- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2024-01-15 19:51.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Papillomas on the neck
The content of the article:
-
Causes of papillomas on the neck
- Information about the pathogen
- Predisposing factors
- External manifestations of the disease
-
How to get rid of papillomas on the neck
- Drug therapy
- Physical methods of destruction
- Video
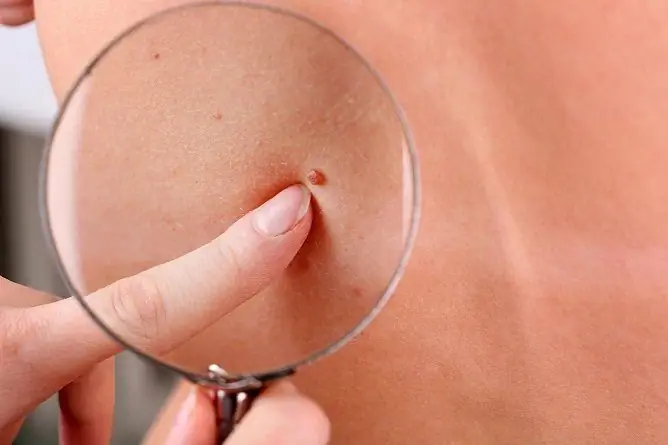
Papillomas on the neck are one of the manifestations of an infectious disease caused by the human papillomavirus. Refers to benign skin formations.

Papillomas on the neck often take on multiple patterns
Causes of papillomas on the neck
There is one etiological reason why papillomas begin to grow on the neck or in any other area of the human body - infection with the human papillomavirus (papillomavirus, HPV), which is a member of the Papovaviridae family. There are more than 100 serotypes of this pathogenic agent, each of which is responsible for the appearance of a different clinical picture of the disease (papilloma, condyloma, warts - these concepts are synonymous, different names are associated with the peculiarities of localization in a particular area).
The main routes of transmission are contact-household and sexual (condyloma of the perianal region). The virus is able to penetrate the skin only in the presence of microdamages or open wounds, in other cases it is not able to pass the protective barrier of the skin.
Information about the pathogen
- It has a high degree of spread regardless of gender (however, it manifests itself in women more often than in men), age or region (according to some sources, 2/3 of the planet is infected with this virus).
- Contains double-stranded circular twisted DNA, which is able to integrate into the human genome.
- Infection with some strains is associated with a high carcinogenic risk, especially in the case of permanent injury. Neck papillomas are caused by non-oncogenic strains of the virus.
- In the process of division, the virus goes through two main stages. At the first stage, it is in episomal (free) form, and in the same period, the main division of the viral particle occurs. This phase is reversible (after treatment, a long-term remission occurs). At the second - integrative - stage, the virus is implanted into the genome of the cell (the first step towards the degeneration of cells and the formation of a malignant neoplasm). The first stage is transient and passes relatively quickly, while the second is latent and explains the existence of carriers.
- The basal layer of the epidermis, where the virus replicates, is affected. In the remaining layers, the pathogen can persist, but not divide. Provided that the virus is in the germ layer, as it grows, the normal differentiation of cells in all layers of this area is disrupted, especially at the level of the prickly layer.
- Has a tendency to long-term asymptomatic carriage in the body (from several months to a year). It is rarely possible to identify a specific moment of infection - this is the reason why treatment begins during a period of intense clinical manifestations, and not at the first vague signs.
- To prevent infection, a bivalent and quadrivalent vaccine is used, which are especially effective against the most oncogenic strains 16 and 18.
Predisposing factors
- Failure to comply with hygiene rules. Since the virus is able to maintain vital activity in the external environment for a long time, it is necessary to carefully observe the rules of personal hygiene when visiting public places (swimming pool, bathhouse, gym).
- Traumatic damage to the skin. Micro cracks or scratches on the skin (for example, caused by rubbing the neck with the collar of a shirt) are enough for the virus to penetrate.
- Disruption of the immune system. With immunodeficiencies of any genesis, favorable conditions arise for the development of any infections. For example, frequent colds and infectious diseases lead to a weakening of the immune system and the appearance of papillomas on the skin.
- Self-infection during skin scratching.
- Systematic violation of lifestyle (stress, lack of physical activity, improper diet). These factors affect the work of all metabolic processes in the body and lead to a decrease in the barrier function of the skin.
- Environmental factors affecting the decrease in the body's defenses (hypothermia, excessive ultraviolet exposure).
External manifestations of the disease
Cervical papillomas in the photo look like this:
- The growth is most often located on a wide base and protrudes significantly above the skin surface. Less commonly, the base of the papilloma is represented by a thin leg (in this case, the formation takes a hanging position). In the second option, the risk of injury is much higher.
- The boundaries of education are even and clear.
- The color does not differ from the surrounding skin. In rare cases, it may be somewhat paler or darker than the adjacent tissues.
- The surface is often even, smooth. Sometimes growths are possible at the top of the papilloma, which makes its surface ribbed.
- The diameter varies widely - from 1-3 mm to several centimeters (papillomas of small diameter are more common).
- Location on any area of the neck (back, side front). Sometimes the face is involved.
