- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Hemorrhagic vasculitis
Hemorrhagic vasculitis is an aseptic inflammation of microvessels, which is accompanied by the formation of microthrombi and damage to the vessels of the skin, and sometimes internal organs.
Features of hemorrhagic vasculitis
With hemorrhagic vasculitis, skin vessels, digestive organs, kidneys and joints are affected. Often, the disease occurs against the background of vaccination or a previous respiratory tract infection.
Hemorrhagic vasculitis in children is associated with food allergies and insect bites, and in adults, inflammation is medication-related.
Often, hemorrhagic vasculitis in children occurs after hypothermia and severe viral illness. This inflammation is acute, fulminant and chronic, and the activity of the inflammatory process can be normal, moderate and high. According to the form of distribution, skin, articular, abdominal, renal and mixed inflammation are distinguished. This inflammation can lead to damage to the vessels of the gastrointestinal tract and cause internal bleeding.
Hemorrhagic vasculitis is likely between the ages of 17 and 22, but the disease peaks in patients between the ages of 10 and 16.
Causes and symptoms of hemorrhagic vasculitis
The main causes of hemorrhagic vasculitis are infectious diseases, including tonsillitis, influenza and ARVI, scarlet fever and chickenpox. In the course of the development of the disease, the walls of the capillaries are damaged, and the production of immune complexes also increases.
Trauma, hypothermia, allergies, drug intolerance and unsuccessful vaccinations are also common causes of hemorrhagic vasculitis.
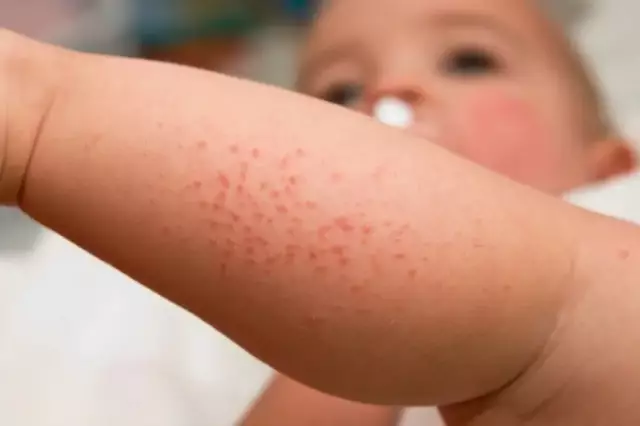
The primary symptoms of the disease are skin lesions, which are manifested by redness, rashes and darkening of the joints, legs and buttocks. Within a few days, the rash increases, and after its elimination, pigmentation and peeling remain.
A serious sign of hemorrhagic vasculitis is joint damage, accompanied by inflammation and joint pain. Basically, patients have large joints pain, periarticular edema develops, and sometimes their deformation occurs.
Hemorrhagic vasculitis can manifest as pain in the gastrointestinal tract, which is combined with indigestion, cramps, and diarrhea. Pain syndrome can be both short-term and permanent. In some cases, patients have intestinal bleeding.
This condition can affect the lungs, causing coughing and shortness of breath. From the side of the cardiovascular system, spasms, arrhythmias and tachycardia can be observed.
As a result of exposure to the brain, hemorrhagic vasculitis in children can cause inflammation of the meninges. Patients experience dizziness, headache, and loss of coordination.
The consequences of hemorrhagic vasculitis can be severe damage to internal organs, as well as thrombopenia, atherosclerosis, sexual dysfunction and impaired functioning of the brain.
Treatment of hemorrhagic vasculitis
Treatment of hemorrhagic vasculitis directly depends on the phase of the course of the disease and the clinical form of its manifestation. Patients with mild and moderate phases of the disease respond most easily to treatment, and at the severe stage of the course of this disease, elements of necrosis, angioedema, severe pain in the stomach, renal failure, bleeding and nephrotic syndrome are observed.

For all forms of the disease, antiplatelet agents are prescribed, including Trental, Curantil, Persantin, etc. At a severe stage of the course of hemorrhagic vasculitis, drugs can be combined. The duration of treatment is: with a mild degree 2-3 months, with an average - up to 6 months and with a severe one - up to 1.5 years.
Treatment of chronic hemorrhagic vasculitis is carried out with regular courses lasting 4-5 months. To eliminate skin rashes and other symptoms, anticoagulants are prescribed, which are selected individually in accordance with the physical condition and diagnostic indications of the patient. The introduction of Heparin into the fiber of the abdomen is prescribed to eliminate serious lesions of the digestive system. The course of treatment lasts 20-30 days.
In the treatment of hemorrhagic vasculitis, nicotinic acid is used as an activator of fibrinolysis, as well as Xanthinol, Theonikol and Complamin.
Transfusion therapy is performed in children in severe stages of the course of the disease. The course of treatment lasts 10-15 days. This therapy includes low molecular weight solutions, novocaine mixtures and antispasmodic drugs.
For the treatment of this allergic type of disease, antihistamines may be prescribed. The doctor prescribes a course of treatment with Tavegil, Suprastin or Fenkarol for 5-10 days.
An additional treatment for hemorrhagic vasculitis is a special diet with the use of hypoallergenic foods containing nutrients. The main diet consists of apples, dietary chicken and rabbit meat, fruit and berry compotes, green tea, oatmeal and herbs.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!