- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Inflammation of the adenoids in children: causes, symptoms, treatment
The content of the article:
- Adenoids and adenoiditis
- Symptoms of inflammation of the adenoids in a child
- Treatment of inflammation of the adenoids in children
- Video
Inflammation of the adenoids, or adenoiditis, is one of the most common otolaryngological diseases caused by the addition of infection to a chronic hypertrophic process in the nasopharyngeal tonsil. In order to understand how to treat this disease, you should know what adenoids are.

With adenoiditis, the general condition of the child suffers and discharge from the nose appears
Adenoids and adenoiditis
The nasopharyngeal tonsil is a peripheral organ of the immune system, which consists mainly of lymphoid tissue and is included in the lymphatic pharyngeal ring, which prevents the spread of infection (bacteria and viruses) in the body that enter the upper respiratory tract with the air. In addition, the amygdala is involved in the process of thermoregulation, ensuring the optimal temperature of the inhaled air.
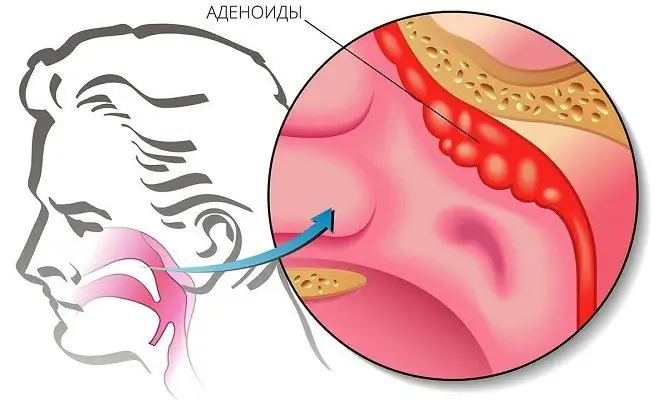
Adenoids (adenoid growths, adenoid vegetations) are a pathologically enlarged (hypertrophied) nasopharyngeal tonsil. Often they are detected only at an advanced stage, since at the early stages of their development, the symptoms are not pronounced and do not attract attention. Meanwhile, the most effective treatment of pathology is carried out precisely in the early stages of development, therefore it is important to regularly conduct a preventive examination of the nasopharynx. In the photo and on examination, the adenoids look like two lumps of loose tissue.
In case of respiratory diseases, the nasopharyngeal tonsil enlarges, and after recovery it returns to its normal state. However, for a number of reasons, which, first of all, refers to childhood, the tonsil does not decrease, the lymphoid tissue remains hypertrophied and is fixed in this state. The peak of adenoid growths occurs at the age of 3-7 years. An increase in adenoids can also occur in adult patients, but this is much less common than in children.
The hypertrophied nasopharyngeal tonsil does not cope well with its functions to fight infection, and very often microorganisms, lingering in the lymphoid tissue, do not die, but develop and cause an inflammatory process in it - this is how adenoiditis develops. In turn, the inflammation of the adenoids contributes to an even greater hypertrophy of the tonsil, the tissue grows more strongly from inflammation to inflammation, the adenoids progress. A vicious circle is formed - an enlarged amygdala often becomes inflamed, and inflammation contributes to its further enlargement.
Frequent adenoiditis indicates the progression of the pathology.
Symptoms of inflammation of the adenoids in a child
Increasing, the adenoids block the lumen of the nasal passages, which causes difficulty in nasal breathing in patients. On this basis, three stages of adenoid vegetation are distinguished:
- Grade 1 - adenoids cover about a third of the height of the nasal passages or vomer;
- 2 degree - about half the height of the nasal passages or opener overlaps;
- Grade 3 - the nasal passages are almost completely blocked.
At the initial stage of the adenoids, nasal breathing is impaired only in the horizontal position of the body, this usually manifests itself at night. The child sleeps with his mouth open, while breathing noisily, sometimes snoring. As the pathology progresses, snoring becomes constant, signs of impaired nasal breathing are present in the daytime. These children have prolonged nasal congestion, but no snot. The appearance of mucopurulent discharge from the nasal cavity indicates adenoiditis, i.e., the addition of inflammation. Discharge, flowing down the back of the pharynx, irritates it, causing a reflex cough. It manifests itself at night or in the morning after waking up, since it is in the lying position that irritation is caused.