As a rule, there are many lesions located along the skin folds.
Signs that may indicate a malignant transformation are as follows:
- color change and heterogeneity (polymorphism);
- border change (blurring, loss of clarity);
- the appearance of asymmetry (when drawing a line through the conditional middle of the formation, two equal halves cannot be obtained);
- intensive growth;
- bleeding or ulceration (a nonspecific symptom, since it is also characteristic of simple trauma to the neoplasm);
- itching, burning, peeling;
- dropouts are formed (small daughter formations around the central one).
The appearance of such signs does not necessarily mean the degeneration of the papilloma, but it means that it is necessary to consult a doctor and undergo differential diagnostics, having found out whether we are talking about an ordinary inflamed mole or skin cancer.
How to get rid of papillomas on the neck
Treatment of papillomas on the neck is carried out only in a complex manner with a simultaneous effect on the pathological focus on the skin and on the pathogen itself in the blood.
There are several ways to fight:
| Way | Description |
| Medication methods | The use of cytostatics, immunomodulators is designed to suppress the replication of the viral agent in the affected area and reduce its concentration in the blood. Some drugs (keratolytics) are applied topically directly to destroy the skin growth (cauterize and cause tissue necrosis). |
| Physical methods |
Cryodestruction, laser therapy, electrocoagulation. They aim to get rid of papillomas on both the neck and other parts of the body. These methods allow you to restore the aesthetic appearance of open areas and remove the viral reservoir - the skin neoplasms itself, but they do not completely remove the virus from the body. |
| Combination therapy | It combines the two previous options and is therefore the most effective. |
To treat papillomas with folk home remedies (celandine juice, for example) is ineffective and often dangerous, in any case, a prerequisite is consultation with a doctor.
Drug therapy
Local remedies:
- Super cleaners. Contains potassium and sodium hydroxide. Has a local cauterizing effect on the pathological focus. On the papilloma on the neck, it is enough to apply it once a day for 3 days. Since this is a traumatic drug, it is necessary to treat the skin around the papilloma with a protective cream before applying it.
- Ointment Viferon. It has a partly anti-inflammatory, partly immunostimulating effect. The drug stimulates local immune responses and leads to inhibition of the multiplication of the virus in the focus. On average, you need to smear 2 times a day for 14 days.
- Solkoderm. A liquid consisting of a combination of acetic, oxalic and lactic acids (you must strictly follow the instructions). Has a pronounced destructive effect. After the papilloma itself has disappeared, an ulcerative defect is formed, which heals by primary intention within 7-10 days. Treat the skin on the neck once, and evaluate the result after 3-5 days.
- Cryopharma. The drug has an effect due to propane and dimethyl ether in its composition. Acts like cryotherapy. It removes papillomas after the first application (the result is assessed after 5-10 days).
Systemic drugs have a general effect on the immune system:
- Interferon. Presented by specific proteins from healthy donors. The average dose is 1.5 to 3 million IU intramuscularly or subcutaneously for 4 weeks. Has a pronounced effect on the work of cellular and humoral immunity.
- Immunomax. It is produced in the form of a powder of 200 units in injection vials. It is prescribed 1 bottle (200 U) 1 time per day for 1,2,3,8,9,10 days. Stimulates antiviral immunity.

Solcoderm is one of the topical preparations that is used to remove papillomas on the neck
Physical methods of destruction
It is possible to effectively reduce formations using the following physical methods:
| Method | Description |
| Local action with solutions of concentrated acids | A 1.5% solution of zinc chloropropionate in 50% 2-chloropropionic acid, a combination of nitric, acetic, oxalic, lactic acids and copper nitrate trihydrate, etc. are used. The procedure is performed on an outpatient basis by a specialist (dermatovenerologist, cosmetologist) in compliance with surgical rules. The agent is applied pointwise with a spatula until the color of the formation changes to a lighter color (as soon as this has happened, further application should be stopped immediately). For a complete cure of papilloma, on average, you need to do 1-2 treatments. |
| Electrocoagulation | With the help of a special electro-knife, a point excision of the formations is performed without affecting the underlying tissues (there is a minimal effect on healthy skin cells). The method is most convenient when the formation has a long stem and small size. |
| Cryodestruction | There is an effect on the focus of liquid nitrogen, ultra-low temperature leads to tissue necrosis. It is good to clean this way of education with a wide base. The time of nitrogen action is selected by a specialist (1-5 minutes). After moxibustion, a burn forms, which heals over an average of 10 days. |
| Laser removal | The most modern and most delicate approach to remove formations in prominent places such as the neck. Has the most positive reviews. With the help of a light guide from 5 sec to 3 min in a continuous mode, they act on the focus. The healing period is much shorter than with other methods (5-7 days). The technique is associated with minimal trauma to the surrounding tissues due to the high precision of the action. |
| Classic surgical removal (excision with a scalpel) | They are used extremely rarely, only if the focus is large or if malignancy is suspected. The reason is that the lesions are often multiple, scattered around the neck, and too small for excision, in addition, after surgical excision, scars may remain, which in themselves create a cosmetic defect. |
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.