- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
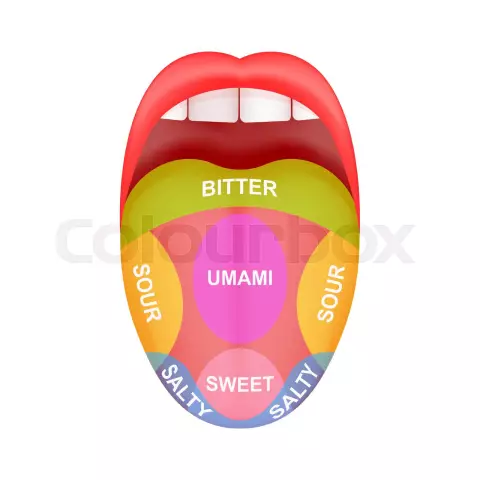
Sour, salty, bitter: what will the taste in the mouth tell about?
The taste usually occurs naturally due to lack of morning hygiene or food intake. However, in some cases, its presence turns out to be a sign of pathologies, which makes it possible to identify them at an early stage. A certain aftertaste - sour, salty, bitter, sweet, etc. - is accompanied by certain diseases. An important task when a pronounced taste in the mouth appears is to understand its nature and, if you suspect a disease, consult a doctor. Let's consider what disturbances in the body the taste may indicate.

Source: depositphotos.com
Sour taste
If the sour aftertaste is not caused by acidic foods, it is very likely that gastrointestinal diseases are the cause. The most common of these is acidic gastritis. The reason for the taste in the mouth in this case is the excess of hydrochloric acid accompanying the ailment. If this symptom is combined with heartburn, the root cause may be reflux esophagitis - a disease in which gastric juice is periodically refluxed into the esophagus. Sometimes sour taste and nausea are associated with overeating and are accompanied by upset stools, vomiting, and "rotten" belching. Such an eructation in itself speaks of problems with the pancreas.
In addition to digestive disorders, a sour taste in the mouth is caused by pathologies of the oral cavity (periodontal disease, caries), taking certain medications, as well as pregnancy - due to the load on the digestive organs created by an enlarged uterus. If this aftertaste is accompanied by a dry mouth, dehydration may be the cause. If bitterness, a violation of the bile secretion system associated with excessive consumption of smoked and fatty foods is possible.
Bitter taste
Common causes of a bitter taste in the mouth are food abuse, which provokes increased production of bile, or diseases of the biliary tract. This is usually interconnected: an excess of salty, fried, pickled foods in the diet can lead not only to a bitter aftertaste, but also to disruption of the liver and gallbladder - chronic cholecystitis, cholelithiasis, biliary dyskinesia, which are accompanied by regular bad breath.
A bitter taste is not always associated with disorders in the body - it is often a consequence of taking antibiotics, antiallergic drugs, as well as drinking a lot of alcohol and smoking.
Salty taste
A salty aftertaste in the mouth is quite rare. The most common cause of the disorder is considered to be fluid deficiency due to excessive use of certain medications, as well as tea, coffee, coca-cola - drinks that dehydrate the body. To eliminate the symptom, it is enough to drink at least 7 glasses of plain drinking water a day and brush your teeth more thoroughly.
If these measures do not help, you need to take a closer look at the state of the oral cavity and nasopharynx - it is believed that a salty taste may be the result of inflammatory and fungal diseases of the nose (for example, sinusitis). And sometimes it indicates inflammation of the salivary glands, caused by streptococcal, pneumococcal, staphylococcal infections entering the ducts. To eliminate it, you need to visit the dentist and undergo treatment.
Sweet taste
A sweet aftertaste in the mouth does not always indicate the pleasure of sweets. Perhaps this is evidence of severe pathologies in the body. One of these diseases is diabetes mellitus, accompanied by a violation of the production of insulin by the pancreas, as a result of which sugar accumulates in the lymph and penetrates into saliva. In order to prevent complications of the disease, when a persistent sweet taste appears in the mouth, it is necessary, without delay, to contact an endocrinologist and take a blood sugar test.
Paradoxically, a sweet aftertaste can also be a symptom of a "savory" life full of emotional turmoil and stress. In this case, sweet saliva becomes immediately after the release of adrenaline, which, in order to help the body overcome stress, causes an increase in blood glucose. It is also believed that a sweet aftertaste often accompanies smoking cessation.
Poisoning with chemicals (phosgene, pesticides) is another major cause of the sweet taste. If, after contact with poisons, such a taste, nausea appears, and the state of health worsens, an urgent need to consult a doctor.

Source: depositphotos.com
Metallic taste
If the aforementioned taste is not associated with the presence of metal crowns in the mouth, it is worth "listening" to your body. Is he experiencing hypovitaminosis, is he suffering from anemia? The most common pathologies associated with a metallic aftertaste are metabolic and gastrointestinal disorders (diabetes mellitus, gallbladder dysfunction, chronic cholecystitis), however, in some cases, the symptom can be observed in dental diseases (periodontal disease, gum disease, etc.) … The most dangerous cause is poisoning with arsenic, salts of mercury, copper, zinc, lead. If a person has had contact with poisonous substances and feels the taste of metal, it is necessary to consult a doctor immediately.
YouTube video related to the article:

Maria Kulkes Medical journalist About the author
Education: First Moscow State Medical University named after I. M. Sechenov, specialty "General Medicine".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.