- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2024-01-15 19:51.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Features of the course and methods of treatment of dry paroxysmal cough in adults and children
The content of the article:
- Features of dry paroxysmal cough in adults and children
-
Causes of dry paroxysmal cough
- Ingress of a foreign body into the respiratory tract
- Acute laryngitis
- Pharyngitis
- Whooping cough
- Pre-attack period of bronchial asthma
- Pleurisy
- The initial stage of obstructive bronchitis
- Heart failure
- Reflex cough
- Diagnostic methods
-
Treatment tactics for dry paroxysmal cough
- Inhalation
- Antitussive drugs
- Video
A dry paroxysmal cough in an adult and a child is a common reason for seeking medical attention. Such a cough is exhausting, does not bring relief, and disrupts general well-being. The causes of dry paroxysmal cough can be different - from a simple infection in the form of laryngitis, to bronchial asthma and whooping cough.

Dry cough attacks can indicate various diseases, and not only the respiratory tract
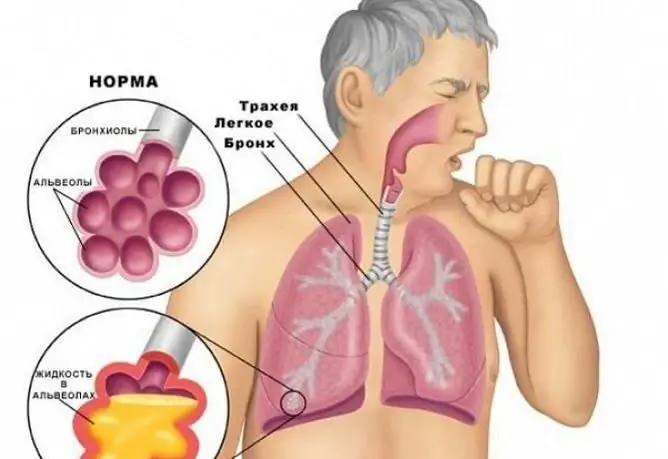
Features of dry paroxysmal cough in adults and children
Cough is a protective reflex that occurs when the cough receptors are irritated. Receptors are located in different parts of the respiratory system:
- nasal cavity;
- throat;
- trachea;
- bronchi;
- pleura.
By its nature, the cough is divided into dry (without phlegm) and wet (with production of phlegm).
According to the duration, a paroxysmal and persistent cough is distinguished. A paroxysmal cough occurs abruptly, in the form of a series of cough tremors lasting from several minutes to half an hour, and sometimes more. Coughing fits can occur at different times - at night, in the morning, during the day.
Causes of dry paroxysmal cough
Ingress of a foreign body into the respiratory tract
These can be beads, buttons, seeds, small parts. Most often (in 70% of cases), foreign bodies enter the bronchial tree. The foreign body irritates the cough receptors in the bronchi, which leads to a paroxysmal cough. Immediately after aspiration, the cough is severe, often accompanied by vomiting at the end of the attack. The cough is aimed at removing a foreign body from the human body, it cannot be suppressed.
Acute laryngitis
Inflammation of the larynx is accompanied by pain, paroxysmal coughing, hoarseness or lack of voice. Often, acute laryngitis is of an infectious nature, the development of the disease is caused by the ingress of viruses or bacteria on the mucous membrane of the larynx. With the infectious nature of laryngitis, an increase in body temperature is observed, a deterioration in general condition - lethargy, weakness.
Pharyngitis
Cough is often a symptom of chronic pharyngitis. The patient is worried about tickling and sore throat, soreness when swallowing, paroxysmal cough. Symptoms arise from damage to the mucous membrane of the posterior pharyngeal wall. Cough with pharyngitis is unproductive and does not perform a protective function.
Whooping cough
Pertussis is an infectious disease caused by the bacteria Bordetella pertussis. Pertussis is more common in children, but unvaccinated adults can also get infected. The disease manifests itself in the form of attacks of spasmodic cough. Frequent attacks (from 10 to 40 per day), may be accompanied by vomiting, hemorrhages.
Pre-attack period of bronchial asthma
Bronchial asthma is characterized by bronchial hyperreactivity, so the slightest irritant can lead to a paroxysmal cough. In addition to coughing, bronchial asthma is characterized by expiratory dyspnea (difficulty breathing during exhalation). For bronchial asthma, the night time of the onset of attacks is characteristic, which is associated with increased activity of the parasympathetic nervous system.
Pleurisy
Pleurisy is a disease characterized by inflammation of the pleura. With pleurisy, irritation of the cough receptors located in the leaves of the pleura occurs, so a dry paroxysmal cough is one of the most common symptoms of the disease. The disease is also characterized by other symptoms: respiratory failure, chest pain, fever.
The initial stage of obstructive bronchitis
In case of obstruction disease, bronchial edema and impaired mucociliary clearance (evacuation of mucus) contribute. At the initial stage, there is no mucus hypersecretion, so the cough is dry. The main symptom of the disease is expiratory dyspnea.
Heart failure
It occurs due to an increase in pressure in the pulmonary circulation. Heart failure is characterized by a dry cough that occurs mainly at night. The symptoms of heart failure come to the fore - shortness of breath, edema, pain in the heart.
Reflex cough
A paroxysmal cough can develop reflexively, without pathology of the bronchopulmonary system. In this case, they talk about the presence of a reflex cough. Reflex cough is a neurotic condition. It is characterized by a paroxysmal, unproductive cough, the onset of which is often associated with stress or a traumatic situation.

