- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Headache in the temples

A headache in the temples is pain that occurs as a result of a violation of the nervous regulation of the vessels of the brain and cerebral circulation. A spasm occurs, provoking pain in the temporal region of the head.
Headache in the temples is one of the twenty most common causes of temporary disability according to WHO statistics. More than 70% of the inhabitants of civilized countries experience headache in the temples periodically or constantly.
Headache in the temples: causes
There are more than 45 known diseases that can cause headaches in the temples. Most often, there are:
- Migraine. Suddenly one side of the head begins to ache, most of all in the forehead and temple. The pain is pulsating, intense, paroxysmal;
- Tension pain. Prolonged forced stay in one position (at the computer, driving a car). Painful aching, continuous, feeling of tightness of the head by a tight hoop;
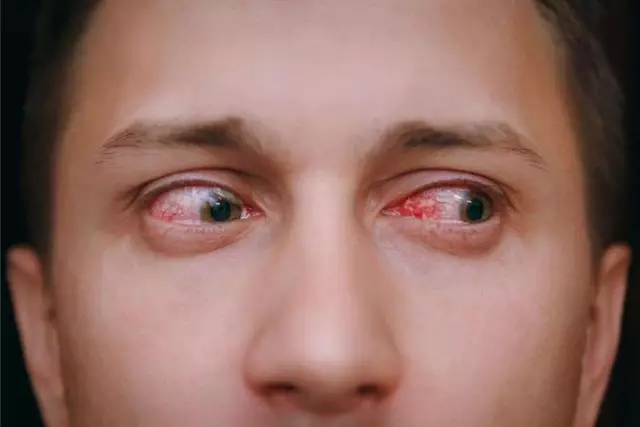
- Cervicogenic pain. Consequence of pathology in the cervical spine. Most often these are age-related changes that occur in people over 40 years old. The pain is moderate or moderate. It begins in the neck or back of the head, moving to the temporal and frontal regions. It is accompanied by blurred consciousness, redness of the eyes, nausea, vomiting, difficulty swallowing;
- Trigeminal neuralgia. One of the forms of cranial neuralgia, caused by compression of the trigeminal nerve, occurs mainly after 40 years. The pain is one-sided, impulsive, shooting;
- Infectious intracranial processes (encephalitis or meningitis). The pain is acute, with increasing intensity. Concentrated in the temporal region, accompanied by fever;
- Temporal (giant cell) arteritis. Chronic arterial inflammation, in which the temporal arteries are primarily affected. The consequence of age-related changes in blood vessels is observed in people over 50 years old. The pain is constant, of varying intensity, concentrated in the frontotemporal region;
- Hormonal disorders Occur periodically in women during PMS or in other phases of the menstrual cycle, during pregnancy or during menopause. The pain is aching, dull, exhausting;
- Atypical pain. May be due to various factors. A sharp change in weather, emotional stress or stress, insomnia, prolonged exposure to the sun or strong winds, hangover syndrome, inhalation of strong odors (varnishes, paints, kerosene, gasoline, perfume), the use of foods with an excess of nitrates, coffee abuse, smoking - all this and much more can cause headaches in the temples. As a rule, when the cause is eliminated, the pain goes away.
Severe headache in the temples

Severe headache in the temples is one of the most difficult problems in medical practice. A severe headache in the temples is accompanied by nausea, vomiting, distraction of attention, dizziness. Such pain completely deprives a person of the opportunity to engage in any kind of activity.
Headache in the temples: treatment
Treatment of headache in the temples should be aimed at eliminating its cause. Pain is an alarming signal that the body gives when one of its systems malfunctions, in this case the brain and adjacent organs and tissues. In order to choose the right one from the mass of reasons that can provoke a headache in the temples, it is necessary to undergo an in-depth examination by a neurologist or neuropathologist and establish an accurate diagnosis. In the future, strictly follow the recommendations for treatment.
For rare headaches in the temples, treatment may consist of analgesics or other pain relievers prescribed by your doctor.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!