- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Brucellosis
General characteristics of the disease

Brucellosis is an infectious disease caused by bacteria of the genus Brucella. The infection is characterized by a long, chronic course, damage to the osteoarticular apparatus, nervous system and heart. The causative agent of brucellosis is widespread in the natural environment, tolerates low temperatures well, retains the ability to reproduce even with a long stay in water and soil. In food, bacteria live from 2 (cow's milk) to 5 (frozen meat) months. When using special means, brucella die within a few minutes.
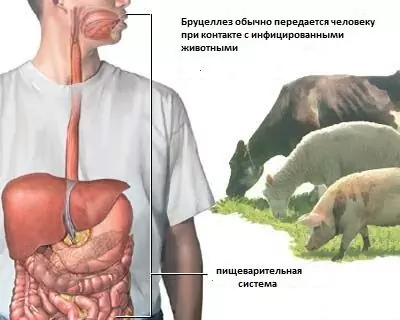
As a rule, brucellosis is detected in domestic animals, the meat and milk of which we eat. The pathogen of brucellosis enters the human body through the mucous membranes of the digestive and respiratory systems. Also brucellosis can be brought in through fresh scratches, abrasions and other injuries. This is especially true for people whose work is related to the processing of leather and wool or caring for sick animals. At risk are veterinarians, shepherds, milkmaids, livestock specialists.
What happens when infected?
Having penetrated the body, brucella quickly spread throughout the body through the lymphatic channels and blood vessels. Soon, new foci of infection appear in the liver, spleen, bone marrow, and lymph nodes. At the same time, brucellosis in humans affects the central nervous system, musculoskeletal system and genitals. In response to the action of bacteria, the body's defense reactions are activated, but, as a rule, the immune system is not able to provide bacteriological cleansing of the blood and lymph nodes due to the constant transformation of pathogens. This means that when brucellosis is diagnosed, treatment should not be carried out at home, but in specialized departments of clinics. Otherwise, brucellosis will develop into a chronic form, and it will be much more difficult to cope with it. Note also,that chronic brucellosis is often accompanied by immunopathological manifestations, provoking the emergence and growth of a whole "bunch" of other diseases.
Brucellosis - symptoms and clinical picture
During the primary latent form, brucellosis in humans practically does not manifest itself in anything. The characteristic symptoms of brucellosis appear only after the incubation period (after 1-5 weeks), when the disease flows into an acute septic or chronic form.
Acute brucellosis in humans has the following symptoms:
- increased body temperature (high temperature can last up to 3 weeks);
- profuse sweating;
- chills;
- fever;
- an increase in peripheral lymph nodes.
In some cases, the treatment of brucellosis in humans ends with complete recovery, but often the opposite process occurs, when the disease turns into a septic-metastatic form. In this case, the patient suffers from regular febrile attacks, severe intoxication, diffuse joint pain, sleep disturbances, and headache. Brucellosis, the symptoms of which indicate damage to the main body systems, leads to serious complications: myocarditis, meningitis, hepatitis, endocarditis, miscarriages in early pregnancy. After 6 months (this period is largely conditional), the acute form of brucellosis flows into a chronic one.
First of all, chronic brucellosis in humans is characterized by focal lesions. Most often, large joints suffer from infection - hip, elbow, knee. Also, patients are worried about the following symptoms of brucellosis:
- persistent pain in the morning;
- deformation of the joints and joints;
- feeling of stiffness;
- neuritis, radiculitis and other lesions of the nervous system;
- may manifest: meningitis, lesions of the optic and auditory nerves, miningoencephalitis.
In the chronic form of brucellosis in humans, focal changes in the genitals often lead to infertility in women and a decrease in sexual function in men. After a while, the infection gradually goes into remission, but leaves behind irreversible changes in the musculoskeletal system. For this reason, patients diagnosed with chronic brucellosis (diagnosis of the disease should be carried out only by experienced doctors) need hospitalization and adequate treatment, which will reduce the risk of disability.
Brucellosis - treatment of the disease

In acute septic form in the treatment of brucellosis, patients are prescribed:
- etiotropic therapy;
- taking antibiotics of the tetracycline group - rifampicin, chloramphenicol, streptomycin. Drugs that penetrate well into cells are recommended, for example, oral doxycycline or intramuscular streptomycin;
- physiotherapy and spa treatment (not earlier than 6 months after the disappearance of clinical symptoms).
When diagnosed with chronic brucellosis, treatment is based on the use of fortifying measures and vaccine therapy. The prognosis in most cases is favorable, however, it is worth remembering that brucellosis often leads to disability.
Prevention of infection is aimed at reducing the incidence of brucellosis in domestic animals and livestock. To this end, specialists carry out sanitary and veterinary measures, during which the pathogen of brucellosis almost always dies. Specific prophylaxis is the use of anti-brucellosis vaccines. They are regularly made not only to animals, but also to livestock workers, employees of meat processing plants and representatives of other professions related to meat processing or the processing of skins and fur.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!