A dry cough attack can be caused by psycho-emotional reasons
Diagnostic methods
Clinical signs are not always enough to determine the cause of dry paroxysmal cough. The doctor may order an additional examination. General clinical methods that are used for dry cough:
- general blood test - allows you to identify signs of inflammation. An increase in the level of lymphocytes in the blood indicates the presence of a viral infection. This is possible with acute laryngitis. With whooping cough in the blood test, an increase in leukocytes is observed due to the lymphocytic fraction;
- chest x-ray - is performed to assess the condition of the bronchial tree, lungs and pleura. If there is bronchial obstruction, the x-ray will show signs of increased airiness. This is typical for obstructive bronchitis, bronchial asthma during an attack. With pleurisy, there is a smoothing of the diaphragmatic angle, darkening with an oblique border.
- electrocardiography (ECG) - used to assess heart function. For example, if a cough is suspected due to heart failure.
If necessary, additional research is carried out:
- laryngoscopy is an instrumental method that allows you to examine the larynx. With the help of laryngoscopy, you can assess the condition of the laryngeal mucosa. With laryngitis, there are signs of inflammation - redness and swelling of the mucous membrane. With a reflex cough, an increased pharyngeal reflex is determined, spasm of the vocal folds on inspiration;
- allergy tests - if you suspect bronchial asthma, allergic skin tests are performed. With the help of research, it is possible to identify an allergen - an irritant that provokes an exacerbation of the disease. Allergy tests need to be carried out during remission, when the symptoms are mild.
- bacteriological examination - a smear is done if whooping cough is suspected. The material for research is mucus from the back of the pharynx.
- fibrobronchoscopy - allows you to assess the condition of the bronchi. With bronchoscopy, a foreign body can be visualized. Typical changes are detected with tracheobronchial dyskinesia - narrowing of the lumen of the trachea and bronchi during exhalation.
Treatment tactics for dry paroxysmal cough
Dry paroxysmal cough is a symptom, not a separate disease, so treatment should be aimed at getting rid of the primary disease.
If you get rid of the primary disease, the cough will disappear.
| Pathology | Treatment |
| The presence of a foreign body | Surgery may be required. If a foreign body is stuck in the bronchi, it can be removed during bronchoscopy. In this case, treating cough with medications is ineffective. |
| Laryngitis and pharyngitis | Treatment consists in following general recommendations: drinking regimen, humidification of the air and mucous membranes. Specific therapy is rarely prescribed, only with the bacterial nature of acute laryngitis. In this case, antibiotics are prescribed - Amoxicillin, Amoxiclav. |
| Whooping cough | Antibacterial agents are used to treat coughs. In the first days of the disease, antibiotics from the macrolide group are prescribed - Azithromycin for 5 days. |
| Bronchial asthma | The main disease is being treated. Inhaled bronchodilators and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. You also need to eliminate the action of the allergen. |
| Pleurisy | With pleurisy, coughing does not clear the airways, so it can be stopped with antitussive drugs. Treatment of pleurisy is complex: anti-inflammatory, analgesic drugs, antibiotics (with a bacterial nature). With exudative pleurisy, pleural puncture is indicated. |
| Heart failure | To get rid of a cough in heart failure, you need to reduce the pressure in the pulmonary circulation. For this purpose, vasodilating drugs (Nitroglycerin, Sodium nitroprusside), diuretics (Furosemide, Hypothiazide), beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors are used. Coughing can be a side effect of taking ACE inhibitors and should be considered when treating heart failure. |
| Reflex cough | We recommend breathing exercises, reflexology, work with a psychotherapist. Less commonly, sedatives are prescribed. |
Treatment of dry paroxysmal cough in adults and children can be symptomatic. Symptomatic treatment is to moisturize the mucous membranes and suppress the cough reflex.
Moisturizing the mucous membranes reduces the reflex stimulation of the cough reflex. To do this, you can humidify the air and carry out inhalation. Special humidifiers are used to humidify the air; in their absence, containers with water can be placed in the room.
Inhalation
For the treatment of infectious and inflammatory diseases, inhalation is effective. At home, you can use steam inhalation with an alkaline solution (water with soda), decoctions of medicinal herbs. You can inhale saline, plant extracts, medications. For children, inhalation is carried out using a nebulizer; steam inhalation is contraindicated for them.

For inhalation in children, use a nebulizer
Antitussive drugs
With a dry paroxysmal cough, the use of antitussive drugs of central or peripheral action is indicated.
- Centrally acting antitussives inhibit the cough center, which is located in the medulla oblongata. Such drugs are contraindicated for a child, since their use can lead to depression of the respiratory center, which is also located in the medulla oblongata, which is dangerous by stopping breathing. Antitussives of central action are narcotic and non-narcotic. In therapeutic practice, non-narcotic drugs are often used, since they are not addictive. Sinekod, Intussin, Tusuprex are used.
- Antitussives of local (peripheral) action reduce the sensitivity of receptors located in the respiratory tract. A decrease in the sensitivity of receptors in the bronchi leads to inhibition of the cough reflex, a decrease in the intensity of cough. The drugs in this group include Libexin, Lidocaine.
The use of antitussive drugs will not cure the disease, but will ease its course. They are contraindicated to be used in conjunction with mucolytics (this group of drugs should not be used for dry cough).
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.