- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Lymphadenitis in children
The content of the article:
- Causes of lymphadenitis in children
- Types of lymphadenitis in children
- Symptoms of lymphadenitis in children
- Diagnostics
- Treatment of lymphadenitis in children
- Potential consequences and complications
- Forecast
- Prevention
Lymphadenitis in children - inflammation of the lymph nodes.
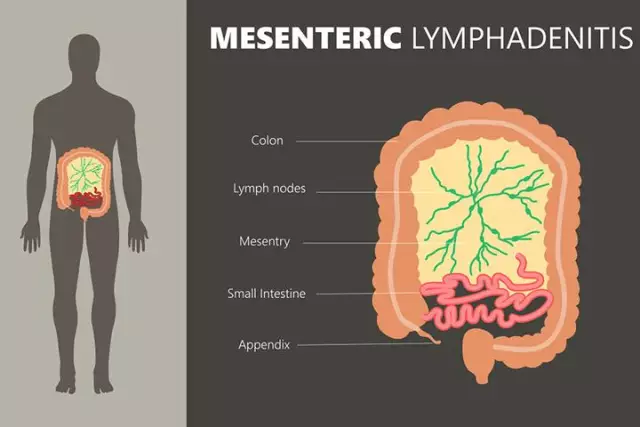
Lymph nodes - peripheral lymphoid organs, which are rounded anatomical formations of connective tissue filled with lymph. The lymph nodes are connected to the circulatory system by lymphatic vessels and postcapillary venules. Passing through the lymph nodes, the lymph is collected in the lymphatic ducts, which open into the venous circulatory system. In this case, the lymph nodes perform the function of biological and mechanical purification of the blood: they retain and accumulate antibodies that make up an important part of the immune system. At the same time, the lymph nodes act as a filter, inactivating the bacterial agents present in the lymph. When foreign particles and bacteria, passing through the lymph node, are retained in its trabeculae and septa, inflammation can develop. In the presence of a focus of inflammation, the lymph nodes become thickened and painful, increase in size, and lymphadenitis develops. Thus, lymphadenitis is not an independent disease, but a symptom of the main pathological process occurring in the body, a signal of a decrease in its protective functions.
In children, the lymph nodes have an incomplete structure, the septa and trabeculae at an early age are not fully formed, which reduces their barrier function. The maturation of the lymph nodes occurs gradually, by the age of 8-9 years the reaction of the immunological response appears, at the age of 12-14 the formation of the lymph nodes is completed.

Causes of lymphadenitis in children
The most common cause of lymphadenitis in children is an infectious inflammation caused by the following pathogens:
- staphylococcus;
- streptococcus;
- Pneumococcus;
- colibacillus;
- mycobacterium tuberculosis;
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa;
- parasitic and fungal infections;
- Epstein-Barr virus;
- AIDS virus.
Lymphadenitis in children is often associated with an inflammatory process in the oropharynx and nasopharynx with angina, flu, otitis media, adenoiditis, chronic tonsillitis. Lymph nodes increase with childhood infections - scarlet fever, rubella, mumps, diphtheria, as well as with skin diseases - pyoderma, exudative diathesis, infected eczema. The penetration of microbes into the body can occur with the flow of lymph, blood, through direct contact.
Non-infectious causes of lymphadenitis in children: lymphoma, secondary (metastatic) cancer of the lymph nodes, contact infection when the infected material comes into contact with the tissue of the lymph node.
Types of lymphadenitis in children
Lymphadenitis is classified according to several criteria.
According to the etiological factor, they are distinguished:
- specific lymphadenitis - develops under the influence of pathogens of tuberculosis, syphilis, brucellosis, toxoplasmosis, actinomycosis, tularemia;
- nonspecific lymphadenitis - caused by pyogenic microbes (staphylococci, streptococci), their toxins, opportunistic bacteria, tissue decay products from the primary foci of the purulent process, fungal microorganisms living on the surface of the skin and on mucous membranes.
By the nature and duration of the course of the infectious process, lymphadenitis is distinguished:
- acute - characterized by a short prodromal period, occurs after wound infection, surgical intervention, when virulent microbial flora enters the tissue; clinical symptoms are pronounced;
- chronic - is often the result of the effects of a weakly virulent infection with protracted sluggish inflammatory diseases, the progression of cancer, an unfavorable outcome of acute lymphadenitis. Has a wave-like course, periods of exacerbation are replaced by remission.
Acute lymphadenitis, in turn, can occur in two forms:
- serous - occurs under the influence of viruses and tumors, usually accompanied by indistinct symptoms, inflammatory phenomena do not go beyond the capsule of the lymph node;
- purulent - develops under the influence of a chronic bacterial infection, inflammation can spread to surrounding tissues, carries a threat of sepsis.
Separate options are hemorrhagic and fibrinous lymphadenitis.
The inflammatory process can affect one or more adjacent lymph nodes. According to the localization of the inflammatory process, lymphadenitis can be local, regional and generalized.
Symptoms of lymphadenitis in children
Symptoms of lymphadenitis in children:
- increased body temperature;
- leukocytosis;
- edema in the area of the affected lymph node, enlarged lymph node;
- hyperemia with a local increase in temperature (with a superficial location of the inflamed lymph node).
The severity of symptoms is determined by the nature of the underlying inflammatory process and the type of disease.
Acute lymphadenitis in children is manifested by an increase and local tenderness of the lymph nodes on palpation, fever, weakness, and headache. Lymph nodes are mobile, but their borders lose their shape and merge with the surrounding tissues. The clinical manifestations of lymphadenitis are superimposed on the manifestations of inflammation in the main focus, pain occurs in the corresponding areas (for example, the cervical lymph nodes become inflamed with angina, which is accompanied by a sore throat).
With serous lymphadenitis, the well-being of a sick child may not change. There is an increase and compaction of regional lymph nodes, moderate pain syndrome, there is no inflammation on the skin. There may be swelling of tissues adjacent to the node.
The development of purulent destruction is evidenced by sharp pain, fever, chills, weakness, loss of sleep and appetite. There is a pronounced hyperemia of the outer covers over the superficially located node. The lymph nodes become immobile, welded together and with adjacent tissues. In the absence of proper treatment, purulent inflammation spreads to the surrounding tissues, areas of softening appear, the boundaries of edema are blurred, diffuse hyperemia is determined, and an abscess of a lymph node or adenophlegmon may develop. This is accompanied by a sharp rise in temperature, the appearance of chills, tachycardia, intense headaches, severe weakness.
Chronic inflammation of the lymph nodes is characterized by the absence of pain or its mild severity. The main symptom of chronic nonspecific lymphadenitis in children is an increase in lymph nodes, while they are usually dense to the touch, not soldered to each other and delimited from the surrounding tissues.
In childhood, the period of primary tuberculosis is often combined with damage to the intrathoracic lymph nodes. Several groups can be involved in the process. A distinctive feature of tuberculous lymphadenitis is the presence of periadenitis (a conglomerate of affected lymph nodes welded together). In acute onset of tuberculous lymphadenitis, there are symptoms of tuberculous intoxication, high fever, swollen lymph nodes, sometimes with severe inflammatory-necrotic changes.
Diagnostics
At the first stage of diagnostics, a physical examination of the child is carried out, an assessment of the clinical picture, anamnesis, and palpation of the lymph nodes. On palpation, localization, size, shape, cohesion, consistency, soreness and mobility of the lymph nodes are noted. The examination of the lymph nodes is performed with two hands, in symmetrical areas, in comparison.

