- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Leptospirosis
Brief description of the disease

Leptospirosis has many names: infectious jaundice, water fever, Vasiliev-Weil disease, canine fever, Japanese daytime fever. All of them characterize an acute infectious disease, which is caused by parasitic microorganisms from the Leptospira family. The disease is characterized by symptoms of intoxication, multiple lesions of the liver and kidneys, and disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system. In severe cases, human leptospirosis leads to jaundice, meningitis, hemorrhagic syndrome, and acute renal failure.
Etiology and pathogenesis
The causative agents of the infection belong to the parasitic species Interrogans of the Leptospiraceae family. They enter the host's body through the skin and mucous membranes, and then settle in the lymph nodes and begin to actively multiply. Further, leptospirosis passes to other organs and systems, accumulating mainly in the kidneys, liver and central nervous system. The activity of harmful microorganisms leads to necrotic and degenerative tissue changes, disruption of the integrity of the epithelium of the renal tubules, the development of DIC and subsequent hemorrhagic rashes.
Epidemiology of the disease
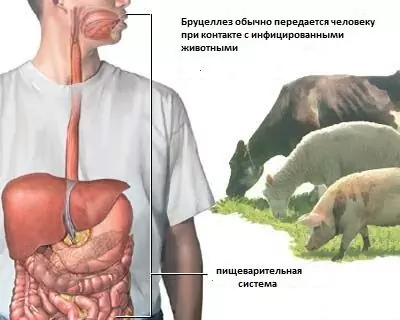
The infection occurs on all continents, with the exception of Antarctica. Leptospirosis is especially widespread in countries with tropical humid climates. Carriers of the disease are forest mice, water rats, dogs, cattle, pigs, rats and some other animals. In people diagnosed with leptospirosis, symptoms appear after eating meat and milk from infected animals, cutting meat, prolonged contact with water infected with the secretions of carriers. The specificity of the entry of the pathogen into the body determines the risk groups. The most common cases of illness are livestock workers, shepherds, milkmaids, veterinarians and people working in swampy meadows. Typically, leptospirosis is diagnosed in humans during the summer months, especially in August, when ideal conditions are created for bacteria to multiply.
Leptospirosis - disease symptoms
The incubation period for infection lasts from 2 weeks to 1 month. The disease begins with acute symptoms:
- severe chills;
- a sharp increase in body temperature up to 39-40 degrees;
- headaches;
- pronounced pain in the muscles (the calf muscles hurt very much);
- changes in the skin of the face - it becomes hyperemic, puffy. Patients have dilated blood vessels and conjunctival hyperemia, which often lead to hemorrhage.
In the first week after the onset of the disease, exanthema of a different nature may appear. In severe forms of the disease, hemorrhagic rashes are observed, localized on the elbow bends and in the armpits. In addition, with the diagnosis of leptospirosis, treatment includes correction of the liver, kidneys and cardiovascular system, since patients develop urinary retention, Pasternatsky's symptom, rapid breathing, lowering blood pressure and tachycardia.
Signs of fever are observed for about a week, after which the temperature returns to normal. After 3-4 days, a new rise in temperature is possible, but this time it subsides in 1-2 days. In some cases, lectospirosis in humans leads to the development of icterus, which is accompanied by a significant increase in the liver and a change in the color of urine.

If untreated, the disease causes serious complications - acute hepatic or renal failure, meningitis, iritis, iridocyclitis and encephalitis. Depending on the state of the human immune system, other severe consequences are possible.
Diagnosis of the disease
To determine the presence of leptospira, blood samples are examined by direct microscopy. In addition, the pathogen is released when blood is cultured on nutrient media. The diagnosis can also be confirmed serologically using the RIGA reaction, RSK, microagglutination-lysis.
Leptospirosis - disease treatment
All patients are subject to compulsory hospitalization. Etiotropic therapy consists in taking penicillin. The standard dosage of the drug is 6,000,000-12,000,000 U / day. The main remedy for leptospirosis is doxycycline. Doctors also use gammaglobulin. Since there is a risk of developing renal pathologies, osmo- and saluretics are recommended for patients. Hemodialysis is prescribed when symptoms of acute renal failure occur.
For prevention purposes, it is necessary to regularly vaccinate the personnel of livestock farms and enterprises engaged in the processing of meat and dairy products.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!