- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Expectorants for wet cough in adults and children
The content of the article:
- Indications for appointment and mechanism of action of expectorant drugs
- Types of expectorants used for wet coughs
-
Expectorants for wet cough in adults and children
- ACC (acetylcysteine)
- Bromhexine
- Herbion
- Gedelix
- Ambroxol
- Fluditek
- Expectorants for pregnant women
- Folk expectorants
- What is forbidden to take with a wet cough
- Video
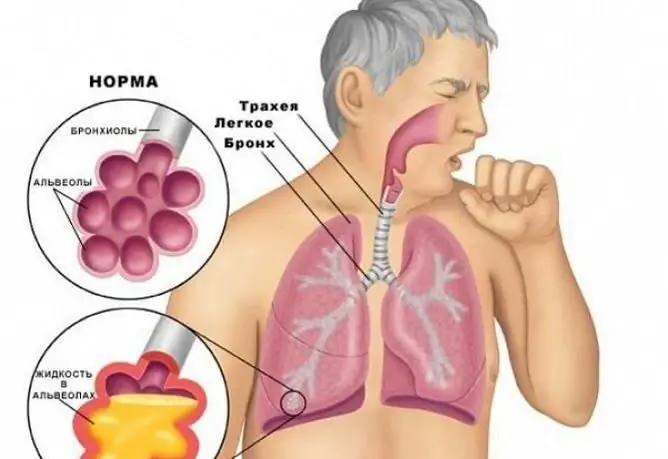
Expectorants for wet coughs are often used in both children and adults. Indications for their appointment are acute and chronic respiratory diseases, in which mucus accumulates in the bronchi. A wide range of these drugs is presented on the pharmacological market, each of which has its own contraindications, dosage regimen. Consider the features of the pharmacological action of the most effective and inexpensive expectorants for a wet cough.
Ambroxol is a mucolytic drug used for wet cough
Indications for appointment and mechanism of action of expectorant drugs
Expectorant medicines are divided into two large groups:
- Mucolytics - improve the work of mucociliary clearance by restoring the structure of the ciliated epithelium and activating the functions of the bronchial glands. In addition, drugs in this group have the ability to destroy disulfide bridges that connect individual molecules of bronchial mucus. As a result, the structure of the secretion becomes more fluid and during coughing it is much easier to remove from the bronchi.
- Mucokinetics - increase the contractility of smooth muscles that form the walls of the bronchi. This creates the physical prerequisites for better excretion of sputum outside.
That is, mucolytics thin mucus, and mucokinetics increase its expectoration. All this contributes to the elimination of accumulated sputum from the bronchial tree, which improves the ventilation function of the lungs and reduces the risk of developing a secondary bacterial infection. The main indications for the appointment of expectorants are:
- inflammatory processes of the lower respiratory system (bronchitis, bronchiolitis, pneumonia);
- chronic lung diseases, accompanied by the formation of difficult to separate sputum (bronchial asthma, chronic obstructive bronchitis, cystic fibrosis);
- congenital anomalies in the structure of the airways (Kartagener's syndrome, lobar emphysema, bronchiectasis);
- preparation for bronchoscopy or bronchography.
Types of expectorants used for wet coughs
Depending on the characteristics of the pharmacological mechanism of action, all drugs with an expectorant effect are divided into several groups:
- Pure mucolytics. The main mechanism of action is to thin the phlegm. However, some drugs of this group are also able to additionally increase the synthesis of surfactant - a special substance that covers the inside of the surface of the alveoli and prevents them from falling. Pure mucolytics include ambroxol hydrochloride, trypsin, ribonuclease, acetylcysteine, exosurf.
- Reflex action preparations (licorice syrup, marshmallow mixture, thyme and plantain extracts, ivy essential oil). The biologically active substances that make up these medicinal plants affect certain receptors located on the gastric mucosa. From here, this minor irritation is transmitted to the vomiting center of the brain, and from it to the nearby branches of the vagus nerve. This leads to an improvement in the motor activity of the cilia of the epithelium and the discharge of sputum.
