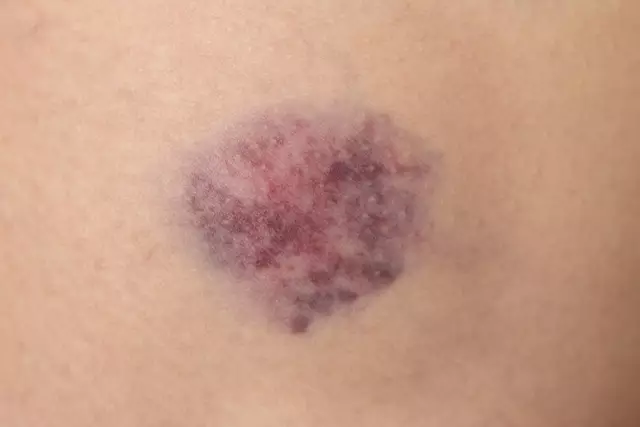
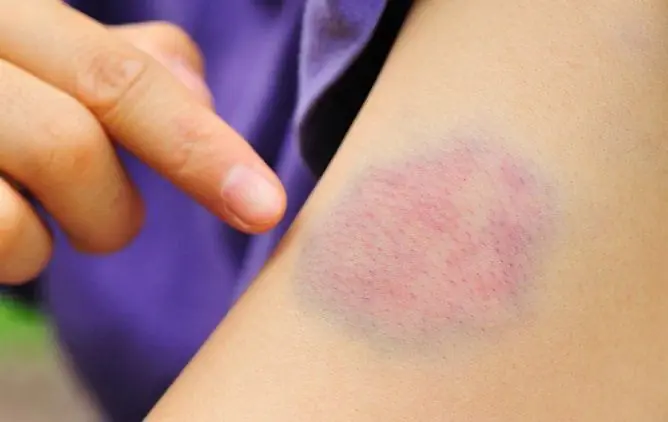
A common consequence of a bruise is the appearance of a hematoma - a subcutaneous hemorrhage resulting from a ruptured blood vessel. A hematoma should not always be regarded as a harmless bruise - hematomas of the brain and internal organs can be extremely dangerous, the situation is aggravated by the fact that their quick diagnosis is not always possible.
Late signs of bruising include restriction or dysfunction of the affected area of the body. So, with a severe injury of the joint, movement in it is often limited or becomes completely impossible, with a bruise of the eyes, the victims often note a decrease in vision, etc.
First aid for bruises

First aid for injury is not difficult - you need to apply cold to the affected area and immobilize it for a while. Cold will help reduce swelling, and therefore pain, it should be applied as soon as possible. The classic first aid tool in this case is an ice pack (ice packs are sold in pharmacies). If this is not at hand, it can be successfully replaced with any other cold object, for example, a bottle of water from the refrigerator, a bag of frozen vegetables, a towel dipped in cold water, etc.
It would be useful to apply a pressure bandage. Its purpose is also to prevent edema and reduce possible hematoma.
In the case of intense pain, it is permissible to take an anesthetic, but this can be done only when there is absolute confidence that the injury that occurred is a bruise and nothing else. In all other cases, you should refrain from taking analgesics until a medical examination, otherwise the symptoms can be distorted - the injury will seem easier than it really is.
If there is no certainty that it was a bruise that has occurred, it is necessary to seek medical help from an emergency room or hospital, since it is highly likely that an X-ray will be required.
Features of first aid for bruises of various localization
Depending on where the injured site is located, first aid may vary somewhat.
In case of a bruised eyeball, before applying cold, it is necessary to apply a sterile (or at least simply clean) bandage to the eye and immediately transport the victim to the hospital. The bruised eye quickly swells and closes, and only a specialist can diagnose it, having accurately determined the nature and severity of the injury. If the injury is severe, the sooner specialized care is provided, the more likely it is to preserve all eye functions.
First aid for a head injury should include express diagnostics for a possible concussion.
The loss of consciousness that has occurred after a bruise, even a short-term one, is a reliable sign of a concussion, but if the loss of consciousness did not occur, this does not mean that everything worked out. The following symptoms may indicate a concussion:
- Nausea and / or vomiting soon after the injury has occurred
- Headache, dizziness, tinnitus;
- Pain with eye movement;
- Pallor of the skin, sweating, hot flushes (feeling of heat in the head, limbs);
- Disorientation in space;
- Inhibition of reactions, answers out of place, difficulty concentrating;
- Temperature rise.
There is a simple test that can quickly and effectively determine if a concussion is present: ask the victim to follow your finger as you move in front of their face. If there is no concussion, the eyes will move smoothly; if there is, there will be movement disorders (twitching, interruption, etc.).
Concussion requires medical attention. In this case, until the arrival of the doctor or the delivery of the victim to the hospital (emergency room), he should not be left alone, as the condition may worsen at any time.
In case of severe bruises of the spine, chest and abdominal cavity, it is necessary to seek medical help if any deviation in the state of health appears after the injury: impaired motor or sensory function, faintness, weakness, cold sweat, fainting, shortness of breath, shortness of breath, etc.. P.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.