- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Grade 3 adenoids in children
The content of the article:
- Causes of hypertrophy of the nasopharyngeal tonsil
- Grade of adenoid growths: grade 3
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment without surgery or surgery?
- Conservative treatment of grade 3 adenoids
- Surgical removal of adenoids
- Postoperative period and rehabilitation
- Video
Grade 3 adenoids - pathological proliferation (hypertrophy) of the nasopharyngeal tonsil - the last stage of the disease, which is associated with impaired nasal breathing and is fraught with many dangerous complications, including irreversible ones.
Most often, adenoids develop in children (from 2-3 years to 6-8). With age, the disease is less common, since the adenoid tissue ceases to be prone to hypertrophy, as in childhood. Adenoids are also found in adults, but they are usually acquired in childhood.

Late adenoids obstruct the nasal passages, interfering with nasal breathing
According to statistics, in 10-12% of children, pathological growth of adenoid tissue of varying severity is recorded. Often, the disease is first detected at a late stage of the process, since at the initial stages they have a low-symptom course and do not attract the attention of either the child or his parents. To help detect adenoids at an early stage, in the absence of symptoms, only a preventive examination by a doctor can.
Causes of hypertrophy of the nasopharyngeal tonsil
Among the causes of hypertrophy of the nasopharyngeal tonsil are frequent colds, childhood infections, allergies, as well as hereditary predisposition. So, if one or both parents had adenoids in childhood, the probability of their appearance in the child is 70%.
The reason is also the childhood itself - children, due to the underdevelopment of the immune system, are prone to colds, and the tissues of their body during inflammation, especially prolonged ones, easily hypertrophy. Adenoid growths create even more prerequisites for the penetration of infection into the respiratory tract, and infectious inflammation contributes to the further growth of adenoid vegetations - a vicious circle is formed.
Risk factors are living in ecologically unfavorable areas, prolonged stay in poorly ventilated and dusty (as well as excessively clean, washed out with a large amount of household chemicals) premises, and poor nutrition.
Grade of adenoid growths: grade 3
In the clinical picture of the disease, 3 stages are distinguished, depending on the degree of hypertrophy of the nasopharyngeal tonsil. The degree is determined by the height by which the adenoids overlap the vomer or the lumen of the nasal passages:
- The adenoids overlap the nasal passages by about a third.
- The nasal passages are blocked by more than 50% (2/3).
- The nasal passages are blocked by more than 2/3.
Having examined how the adenoids of grade 3 look in the photo, you can see that the overgrown nasopharyngeal tonsil overlaps the lumen of the nasal passages almost completely.
Symptoms
Adenoids at a late stage of their development are manifested by the absence of nasal breathing, and since the nose does not breathe, the child is forced to breathe through the mouth most of the time. Because of this, the body does not receive 18-20% of oxygen, which in childhood can have extremely unfavorable consequences.
Chronic oxygen starvation leads to sleep disturbance (restless sleep), headaches, rapid fatigue, which, in turn, causes impaired cognitive functions (intelligence, memory, concentration), mental and physical development lag.
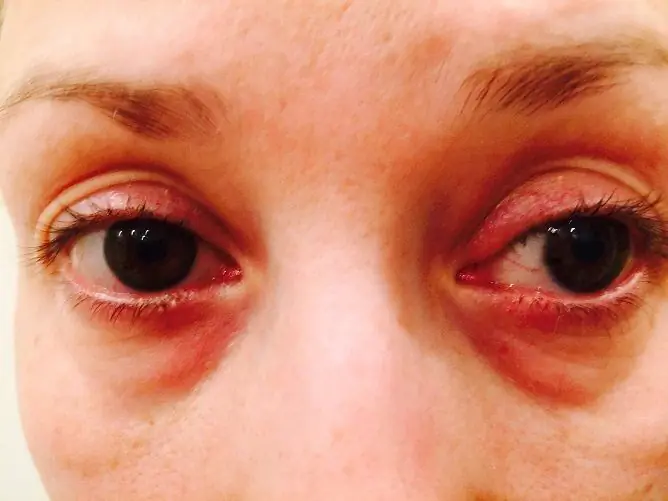
The appearance of the child also changes. The constantly open mouth causes the formation of an "adenoid" face - with an elongated lower jaw and an irregular bite. The patient's skin is pale, and there are often dark circles under the eyes.
Often third-degree adenoids are accompanied by nasal discharge, mucous or mucopurulent. This discharge in young children, flowing down the back of the nasopharynx, causes an unproductive cough.
Since the inhaled air is not cleaned and warmed in the nose, these children are susceptible to respiratory infections. The adenoids themselves also become inflamed, adenoiditis develops. The tonsils (tonsillitis), the auditory tube (eustachitis), and the middle ear (otitis media) are often involved in inflammation. Hearing impairment often develops.
In the case of the development of inflammation, the patient's body temperature rises and the general condition worsens - this differs adenoiditis from adenoids.
In the absence of timely and adequate treatment, adenoids are a constant source of infection in the body, the upper and lower respiratory tract (rhinitis, sinusitis, bronchitis, pneumonia), the cardiovascular, urinary system, and the gastrointestinal tract can be involved in the pathological process.
Diagnostics
Anamnesis and rhinoscopy data are used to make a diagnosis. For the purpose of differential diagnosis, radiography, computed tomography, endoscopic rhinoscopy can be used.
In most cases, a conventional rhinoscopy and external examination are sufficient.
Treatment without surgery or surgery?
The well-known pediatrician Komarovsky notes that the indications for surgical removal of adenoids are not the stage of the disease and the size of the hypertrophied nasopharyngeal gland, but the existing clinical signs. So, in some cases, with grade 3 adenoids, treatment without surgery is possible, and in some patients, even at the initial stage of the disease, with persistent hearing loss, surgical intervention may be required.
The decision on whether or not to remove the adenoids is made by the attending physician together with the child's parents. The physician must detail the pros and cons to the parents so that they can make an informed decision.
The operation is necessary when there is a deformation of the facial skeleton, prolonged hypoxia, hearing impairment, recurrent otitis media, frequent infectious diseases in the absence of nasal breathing. In the presence of absolute indications, the operation to remove adenoids can be performed at any age.
Conservative treatment of grade 3 adenoids
Conservative therapy is most effective in the early stages of adenoids, however, in some cases, its active implementation may be effective in third-degree adenoid vegetations. Treatment is mainly local, it includes rinsing the nasopharynx with saline solutions and antiseptic solutions, the use of antihistamines, anti-inflammatory drugs in the form of drops or inhalation with a nebulizer. With adenoiditis, antibiotic therapy, taking antipyretic drugs may be required.

Seawater sprays can be used to rinse the nose
In the absence of acute inflammation, physical therapy is also resorted to. Electrophoresis of drugs, UHF therapy, ultraviolet radiation, inhalation, laser therapy are effective.
Folk remedies at this stage of the disease play only an auxiliary role. From folk remedies for adenoids, drops based on thuja oil are actively used, reviews of those who used this drug suggest its effectiveness. In addition, nasal drops are made from anise oil, St. John's wort tincture, beet juice, propolis. All such procedures must be approved by the attending physician.
Surgical removal of adenoids
Before removing the adenoids, preparation is necessary, which primarily consists in a medical examination. Laboratory tests are prescribed: general blood and urine analysis, biochemical blood test, tests for HIV, hepatitis, syphilis, determination of blood group and Rh factor, coagulogram. The oral cavity is sanitized, if there are other foci of infection, they are first cured and only then the operation is performed.
Surgical excision of adenoid vegetations is performed, as a rule, under local anesthesia, which is accompanied by sedation (sedation). General anesthesia is used on rare occasions when local anesthesia is undesirable.
Removal of the adenoids takes 10 to 15 minutes. A modern modification of the operation - endoscopic adenotomy, which differs from the classical one in fewer complications, and therefore is preferable, especially for children.
In addition, adenoids can be removed using a laser, radio waves, coblation methods, electrocoagulation. The most popular is laser removal of adenoids, which can be one-time or gradual. In both cases, a lasting result and a practical absence of side effects are provided.
Postoperative period and rehabilitation
After the surgery, the patient goes home the same day or every other day. On the first day or two after surgery, vomiting of blood clots may occur, after surgery or the next day, the patient's body temperature may rise. In case of vomiting, no treatment is required. When the temperature rises, the child can be given an antipyretic, but drugs that contain acetylsalicylic acid cannot be taken, as this can provoke bleeding.

Modern methods of removing adenoids are associated with minimal risks
What to do in the recovery period? During the week, the child should avoid crowded places, since the body is weakened during this period, and there is a high risk of infection. For two to three weeks, patients are not recommended to visit baths, saunas, stay in the heat for a long time, in direct sunlight. Stress should be avoided for a month after surgery.
A sparing diet is prescribed for the period of healing of the surgical wound. In the first few days, it is recommended to eat liquid and semi-liquid food, which should be at a comfortable temperature and not contain products that irritate the mucous membrane. Salting, pickles, spicy, spicy foods, sour foods, carbonated drinks, concentrated juices and compotes should be excluded from the diet. As the tissues heal, the diet is expanded, while still making sure that the food is not solid, too cold, hot or irritating.
In the postoperative period, regular breathing exercises are recommended, which will help to quickly relieve swelling, restore tissues, and also get rid of the habit of breathing through the mouth.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Aksenova Medical journalist About the author
Education: 2004-2007 "First Kiev Medical College" specialty "Laboratory Diagnostics".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.