- Resorptive drugs (sodium iodide, sodium bicarbonate, terpinhydrate). These drugs are excreted from the body through the bronchopulmonary system, while causing irritation, forming the walls of the bronchi of smooth muscles and increased secretion of sputum.
- Combined funds (Ascoril, Bronholitin). In addition to expectorants, they also contain other components (antihistamines, bronchodilators, anti-inflammatory).
It is impossible to say unequivocally which expectorant is the best for a wet cough, since each of them has its own mechanism of action, contraindications, side effects.
Expectorants for wet cough in adults and children
The choice of an expectorant should be carried out by a doctor, taking into account the characteristics of the course of the disease, the data of the physical examination, the patient's complaints, his general state of health and the expected effect of the therapy.
ACC - a drug for wet cough with expectorant action
The most commonly prescribed drugs are:
- ACC;
- Gedelix;
- Herbion;
- Bromhexine;
- Ambroxol;
- Prospan;
- Fluditek.
Let's consider these drugs in more detail.
ACC (acetylcysteine)
The basis of the drug is represented by a substance in the structure of which there are sulfhydryl groups that destroy disulfide bonds in the molecules of bronchial mucus. The drug is effective even with purulent inflammation (manifested by green sputum). ACC is available in the form of a powder for the preparation of a solution for oral administration, tablets and injection forms. Contraindications to its appointment are:
- pregnancy;
- individual intolerance;
- hepatic or renal impairment;
- pulmonary bleeding;
- peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum in the acute stage.
Bromhexine
Bromhexine belongs to complex drugs. It has a secretory and secretolytic effect, restores and activates the functions of the ciliated epithelium, increases the volume and reduces the viscosity of sputum, thereby improving its excretion. After the cleavage of bromhexine in the liver, substances are formed that enhance the synthesis of a surfactant, which provides the alveoli with stability in the respiratory cycle. The drug should not be taken by persons with hypersensitivity to it, suffering from gastric ulcer and duodenal ulcer in the acute stage, lactose deficiency, as well as pregnant women (especially in the first three months of gestation).
Herbion
Herbal antitussive drug, which includes extracts of plantain, primrose, ginseng. Herbion has a pronounced mucolytic, anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effect. Adults are usually prescribed 3 scoops (15 ml) 3-4 times a day. For children, the dosage is prescribed by the doctor, based on the age and body weight of the child. Contraindications to the use of the drug:
- malabsorption syndrome;
- diabetes;
- severe course of bronchial asthma.
Gedelix
The main active ingredient of Gedelix is ivy extract. Available in drops and syrup. Possesses the following properties:
- changes the physical and chemical properties of bronchial mucus, making it more fluid;
- stimulates the contractile activity of the smooth muscles of the bronchi;
- reduces swelling of the bronchial mucosa.
Gedelix is a herbal preparation and does not have a toxic effect on the human body, therefore, it can be used even in pregnant women. Contraindications to it are only the presence in the patient of hereditary fructose intolerance or individual intolerance.

Gedelix is a plant-based wet cough medicine that can be used during pregnancy
Ambroxol
Ambroxol hydrochloride improves the motor activity of the cilia of the ciliated epithelium lining the bronchial walls. In addition, the drug also stimulates the secretory activity of the bronchial glands. All this contributes to the improvement of mucociliary transport. The results of clinical studies have shown that Ambroxol is also involved in the process of surfactant synthesis.
The drug is available in the form of tablets, syrup and solution for intramuscular injection. The syrup can be given to children of any age, even under 1 year old. The dosage is determined by your doctor. After 12 years, the drug can be used in tablet form.
For children 2 years and older, it is possible to carry out inhalations with Ambroxol (the syrup is diluted in a 1: 1 ratio with warm boiled water). Such inhalations can be carried out at home using a special inhaler or nebulizer.
