- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Rabies
Brief description of the disease

The rabies virus enters the human body after being bitten by sick wild or domestic animals. Infection occurs when the saliva of the carrier enters the damaged skin or mucous membranes. The incubation period for rabies virus is 2 weeks to 2 months. In some cases, this period is extended to one year. When communicating with a sick person, elementary caution should be observed, since after infection, the rabies virus is also contained in his saliva.
Bites (multiple and deep), as well as any damage to the neck, arms, head and face are dangerous. Moreover, with direct contact with a carrier, the rabies virus can enter the bloodstream even through small fresh scratches, open wounds, abrasions, mucous membranes of the eyes and mouth. With bites to the head and face, the risk of getting the virus is 90%, injuries to the hands - 63%, legs - 23%. However, these statistics are of no value to ordinary people. Remember that any bite should be regarded as a potential source of life-threatening disease. At the same time, it does not matter who exactly bit you, because, catching rabies, the cutest doggie can turn into an evil, uncontrollable creature.
Rabies - disease symptoms
After entering the human body, the rabies virus begins to multiply rapidly. During this process, rabies symptoms go through 3 distinct phases:
- prodromal - the first signs of rabies appear at the bite sites: itching, pain, swelling and redness of the scar. In addition, the person begins to feel general malaise, headache, lack of air. He has a fever and has trouble swallowing food. Perhaps the appearance of symptoms indicating a disorder of the central nervous system (nightmares, insomnia, causeless fear);
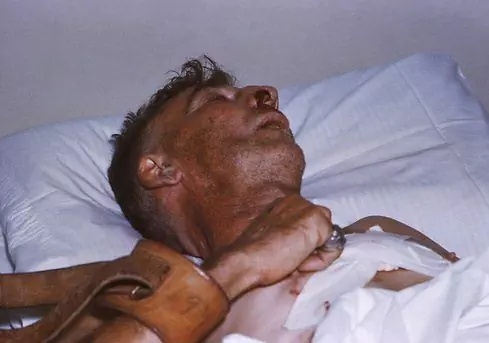
- encephalitis - the period of arousal occurs 2-3 days after the onset of the first symptoms. This phase is characterized by the development of painful spasms of the muscles of the body, provoked by a variety of factors (noise, bright light, stale air). Patients become aggressive. They scream, rip their clothes, break furniture and other interior items. Between attacks, the appearance of auditory and visual hallucinations, incoherent delirium is possible. In such a state, a person is very dangerous, as he has an abnormal "mad" strength. Along with the above symptoms, rabies in humans leads to severe tachycardia, excessive sweating and excessive salivation. Foam at the mouth is also a characteristic feature;
- the final phase - the rabies virus causes paralysis of the limbs and damage to the cranial nerves, but the psychomotor agitation weakens. The patient becomes calmer, can eat and drink on his own, suffer less from convulsions and spasms. But this is just an appearance of normalization of the state, because after 10-20 hours a person will inevitably die from cardiac arrest or paralysis of the respiratory center. Death comes suddenly, without agony.
One important fact should be especially noted: rabies, the symptoms of which indicate the onset of the third phase, does not leave the victim a single chance for life. Keep in mind that the rabies virus is deadly and, if untreated, is 100% fatal. For this reason, it is necessary to consult a doctor not when the first signs of rabies appear, but immediately after bites and other injuries associated with animal attacks. This is especially important against the background of the fact that in some cases patients develop so-called silent rabies, which does not have pronounced symptoms of arousal. With such a development of signs of rabies, the person does not feel any special changes in the general condition and believes that everything worked out. The fallacy of inaction becomes clear only after the first paralysis,when it is no longer possible to save the patient's life.
How is rabies in humans treated?

Once again, we note that any animal bite should be considered as a potential source of rabies virus infection. Accordingly, the victim needs to see a doctor and undergo a course of treatment. Antiviral vaccinations against rabies are given at trauma centers. In our country, the drug COCAV is used for this. The vaccine is administered intramuscularly at 0, 3, 7, 14, 30 and 90 days after the bite. If the injury was caused by accident, for example, while playing with a familiar pet, treatment can be stopped after 10-15 days if the animal does not show signs of rabies.
Multiple injuries and bites, even in the absence of signs of rabies, require the use of rabies immunoglobulin. It is used simultaneously with vaccination in the first hours after injury. It is also very important to treat the wound properly. It is washed with warm water and a disinfectant. The edges of the wound are wiped with alcohol or 5% iodine tincture. In addition, tetanus serum is administered to the patient.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!