- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
How to tell a dry from a wet cough
The content of the article:
- How to tell a dry cough from a wet cough
-
Types of cough and accompanying symptoms for various diseases
- Pharyngitis
- Laryngitis and laryngotracheitis
- Tracheitis
- Bronchitis and pneumonia
- Whooping cough
- Allergy
- Bronchial asthma
- Tuberculosis and malignant tumors of the respiratory system
- Pulmonary edema
- Foreign body obstruction of the airway
- The reasons for the development of dry and wet cough
- Treatment Approach
- Traditional methods of treatment
- Video
Many patients have the question of how to distinguish a dry cough from a wet one, since the approach to their treatment is somewhat different. However, the cough therapy regimen depends not only and somewhat on its type, as on the cause, accompanying signs, existing contraindications, and the patient's age.
Cough can be either the only symptom (with tuberculosis, malignant neoplasms, bronchial asthma), and it can be accompanied by other clinical signs (with colds). In any case, a doctor should treat it, who will determine the primary pathology, since the suppression of just one symptom cannot be effective.
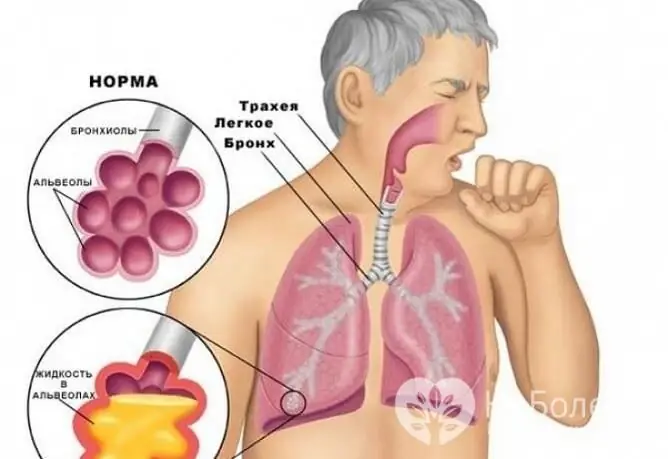
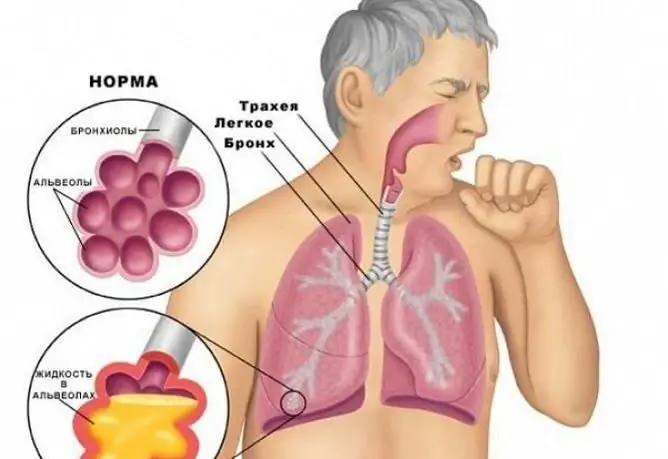
With a dry cough, the sputum is not separated, and with a wet cough, it is separated
How to tell a dry cough from a wet cough
The duration of the cough is usually classified as follows:
- acute - up to 2 weeks;
- protracted - from 2 to 4 weeks;
- subacute - from 4 to 8 weeks;
- chronic - more than 2 months).
Depending on whether the sputum is separated, the cough is divided into:
- dry (unproductive) - sputum is not separated;
- wet (productive, wet) - the sputum is separated.
The table shows a number of differences between them:
| Dry | Wet |
| A cough attack does not bring relief | Coughing Relief |
| Attacks can last for a long time, occur frequently | After coughing, the attack ends, attacks occur less often |
| During an attack, pain in the chest, pain and a burning sensation in the pharynx may occur, after numerous attacks, the patient is worried about chest pain caused by muscle strain | A cough attack can be painless or painful, after coughing up pain does not bother |
| The attack occurs suddenly, there are no harbingers | The patient feels the need to clear his throat, often deliberately causes an attack |
| Often accompanied by shortness of breath | Wheezing can be heard, in rare cases shortness of breath occurs |
Types of cough and accompanying symptoms for various diseases
Cough seizures and their nature in different diseases have their own characteristics. The nature of the secreted sputum also depends on the disease.
Pharyngitis
With pharyngitis, the patient has a sore throat and a feeling of dryness in the throat, pain when swallowing, hyperemia and swelling of the posterior pharyngeal wall, fever, weakness. Sputum in the acute form of the disease is usually not separated, a dry cough is painful. In the chronic form of the disease, symptoms are less pronounced; viscous sputum can be separated during coughing.
Laryngitis and laryngotracheitis
In the initial stages of laryngitis, the cough is dry, after a few days sputum begins to separate. Also noted:
- pain when swallowing;
- burning and dry throat;
- headache;
- temperature increase;
- lethargy and fatigue.
Tracheitis
With tracheitis in the initial stages, the patient is usually worried about a dry cough, which does not bring relief. Cough attacks can be triggered by a deep breath, screaming, laughing, inhaling cold air, smoke. There are also pain and burning sensation behind the sternum, fever. After some time, the patient begins to sputum.