Fluditek
The main active ingredient of this drug is carbocisteine, which activates enzymes in the goblet cells, which leads to the dilution of bronchial mucus. Contraindications to the appointment of Fluditek are:
- chronic glomerulonephritis;
- acute cystitis or exacerbation of chronic;
- peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum;
- individual intolerance.
The duration of therapy with expectorant drugs is determined by the doctor and depends on the characteristics of the disease. For example, in acute bronchitis, these drugs are prescribed for 7-10 days, and in cystic fibrosis, they should be drunk constantly throughout the patient's life.
Expectorants for pregnant women
During pregnancy, many drugs are contraindicated for women, since they can have a negative effect on the development of the fetus or increase the tone of the uterus, which can provoke a spontaneous miscarriage. You should be especially careful when choosing a remedy for a wet cough in the first trimester of gestation. During this period, preference is given to herbal preparations (Gerbion, Mukaltin) or folk recipes are used.
Starting from the second trimester of pregnancy, if there are contraindications for the treatment of wet cough, the following can be used:
- Gedelix;
- Mukaltin;
- Herbion;
- Bromhexine;
- Ambroxol.
Folk expectorants
Traditional medicine recipes in many cases have a quick effect in the complex therapy of wet cough. The most effective of these are:
- decoction of licorice roots;
- inhalation with eucalyptus oil;
- tincture of leaves of mother and stepmother;
- breast collection;
- medicine with marshmallow extract;
- broth of sage or anise.
Sometimes patients have coughing up sputum without coughing. The cause of this condition is inflammatory diseases of the ENT organs. In this case, gargling with decoctions and infusions of herbs with pronounced anti-inflammatory and antiseptic properties (pharmacy chamomile, eucalyptus leaves, sage) is shown.
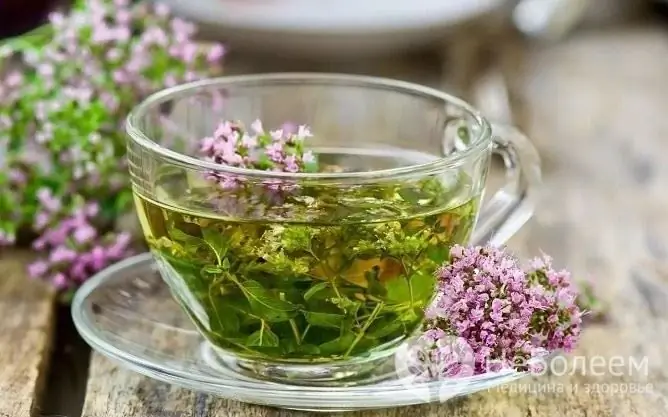

Sage is one of the medicinal plants used by folk medicine for wet coughs.
It should be remembered that herbal medicine can also be accompanied by the development of side effects and therefore should be carried out only as directed by a doctor.
What is forbidden to take with a wet cough
We examined in detail the main drugs that have an expectorant effect. In conclusion, a few words should be said about which drugs are contraindicated for productive cough, accompanied by sputum discharge.
In no case should a wet cough be suppressed, as this promotes stagnation in the bronchi of sputum, which is an excellent breeding ground for pathogenic bacteria and can cause the development of pneumonia, lung abscess. Therefore, when coughing up sputum, doctors do not prescribe drugs such as Codelac, Codterpin, Stoptussin, Omnitus, Sinekod.
Expectorants should be prescribed very carefully for wet coughs in children under 3 years of age. At this age, their cough impulse does not reach the necessary strength, and they cannot effectively cough up phlegm that collects in the bronchi. Therefore, for young children, it is more justified to prescribe not mucolytic, but mucokinetic drugs.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Elena Minkina Doctor anesthesiologist-resuscitator About the author
Education: graduated from the Tashkent State Medical Institute, specializing in general medicine in 1991. Repeatedly passed refresher courses.
Work experience: anesthesiologist-resuscitator of the city maternity complex, resuscitator of the hemodialysis department.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.