The survey plan includes:
- peripheral blood test - an increased level of leukocytes (characteristic of diseases of bacterial etiology), the predominance of lymphomonocytes in the blood formula (evidence in favor of herpes and other viral etiology);
- microbiological study of microflora from the oropharynx;
- complex of serological blood tests by ELISA and PCR;
- allergy tests;
- analysis for HIV infection;
- ultrasound examination of lymph nodes;
- X-ray examination;
- puncture biopsy of the lymph node.
Based on the results of the main examination, additional laboratory and instrumental studies may be prescribed in order to diagnose the primary disease.
Treatment of lymphadenitis in children
Treatment of lymphadenitis in children is aimed at eliminating the primary focus and stopping the inflammatory process in the lymph nodes. If the cause of lymphadenitis is a bacterial infection, then antibiotic therapy is prescribed using macrolides, aminopenicillins, cephalosporins, macrolides, semisynthetic penicillins. The therapy regimen depends on the type of infectious agent and the characteristics of the child (weight, age). According to the indications, desensitizing, restorative agents are prescribed, symptomatic (analgesic and anti-inflammatory) therapy is carried out.
During the recovery period after acute lymphadenitis and during the treatment of chronic lymphadenitis, physiotherapeutic procedures are used (UHF therapy, laser therapy, quartz irradiation, galvanization).
With purulent melting of the lymph node, surgical intervention is indicated, which consists in opening purulent phlegmon and abscesses, removing their contents, treating the cavity with an antiseptic and establishing wound drainage. In the postoperative period, antibiotic therapy is performed.
In case of confirmation of tuberculosis, treatment is carried out in a specialized (phthisiatric) department of the hospital.
Potential consequences and complications
Complications of lymphadenitis in children can be:
- lymph node abscess, adenophlegmon, purulent decay of lymph nodes, followed by replacement with connective tissue;
- sepsis;
- encephalitis;
- thrombophlebitis of adjacent veins;
- disorders of lymphatic circulation, lymphostasis, elephantiasis of the extremities.
Forecast
The success of the treatment of lymphadenitis in children depends on the timely detection of the disease and the adequacy of therapy. In general, the prognosis is favorable, with the exception of cases of development of malignant formations in the parenchyma of the lymph node.
Prevention
Since the development of lymphadenitis is caused by a primary disease, the main measure for preventing inflammation of the lymph nodes is the timely diagnosis and treatment of the primary pathology. Other preventive measures:
- prevention of injury, in the event of an injury - timely sanitation (skin lesions are treated with iodine, sealed with adhesive plaster or bandages are applied);
- teaching the child to observe the rules of personal hygiene;
- careful caring for young children;
- fortifying activities: proper nutrition that covers age-related needs, routine vaccinations, daily walks in the fresh air, an active lifestyle, hardening.
YouTube video related to the article:

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!