Adenoiditis responds well to treatment, but if the adenoids are not cured, it will recur
If adenoids are a chronic pathology, then adenoiditis can be both acute and chronic.
Acute inflammation of the adenoids in children is accompanied by high fever (38-39 ° C and above), nasal discharge, pain in the ears, nasopharynx may occur, regional lymph nodes (cervical, submandibular, occipital) increase.
Often, nearby structures are involved in the inflammatory process - the middle ear (otitis media), the Eustachian tube (eustachitis), palatine tonsils (tonsillitis).
Signs of inflammation of the adenoids in a child, when the disease is chronic, differ little from those in adenoids. Chronic inflammation of the adenoid tissue contributes to its edema, which further complicates nasal breathing. This leads to drowsiness, fatigue, frequent headaches, sleep disturbances, impaired appetite, changes in behavior (the child becomes moody, whiny, irritable).
Children with chronic adenoiditis often get sick, especially acute respiratory viral infections (ARVI), pharyngitis, laryngitis, tracheitis, stomatitis - this is due to the fact that since the inflamed nasopharyngeal tonsil performs its functions poorly. In addition, chronically inflamed adenoids themselves are the focus of infection in the body, which leads to a weakening of its defenses and contributes to the development of many diseases, in particular, severe forms of allergy (up to bronchial asthma), pathologies of the kidneys, joints, etc.
Treatment of inflammation of the adenoids in children
One of the differences between adenoiditis and adenoids is that adenoiditis, especially acute, responds well to therapy and usually heals within 3-5 days. However, it should be understood that the presence of adenoids in itself is a constant risk factor for adenoiditis, therefore, after the adenoiditis has been cured, it is necessary to start complex treatment of adenoids.
Drug therapy for adenoiditis consists in the use of anti-inflammatory, antihistamines of general action. If the child has a fever, antipyretic drugs are used - paracetamol or ibuprofen preparations. In acute adenoiditis caused by a bacterial pathogen, broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed, which, after establishing the sensitivity of the microflora, are replaced by a targeted antibiotic. In chronic adenoiditis, the pathogen and its sensitivity are first determined, after which, if necessary, antibiotic therapy is carried out.
The inflammatory focus is sanitized by rinsing the nose with antiseptic solutions, saline, after which vasoconstrictor, anti-inflammatory, antiseptic drugs are instilled into the nose.
To reduce the inflammatory process and relieve swelling of the nasopharyngeal mucosa 3-4 times a day, inhalation of anti-inflammatory drugs is carried out. It is important to know that in case of acute inflammation, thermal procedures, including steam inhalation, are prohibited; a nebulizer should be used for inhalation.

Inhalation for children is carried out using a nebulizer
Doctor Komarovsky, the famous Ukrainian pediatrician, calls for paying special attention to the microclimate in the room where the sick child is. The room must be constantly ventilated and kept at a humidity of 50-60% so that the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract does not dry out (drying out makes it vulnerable).
In chronic adenoiditis, physiotherapy demonstrates a good therapeutic effect. Ultraviolet irradiation (UFO) of the nasal cavity, electrophoresis of drugs, laser therapy, ultra-high-frequency therapy (UHF) are used.
The issue of an operation to remove adenoids is considered only after adenoiditis has been cured. Surgical treatment is indicated for grade 3 adenoids, when the absence of nasal breathing causes prolonged hypoxia of the brain, which can have serious consequences (changes in the facial skeleton, mental and physical lag), with persistent hearing loss, failure of long-term conservative therapy, etc. uncomplicated, usually performed on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia (sometimes general anesthesia is used). However, since it is almost impossible to remove the tissue of the tonsil completely, the operation does not guarantee a relapse while maintaining the favorable conditions.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Aksenova Medical journalist About the author
Education: 2004-2007 "First Kiev Medical College" specialty "Laboratory Diagnostics".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.