- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2024-01-15 19:51.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Median neck cyst
The content of the article:
- Causes of the median neck cyst
- The mechanism of formation of the thyroglossal cyst of the neck
- Symptoms of the thyroglossal cyst of the neck
- Diagnostics of the median cystic formations on the neck
- Differential diagnosis of a thyroid cyst
-
Treatment of thyroglossal cyst
- Operation
- Possible postoperative complications
- Video
The median cyst of the neck refers to congenital anomalies and is a pathological cavity filled with liquid or semi-liquid contents. It is located on the front of the neck, usually grows slowly and painlessly, and is more common in children and young people. It is capable of suppuration, in this case pain occurs, difficulty in swallowing appears, fistulas form. Treatment of neoplasms is only surgical.

Midline whale neck is more common in younger patients
Causes of the median neck cyst
The formation of median (thyroglossal, thyroglossal) cysts and fistulas of the neck is most directly associated with a violation of the embryonic development of the thyroid gland, hyoid bone, tongue. Pathology is congenital, many factors contribute to its occurrence during gestation, including:
- hereditary predisposition;
- stress loads;
- smoking;
- alcohol abuse;
- industrial hazards;
- taking medications with a teratogenic effect.
The implementation of the negative impact is carried out in the early stages of pregnancy.
The mechanism of formation of the thyroglossal cyst of the neck
The hollow rudiment of the thyroid gland appears in the area of the future blind hole of the tongue at the 2nd month of intrauterine development. As the tongue forms, it descends onto the neck, remaining connected to the blind lingual opening. At the same time, the hyoid bone is formed. The duct runs next to it or through it.
Normally, the thyroid duct should disappear by the time the gland reaches the cervical surface. Pathological cavity formations are formed in the event of its non-closure. This occurs when the process of lowering for some reason stops, and the duct is not obliterated at any level of migration: from the blind hole in the root of the tongue to the isthmus of the thyroid gland. As a result, a closed cavity is formed in which a secret accumulates, and when it is opened, a fistula is formed.
Congenital fistula is not an independent disease, but is always combined with a lateral or median cavity cervical formation. Distinguish between complete and incomplete types of fistulas. The first have two outlets: on the skin of the anterior surface of the neck and the oral mucosa, the second - only one. If it is located on the skin, then an incomplete fistula is called external, if in the area of the blind opening of the root of the tongue - internal.
Symptoms of the thyroglossal cyst of the neck
The thyroid cavity formations are located deep in the thickness of the soft tissues of the neck. Despite the presence of pathology in the fetus already at birth, the median cyst of the neck in a child is found, as a rule, at an older age. This is because the severity of subcutaneous fat in infants greatly complicates its visualization, and there are no clinical manifestations.
The appearance of complaints is due to the development of complications.
| Complication type | Clinical manifestations |
| Infection | An increase in cystic formation in size, redness of the skin above it, the appearance of pain, local edema, weakness, an increase in body temperature to subfebrile numbers. |
| Opening a suppurative cavity | If pus breaks out into the oral cavity, then the appearance of an unpleasant taste (sometimes iron) in the mouth, the appearance of nausea, vomiting; when purulent contents are poured out - hyperemia, crusts, irritation of the skin. |
| Formation of a sinus tract |
The location of the external opening of the fistula, punctate or wide, between the thyroid cartilage and the hyoid bone, the internal one on the front surface of the tongue, on the border between its root and body; redness, maceration, scarring of the skin; when the fistula opens, the discharge of pus, when the inflammatory process subsides, there is a scanty mucous discharge. |
| Compression of nearby organs with a significant size of education | The occurrence of neck deformity when localized in the region of the hyoid bone, when located in the region of the root of the tongue - difficulty in the swallowing process, speech impairment, in some cases even breathing. |
The median cyst of the neck in adults is also accompanied by complaints if suppuration occurs. This is facilitated by a decrease in general immunity, often provoked by:
- hypothermia;
- an infectious disease;
- trauma;
- oncological process.
Clinical manifestations are similar to those in children and adolescents.
Diagnostics of the median cystic formations on the neck
The diagnosis begins with interviewing and examining the patient. Thyroglossal cyst in most cases is a round-shaped formation with clear boundaries, having an elastic or dense-elastic consistency, located along the midline of the neck. Since its dimensions rarely exceed 2-3 cm, it does not hang down, but is determined in the thickness of the tissues. Palpation in the absence of complications is painless.
