- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Hydronephrosis
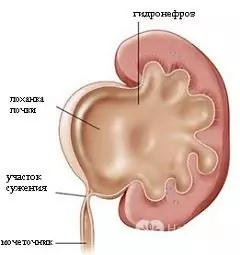
The word "hydronephrosis" consists of two parts: "hydro" - water, "nephro" - kidney. That is, hydronephrosis means an increased fluid content in the kidney when the normal outflow of urine is impaired. It is a serious condition because, if left untreated for hydronephrosis, the affected kidney can lose its function, which is a life-threatening condition.
Types and causes of hydronephrosis
Hydronephrosis is congenital, or primary, and acquired, or secondary. Hydronephrosis in children is usually congenital, in adults it is acquired.
The most common causes of hydronephrosis in children are congenital anomalies in the structure of the kidney or its vessels. Secondary hydronephrosis is a consequence of changes in the structure of the kidney or urinary tract (ureter, urethra, and sometimes the bladder) as a result of any disease. It can be inflammation of the renal pelvis or ureter, prostate adenoma, cysts and strictures (narrowing) of the urinary tract, etc.
Hydronephrosis can be unilateral, affecting only one kidney, or bilateral. Bilateral hydronephrosis occurs when the outflow of urine in the lower parts of the urinary tract - the bladder and urethra - is impaired, as a result of which both kidneys suffer from an increased fluid content. Hydronephrosis in children is usually unilateral.
In the case when not only the renal pelvis, but also the ureter underwent pathological expansion under the pressure of urine, they speak of ureterohydronephrosis.
Hydronephrosis degrees
There are three degrees of hydronephrosis:
- Hydronephrosis in the first degree. Distension of the renal pelvis (pyelectasis) occurs as a result of increased urine pressure. At this stage, the function of the kidney is not yet impaired, but the kidney is already enlarged in size;
- Hydronephrosis in the second degree. There is a further, more significant expansion of the renal pelvis and renal calyces (hydrocalicosis). As a result, the fluid contained in the tubules squeezes the kidney parenchyma, which becomes thinner (atrophies) under pressure. At this stage, kidney function is significantly impaired;
- Hydronephrosis in the third degree. The atrophy of the renal tissue is increasing, becoming irreversible. Kidney function is gradually lost, in the final stage of hydronephrosis, the kidney dies. A kidney that has lost its function in this case poses a significant threat to health.
Hydronephrosis symptoms
The severity of the symptoms of hydronephrosis depends on the degree to which the disease is. The early symptoms of hydronephrosis are not pronounced, so the disease is sometimes found already in a neglected state.
Hydronephrosis in newborns, and indeed hydronephrosis in children, usually does not manifest itself in any way until the third degree of the disease, except that the increased anxiety of the baby may draw attention to itself, sometimes with hydronephrosis in newborns, an admixture of blood is found in the urine. Hydronephrosis in newborns is usually known in advance, since it is detected even during prenatal ultrasound diagnostics of the fetus. Hydronephrosis in children of a later age, like in adults, can be detected by chance, when examined for another reason.
Sometimes an early symptom of hydronephrosis is renal colic, especially hydronephrosis caused by urolithiasis. When the disease reaches a significant degree of development, the main symptoms of hydronephrosis are aching dull and constant pain in the kidney area and signs of reduced renal function: edema, increased pressure due to impaired water metabolism. One of the common symptoms of hydronephrosis is the appearance of blood in the urine (hematuria).
Diagnosis of hydronephrosis
The leading method in the diagnosis of hydronephrosis is ultrasound examination of the kidneys and urinary tract. As an addition, color Doppler mapping (CDM), radioisotope renography, and sometimes computed or magnetic resonance imaging are used. