- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Removal of hemorrhoids: invasive and minimally invasive methods
The content of the article:
-
Invasive Hemorrhoid Removal Methods
- Milligan-Morgan hemorrhoidectomy
- Hemorrhoidopexy, or Longo's operation
-
Minimally invasive methods for removing hemorrhoids
- Laser removal
- Desarterization
- Radio wave method
- Sclerotherapy
- Ligation with latex rings
- Cryodestruction
- Focal infrared coagulation
- Indications and contraindications for surgical removal of hemorrhoids
- Preparing to remove hemorrhoids
- Recovery period
- Possible complications
- Hemorrhoid treatment depending on the stage
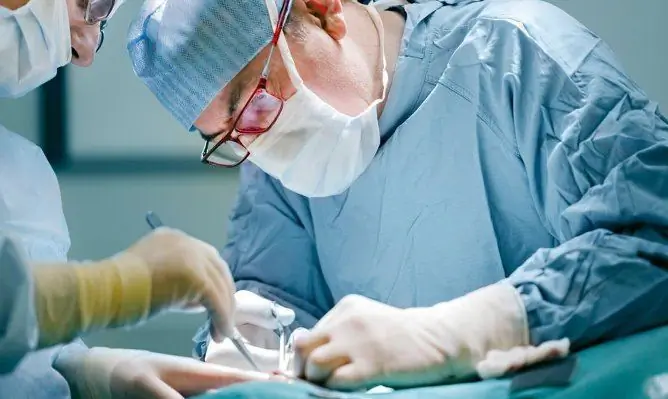
Removal of hemorrhoids is most often carried out at the fourth stage of the disease, when drug therapy and minimally invasive treatment methods are ineffective. The choice of the method of surgical intervention, as well as the assessment of the presence of contraindications, is carried out by the attending physician.
Hemorrhoids are caused by enlargement and weakening of the choroid plexus of the rectum. There is a stagnation of blood in the pelvic area, the tone of the vascular walls decreases, the thinned veins overflow with blood and stretch. Over time, hemorrhoids form, which gradually increase in volume, systematically inflame and bleed.
The characteristic symptoms of hemorrhoids are pain, burning and itching in the anus, discomfort during bowel movements, perianal edema, enlargement, inflammation and prolapse of hemorrhoids, the appearance of blood during bowel movement. With the development of thrombosis of hemorrhoidal veins, depletion and necrosis of rectal tissues may occur.
Invasive Hemorrhoid Removal Methods
There are two main types of radical surgery: hemorrhoidectomy by the Milligan-Morgan method and hemorrhoidopexy, or Longo's operation.

Radical removal of hemorrhoids is carried out at a late stage of the disease, when other methods are ineffective
Milligan-Morgan hemorrhoidectomy
The operation consists in removing the thrombosed node under local anesthesia using a scalpel, laser or electric coagulator. The method was developed in 1937, since then several options have appeared:
- open hemorrhoidectomy - consists in removing both the hemorrhoidal lump itself and the affected mucous membrane around it. The tissues heal naturally;
- closed hemorrhoidectomy, during which the edges of the wounds are sutured after the removal of growths;
- submucosal hemorrhoidectomy (Parks method), during which only the nodule itself is removed. In order not to injure the mucous membrane, the base of the growth is left intact.
The Milligan-Morgan method allows not only to remove a blood clot, but also to get rid of the cause of its appearance. Currently, it is rarely used due to the duration of the procedure, the need for general anesthesia, the risk of massive blood loss and complications, prolonged hospital stay, and a long recovery period after surgery.
Hemorrhoidopexy, or Longo's operation
The more common surgery to remove hemorrhoids is hemorrhoidopexy. The essence of the method is to dearterize hemorrhoids. A circular excision of the rectal mucous membrane above the hemorrhoidal node is performed, the blood supply to the node is cut off, the weakened suspension ligament is restored, which pulls the node up. Hemorrhoids are pulled up by excision of a portion of the mucous membrane, and not removed.
How to remove hemorrhoids according to the Longo method:
- The skin of the perianal area is stretched to the sides using special clamps.
- A dilator is inserted into the lower end of the anal canal, which is fixed with sutures.
- An operational anoscope (proctoscope) with an obturator is inserted into the expander.
- Above the level of the dentate line of the anal canal, a purse-string suture is applied.
- A circular surgical stapler is inserted into the rectum. The surgeon in a circle excises the area of the mucous membrane around the hemorrhoid.
- The affected tissues are connected using titanium staples. The threads used for the purse-string suture are tightened. The ends of the threads are tied in one knot, taken out through the side holes of the stapler and fixed.
- Take out the stapler and examine the removed piece of the mucous membrane in order to make sure that the operation is performed correctly.
- Check the line of paper clips, remove the anoscope.
- A gas outlet and a gauze turunda soaked in medicinal ointment are introduced into the anus for a day.
The procedure is performed in a hospital under general or local anesthesia. During the operation, it is possible to remove multiple internal nodules, the procedure takes no more than twenty minutes, the recovery period does not exceed five days. Within a week, the patient can start working. Does it hurt after Longo's surgery? The advantages of the operation include its painlessness and bloodlessness, the absence of an extensive postoperative wound. The disadvantage of this method is the inability to remove external hemorrhoids.
Minimally invasive methods for removing hemorrhoids
Minimally invasive methods of removing hemorrhoids are used at earlier stages of the disease, their advantage is in reducing operational risks, speed, painlessness and the absence of a long postoperative healing period.
Laser removal
Excision and coagulation of the affected tissue is carried out using a laser beam. A directed stream of light waves painlessly burns out the tissue of the internal growth, cauterizes the dilated vessel, stopping the blood flow in it. Thus, the blood supply to the dropped node stops, it remains without food, and is subsequently rejected by the body. When removing external hemorrhoids, the growths are cut off with a laser beam, then the bleeding vessels are cauterized. The disadvantages of the method include the impossibility of removing large hemorrhoids completely, which can lead to a relapse.

Laser removal of hemorrhoids has the advantage of no bleeding
Desarterization
The method of ligating the arteries in the area of hemorrhoidal cones with special threads, after which the blood supply to the node stops and it involutions. The procedure for suture ligation of hemorrhoidal arteries is performed using ultrasound.
Radio wave method
The destruction of nodes is carried out by radio waves of a certain frequency. When high-frequency waves penetrate into the tissue structure, a thermal effect is created, resistance arises, due to which the tissue is dissected. Excision of growths is carried out with a radio knife (apparatus "Surgitron").
Sclerotherapy
Sclerotherapy of internal hemorrhoids consists in the introduction of a special substance into the tissues of the hemorrhoidal growth - sclerosant. Under its action, the blood vessels are hardened, the vascular cavities are replaced by connective tissue.
Ligation with latex rings
The method consists in placing an elastic ring on the base of the hemorrhoidal lump. As a result, blood circulation in the vessel stops, the external node dies off and is rejected along with the ring during bowel movements.
Cryodestruction
The method of freezing the assembly with liquid nitrogen. The inflamed hemorrhoidal lump is exposed to ultra-low temperatures, the manipulation is carried out using a cryoprobe.
Focal infrared coagulation
During the procedure, the hemorrhoids are exposed to infrared rays. The infrared flux is converted into heat energy, under the influence of which tissues are coagulated. Subsequently, a crust forms in their place, which comes out during bowel emptying.
Indications and contraindications for surgical removal of hemorrhoids
In the later stages of the process, with a tendency to thrombosis of hemorrhoidal veins, removal of hemorrhoids is recommended. Indications for surgery:
- hemorrhoids of significant size;
- prolapse of hemorrhoidal veins, which occurs not only with every act of defecation, but also with any physical effort (for example, when coughing or sneezing);
- involvement of the surrounding fatty tissue in the inflammatory process;
- the development of anemia caused by recurrent heavy bleeding;
- pinching and ischemic nodes.
Sometimes surgical removal of fringes is required after hemorrhoids. These small folds around the anus are not considered a medical condition and are often viewed only as a cosmetic defect. If necessary, they are excised under local anesthesia.
Contraindications to the prompt removal of hemorrhoids:
- acute diseases of the large intestine, exacerbation of chronic inflammatory processes in the rectum and perineum;
- Crohn's disease;
- low blood clotting;
- diabetes;
- severe arterial hypertension;
- decompensated stage of respiratory and cardiovascular diseases;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- immunodeficiency states;
- malignant tumors of the rectal canal;
- pregnancy, breastfeeding.
Due to the use of general anesthesia during the operation and a long recovery period, elderly patients are shown mainly non-surgical methods of treatment.
Preparing to remove hemorrhoids
To choose the best way to treat hemorrhoids, remove nodes, the patient is prescribed an examination: general blood and urine tests, biochemical blood test, coagulogram, digital rectal examination, ultrasound of the abdominal cavity. Modern methods of instrumental diagnostics include sigmoidoscopy and anoscopy, with their help they determine the exact localization and size of hemorrhoids, the presence of pathologies (fistulas, polyps in the lower rectum, anal fissures).

Before removal of hemorrhoids, the patient undergoes a complete medical examination
Before surgery, the patient is cleansed of the intestines with laxatives or enemas. To normalize bowel function and eliminate stool disorders, it is recommended to follow a special diet. Do not eat or drink water before surgery.
Recovery period
The pain syndrome that occurs after hemorrhoidectomy is stopped by intramuscular administration of anesthetic drugs. Tampons and drains can be a significant concern in the first days after surgery.
To accelerate the healing process of rectal tissues, ointments and rectal suppositories with methyluracil are used. Accelerate the regeneration processes of the bath with a decoction of chamomile flowers or a solution of potassium permanganate. It is important to follow all hygiene procedures, not to skip dressings.
On the first day of the recovery period, a complete refusal of food and an abundant drinking regime are shown. Food is gradually introduced from the second day. Diet after surgery should not contribute to intestinal irritation and the formation of hard feces. It is recommended to eat cereals, light soups, vegetables and fruits, dairy products, boiled meat and fish.
When can I play sports? Doctors recommend starting physical activity with light exercises, Kegel gymnastics, and hiking. This will prevent the development of blood stasis, help the tissue healing process, eliminate possible pain in the anus, and restore the tone of the muscles of the pelvis and perineum. It is necessary to reduce the load on the veins of the pelvic floor, to avoid heavy lifting.
To exclude the formation of narrowing of the lumen of the intestine, one and three weeks after the operation, a digital examination is performed.
Possible complications
According to reviews, the removal of hemorrhoids is rarely associated with any undesirable consequences. However, as a result of improper wound closure or violations of aseptic rules after surgery, complications may arise:
- intra-abdominal bleeding. If there is blood after the operation, the rectum is examined using an anoscope to find out the cause and eliminate it;
- retention of urine;
- fecal or urinary incontinence;
- stenosis of the anal canal;
- formation of rectovaginal fistulas;
- infectious process, wound suppuration.
Hemorrhoid treatment depending on the stage
From the moment of the onset of the initial symptoms of the disease to its pronounced signs, it can take from several months to several years. The onset of the disease is usually asymptomatic. Most patients do not attach importance to the first manifestations of the disease.
Hemorrhoids of the initial stage are said to be when hemorrhoids protrude into the lumen of the rectum, without leaving the lower extremity of the anal canal.
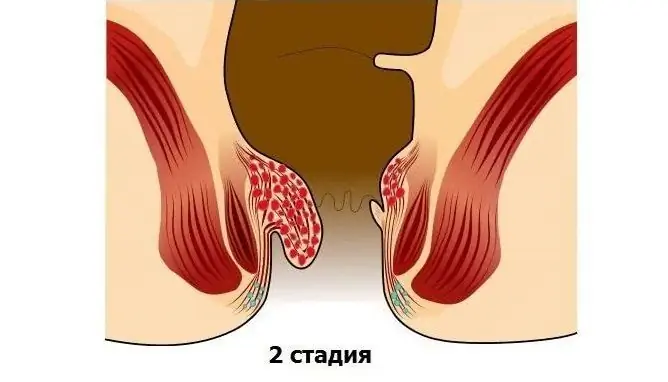
At the second stage, the hemorrhoids increase, begin to sag from the anus (fall out), but are drawn into the rectum when the body position changes.
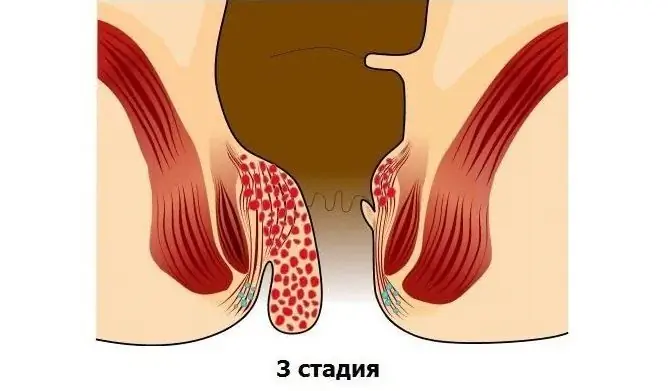
At the third stage, the hemorrhoids no longer adjust into the rectum on their own, but they can be carefully adjusted by hand.
In the first three stages, surgery is avoided; to alleviate the patient's condition, methods of conservative drug therapy are used. The therapeutic complex for hemorrhoids includes adherence to the regime and rules of a balanced diet, the implementation of special physical exercises to increase the tone of the veins and relieve congestion in the venous plexuses.
If the disease enters the fourth stage, and minimally invasive methods of treatment are recognized by the attending physician as ineffective, the only correct solution would be to remove hemorrhoids by surgery.

There are four stages in the development of hemorrhoids, the last one shows surgical treatment
The fourth stage of hemorrhoids is characterized by the following symptoms:
- constant prolapse of bleeding hemorrhoids;
- the nodes are significantly enlarged, they cannot be adjusted;
- complete loss of elasticity of the connective and muscle tissues of the rectum;
- piercing pain when emptying the intestines, excruciating itching and burning in the anal region. Acute pain makes it difficult to sit and move;
- massive bleeding during bowel movements;
- mucous and purulent discharge;
- purple nodes;
- perianal edema;
- involuntary discharge of feces and gases;
- erosion in the anorectal region;
- thrombosis of hemorrhoids, tissue necrosis.
YouTube video related to the article:

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.