More than half of thyroglossal cysts suppurate. In this case, the characteristic clinical signs of infection come to the fore, and the specialist, when making a diagnosis, focuses on them.
The following are most often used as additional instrumental methods:
- ultrasound procedure;
- magnetic resonance imaging;
- computed tomography;
- cytological analysis of the content obtained by puncture;
- cystography (X-ray examination with the introduction of contrast into the cavity);
- probing and fistulography (radiography with contrasting fistulous tract).
With ultrasound on the monitor and photo, the thyroid cyst looks like a round, anechoic or hypoechoic avascular formation with a clear and even contour, with acoustic amplification behind. There may be hyperechoic inclusions in the cavity without an acoustic shadow.
Differential diagnosis of a thyroid cyst
When making a diagnosis, a thyroglossal cyst should be distinguished from tumors of the neck and cavities of other etiology.
| Pathological formation of the neck | Distinctive features |
| Dermoid cyst | It is located more superficially, has a denser consistency, is not associated with the hyoid bone, therefore it does not shift during swallowing movements. |
| Struma, or goiter of the tongue | An embryonic malformation, which is rare, is an accessory or abnormally located thyroid gland: a tumor-like formation on a broad basis in the region of the root of the tongue, having a mucous membrane and a dense vascular network. |
| Cystic hygroma | Benign neoplasm, the result of a violation of the processes of formation of the lymphatic system: asymmetric cystic formation with thin walls and internal partitions, not associated with the lymphatic system, often infiltrating soft tissues, subcutaneous fat, skin. |
| Adenopathy of the cervical lymph nodes | An inflamed lymph node, painful on palpation, is a formation with an uneven surface, dense or densely elastic consistency; the skin over it is stretched, often hyperemic, possibly an increase in temperature. |
Treatment of thyroglossal cyst
Therapeutic tactics when detecting a thyroid cyst involves surgical intervention, it is necessary to prevent infection, as well as eliminate a small possible risk of malignancy (about 1%).
The operation is not indicated only during the period of exacerbation of the inflammatory process, during which they carry out:
- puncturing;
- removal of mucopurulent contents;
- drainage;
- rinsing the cavity with antiseptic solutions;
- dressings.
The operation is carried out after the complete elimination of inflammatory phenomena.
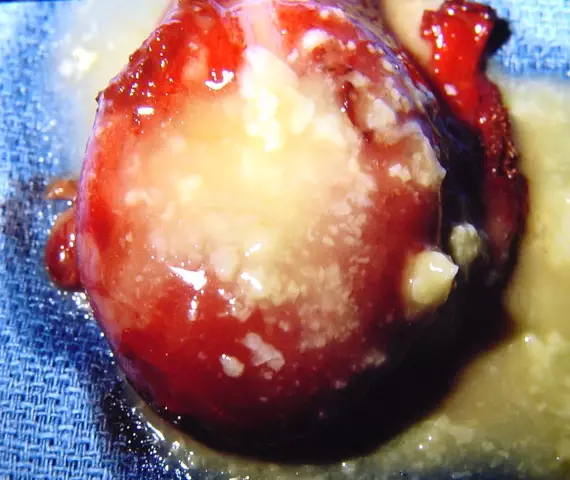
Attention! Photo of shocking content.
Click on the link to view.
Operation
The optimal period for surgical treatment of children is the age of 9-10 years. Carrying out a planned intervention at an earlier age is considered inappropriate due to the technical difficulties arising from resection of the hyoid bone, and it is the main condition for the radical nature of the surgical operation.
Removal of the cyst is performed under endotracheal anesthesia. The incision is made along the skin fold. Together with the formation, part of the hyoid bone is resected, which prevents the development of a relapse. After removing the head of the hyoid bone, the muscles are pulled together and sutured with threads that do not dissolve. Sometimes a safety drain is required.
The introduction of a 1-2% alcohol solution of brilliant green into the cavity of a cyst or fistula before surgery clearly stains the membrane of the formation and facilitates the detection of all fistulous branches.
Possible postoperative complications
Very rarely, bleeding from the wound surface is possible, leading to the formation of a hematoma. Careful hemostasis and draining for control prevents this complication. Damage to the thyroid gland, laryngeal cartilage, nerves is possible. To exclude them requires a high qualification of the surgeon and experience in such operations.
Relapses are usually caused by incomplete removal of the diseased tissue and inadequate resection of the hyoid bone.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.