- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Treatment of adenoids: how to treat adenoids in adults and children
The content of the article:
- Adenoids and adenoiditis
- How are adenoids treated in adults?
- How to treat adenoids in children?
- Surgical removal of adenoids
- Treatment of adenoids with folk remedies
- Video
Treatment of adenoids should be carried out in the early stages, despite the fact that at first glance, enlargement of the tonsils does not seem to be a dangerous pathology. But a sluggish process can worsen, turn into a purulent infection, which can spread from the nasopharynx between the fascia of the neck downward, quickly reaching the mediastinum. In this case, therapeutic methods may not be enough, and then an operation will be required.
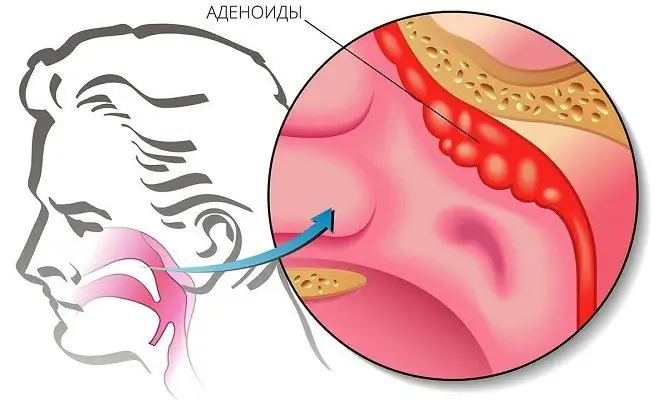
Adenoids and adenoiditis
To understand the principles of treatment, it is necessary to distinguish adenoids from adenoiditis, since the pathogenesis in these cases is different, and pathologies require a different approach.

Adenoids are growths of the pharyngeal tonsil
Adenoids, they are also adenoid growths, are enlarged pharyngeal tonsils, which, due to their diameter, block the air passage, making breathing difficult and causing various complications.
Adenoiditis is an inflammation of the adenoids that develops in response to the ingress of an infectious agent into the lymphatic tissue (and the amygdala is nothing more than a large area of lymphatic tissue that takes part in the body's immune response and belongs to the Pirogov-Waldeyer ring, the first protective barrier at the entrance into the body).
Symptoms of adenoiditis may be similar to those of adenoids, but it is important to carry out differential diagnostics in order to choose the correct treatment tactics. Adenoids persist for a long time, and their inflammation is unstable, it arises, develops and disappears - sometimes spontaneously, sometimes under the influence of anti-inflammatory therapy. The second difference is that with adenoiditis, as with any inflammation, there is a classic systemic reaction of the body, which is manifested by significant redness of the mucous membrane, increased mucus secretion, increased body temperature, general malaise, changes in the blood test (leukocytosis and a shift in the leukocyte count to the left). The comparative short duration of this process is not its main feature and should not deprive one of vigilance - any inflammatory process in this area is dangerous with delayed complications. The next difference is that adenoiditis responds better to conservative therapy.
The proliferation of adenoids arises as a response to frequent respiratory diseases or allergic reactions, then they speak of compensatory hypertrophy of the lymphoid tissue. Due to the adenoids, breathing through the nose is significantly affected, hypoxia, deformation of the turbinates occurs. This process can last for years, and the hypertrophied node can last a lifetime. This type of pathology is less susceptible to drug therapy, and the most common method of treatment is surgical removal, the pros and cons of which will be discussed below.
How are adenoids treated in adults?
The actual treatment is divided into pathogenetic, aimed at getting rid of the root cause of the disease, and symptomatic, the main purpose of which is to alleviate the patient's condition, improve the quality of his life. Conservative therapy consists in taking drugs of the following groups:
- antibacterial agents. The cause of inflammation and hypertrophy of the tonsils is often a bacterial infection, so antibiotics may be prescribed for adenoids. They are used both in tablets and in the form of a solution; they are included in the complex of preparations for the rehabilitation of the tonsils;
- anti-inflammatory drugs together with pain relievers are used to reduce pain, reduce swelling, eliminate inflammation;
- vasoconstrictor - the basis of symptomatic treatment, relieve puffiness, increase ventilation, prevent hypoxia. They can be used throughout the course of the disease in the form of nasal drops or a nebulizer (this form of administration is especially good for the rapid delivery of the drug to the target organ and high bioavailability). This helps to restore airway patency, improve well-being, reduce the possibility of reflex vasospasm, prevent fibrotic changes after massive inflammation;
- antiallergic agents - histamine blockers can reduce allergic manifestations, prevent hypertrophy, relieve allergic rhinitis (runny nose), eliminate edema, improve nasal breathing.
Important! You cannot select therapy yourself, based on feedback on the treatment of adenoids. Before starting treatment, you should consult an ENT doctor who will establish an accurate diagnosis, the degree of the disease, organic and functional disorders and, depending on these factors, will select the optimal treatment. Perhaps the disease will be at such a stage that it will not be necessary to use systemic drugs, and the treatment will consist in inhalation and regular sanitation of the oral cavity, or it may be so that therapeutic treatment will not be shown, and you will have to resort to surgery.
How to treat adenoids in children?
The disease occurs much more often in childhood, on the one hand, due to the immaturity of the immune system, on the other, due to the high proliferative capacity of tissues, i.e., their tendency to overgrow. Inflammatory processes in children are more acute.
Adenoids in children are dangerous in their consequences. If an adult has an enlarged tonsils, it brings discomfort and increases the risk of bacterial infection, but does not cause damage that will last for life. In children, due to long-term disturbed breathing, cerebral hypoxia occurs - if the brain does not receive enough oxygen, it works worse and develops worse. Six months of a hypoxic state discard the child in development, he begins to lag behind his peers.

Long-term existing adenoids form an "adenoid face" in a child
Due to adenoid growths and shortness of breath in children, there is a deformation of the nasal passages. The mucous membrane thickens, changes, the child breathes through the mouth. The so-called adenoid face is formed - a constantly open mouth, an elongated oval of the face, an irregular bite.
Adenoids, enlarged in childhood and not cured in time, make a person susceptible to chronic diseases of the upper respiratory tract for life, since there is practically no barrier protecting them from infectious agents.
The treatment regimen for adenoids in children is somewhat different from that in adults. It is determined after the otolaryngologist examines and determines the degree of proliferation of the adenoids. The scheme includes the following activities:
- rinsing the nasal passages with antiseptics and isotonic solutions, which allows you to remove the contents of the cavity, cleanses it, disinfects and helps relieve inflammation;
- inhalation procedures - inhalers or nebulizers with vasoconstrictor and anti-inflammatory drugs are convenient for use in children, they allow you to quickly deliver the drug directly to the site of exposure without any unpleasant sensations for the child. Warming inhalations with warm (but not hot!) Air with a minimum amount of pharmacological preparations, as well as inhalations with mineral water can be prescribed;
- other physiotherapy procedures.
Physiotherapy occupies a separate place in the treatment of childhood adenoid vegetations - these are non-invasive methods that help provide additional conditions for resolving the pathological process. The main method is therapeutic electrophoresis, which allows the place to inject drugs deep into the tissues, directly into the focus of hypertrophy or inflammation, and not just apply them to the surface - this effect of antiseptics, antiallergic and antibacterial drugs in the thickness of the tonsil is the most effective.
UHF therapy is also used, that is, treatment with ultra-high-frequency current. It does not damage tissues, while it has an excellent biological effect, which consists in improving the blood supply to the area, uniform heating of the tissue thickness. Ultraviolet radiation is used to completely destroy pathogenic microflora in the nasal cavity. The disadvantage of this method is the shallow penetration of UV rays, therefore, UV radiation is usually combined with other antiseptic procedures.
Surgical removal of adenoids
The feasibility of removing adenoid growths has been the subject of fierce debate in the medical community for many years. Most clinicians agree that active conservative treatment is needed, several courses of which usually allow getting rid of the disease without surgery. Surgical intervention is carried out only in cases where several courses of conservative therapy did not bring any result, and the size of the adenoids is so large that they block almost the entire lumen of the nasal passage, significantly complicating breathing, contributing to the occurrence of wheezing and apnea (respiratory arrest) during sleep and causing hypoxia brain. In such cases, the doctor may prescribe an adenotomy - the surgical removal of the adenoids.

Removal of adenoids is performed on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia
The operation is preceded by preoperative preparation - before the intervention begins, adenoiditis must be cured. The intervention is carried out under local anesthesia, less often general anesthesia is used. Everything happens on an outpatient basis, no hospitalization is required.
After processing the operating field, the surgeon inserts an adenotome into the oral cavity - a special knife with rounded pointed edges, the shape of which allows you to grasp the adenoids and remove them. If surgical manipulations are performed without proper visual control, after removal, small lobules of the adenoids may remain, which will subsequently begin to increase in size again and provide a relapse of the disease - the doctor's task is to prevent this option. In some clinics, adenotomy is performed under supervision, for which a probe with a camera is used, which significantly increases the efficiency of the operation.
After removing the adenoids, the surgeon stops bleeding, tampons the wound and sterilizes the oral cavity again. The recovery period lasts up to two weeks, during which pain syndrome, minor bleeding, swelling of the mucous membrane, and a runny nose may persist. After tissue healing, airway patency is restored.
In recent years, laser treatment of adenoids has become increasingly popular. There are two options for this procedure:
- Laser therapy - several sessions of laser irradiation of the adenoids are performed, which leads to their degeneration and significant reduction.
- Single removal of adenoids with a directed laser beam. This procedure takes little time, causes minimal harm to the mucous membrane, minimizes bleeding (high temperature immediately coagulates the vessels, cauterizing them) and ensures quick recovery.
After the operation, breathing exercises and moderate washing of the nasal cavity from blood clots are indicated. You should refrain from physical activity, hot baths, prolonged exposure to the sun.
Treatment of adenoids with folk remedies
An integrated approach to the treatment of adenoid growths may include, in addition to traditional therapy, treatment at home with folk remedies. There are many herbal decoctions for rinsing the nasal cavity, which are advisable to use at any stage - natural phytoncides have antibacterial and restorative effects. Before use, you must make sure that there is no allergic reaction to the herbal preparation.
Suitable for the preparation of medicinal infusions: marshmallow root, rose hips, birch leaves, yarrow, thyme, raspberry leaves, blackberry leaves, coltsfoot, calendula flowers, viburnum and clover, chamomile flowers, strawberry leaves, flax seeds, and others medicinal plants with anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effect. A tablespoon of medicinal raw materials is poured with a glass of boiling water and insisted for two hours. Then the nasal passages are filtered and washed with the resulting preparation every 3-4 hours.

Thuja oil is a popular folk remedy for the treatment of adenoids.
Thuja oil is a common treatment for adenoids. This essential oil has a range of beneficial properties, from immunostimulation to antibacterial effects. It is used at a concentration of 15%, since pure oil can cause burns to the mucous membrane. The nose is rinsed with an antiseptic and then a few drops of diluted thuja oil are dripped into each nostril. The procedure is repeated 3-4 times a day.
In the fight against adenoids, propolis can help. This natural bee product is known for its versatility and wide range of medicinal properties. You can use both prepared independently and purchased in the pharmacy an aqueous solution of propolis, they wash the nasal passages from 2 to 5 times a day.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Nikita Gaidukov About the author
Education: 4th year student of the Faculty of Medicine No. 1, specializing in General Medicine, Vinnitsa National Medical University. N. I. Pirogov.
Work experience: Nurse of the cardiology department of the Tyachiv Regional Hospital No. 1, geneticist / molecular biologist in the Polymerase Chain Reaction Laboratory at VNMU named after N. I. Pirogov.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.