Bronchitis and pneumonia
The initial stages of bronchitis are accompanied by a dry cough, which then turns into a moist one. With inflammation in the bronchi, lungs, some infections of a bacterial nature, sputum may acquire a yellowish or greenish color. With pneumonia, it is also possible to release rusty sputum due to the admixture of blood.
Whooping cough
With whooping cough, which is more common in unvaccinated children, but can also occur in adults, a cough attack without sputum separation can turn into vomiting, an increase in body temperature is also possible, rhinitis, swelling of the mucous membranes, nasal congestion, rapid heart rate, and difficulty breathing may occur.
Allergy
In case of an allergic reaction, in addition to a dry paroxysmal cough, the patient may experience:
- hives;
- sneezing;
- runny, clear nasal discharge;
- itchy nose and / or throat;
- lacrimation, redness of the eyes.
If sputum comes out, it is usually scanty and clear. The body temperature does not rise.
Bronchial asthma
Cough attacks in patients with bronchial asthma can turn into dyspnea, accompanied by episodes of shortness of breath, wheezing. The attack may be preceded by sneezing, hives, nasal discharge, usually it is provoked by some kind of respiratory irritant (strong smell of perfume, vapors of household chemicals, smoke from burning fallen leaves, etc.).
Tuberculosis and malignant tumors of the respiratory system
With tuberculosis and oncological diseases, the patient's cough becomes painful, it can be both productive and dry (depending on the stage), bothers the patient a significant part of the time during the day, he is accompanied by chest pains. The amount of sputum separated depends on the stage of the disease, it may contain blood, sometimes in significant quantities. Signs of intoxication join: weight loss in the absence of dietary changes, profuse night sweats, increased fatigue.
Pulmonary edema
It is an acute, life-threatening condition. Patients with pulmonary edema have hard breathing, wheezing, inspiratory dyspnea, pallor and cyanosis of the skin, increased sweating. The sputum is frothy, may contain blood impurities (it looks like pink foam), is separated in large quantities.
Foreign body obstruction of the airway
When a foreign body enters the respiratory tract, the patient has an intense coughing attack, while sputum is not separated. If the object enters the lower parts of the respiratory tract, voice disturbances, cyanosis of the skin, and stenotic breathing may occur.
The reasons for the development of dry and wet cough
In some diseases, both dry and wet coughs can be observed, it depends on the stage of the pathology.

The most common cause of both dry and wet coughs is respiratory infections
A dry cough occurs at the initial stages of viral infections and inflammatory diseases of the respiratory system, after a few days sputum begins to separate, and it turns into a wet one. This symptom is observed with the following pathologies:
- whooping cough;
- ingress of foreign bodies into the respiratory tract;
- allergy;
- inhalation of dry, excessively cold or hot air, chemicals, smoke;
- stressful situations.
A wet cough develops with colds, inflammatory diseases of the respiratory tract, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, pathologies of the cardiovascular system, and experienced smokers.
Treatment Approach
If cough attacks are painful, debilitating and unproductive (dry) in nature, central antitussives can be used to suppress them. These funds are used according to strict indications, only as prescribed by a doctor, and are extremely rarely prescribed to children, as they can cause respiratory arrest in them.
It is important to know that in a number of pathological conditions, when the patient does not cough up mucus, accumulations of difficult sputum may be observed in the patient's respiratory tract. It is with such pathologies that antitussive drugs are categorically contraindicated. Prescribed drugs that enhance production, thinning and excretion of sputum.
Despite the differences between dry and wet coughs, there are general rules of therapy for them:
- Proper nutrition. Foods that can irritate the mucous membranes of the throat (sharp, overly salty, spicy, cold or hot, alcohol) should be excluded from the diet.
- Regular wet cleaning in the room where the patient is located, airing and (if necessary) humidifying the air.
- Enhanced drinking regime - plentiful warm drink improves production and excretion of sputum.
- To give up smoking.
- Stay in the fresh air, daily walks (if there is no temperature).
Traditional methods of treatment
The main therapy, after consulting a doctor, can be supplemented with traditional medicine methods.
Milk-based products are popular:
- warm milk with honey (1 teaspoon of honey for 1 glass of milk);
- milk with soda (0.5 teaspoon of the substance per 1 glass of milk);
- warmed milk with alkaline mineral water, for example, Borjomi (in a 1: 1 ratio).
Popular methods of treating cough attacks include black radish juice with honey. This medicine can be prepared in several ways:
- Grate the radish, squeeze the juice and mix it with honey in a 1: 1 ratio.
- Cut a notch in the radish, fill it with honey and leave for several hours to extract juice.
Adults take a mixture of 1 tablespoon, and children take 1 teaspoon 3-4 times a day.
To improve expectoration, you can use home remedies from coltsfoot, wild rosemary, chamomile, ivy, plantain, licorice root, eucalyptus, sage, thyme. Pharmacy breast fees can also be used.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Aksenova Medical journalist About the author
Education: 2004-2007 "First Kiev Medical College" specialty "Laboratory Diagnostics".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.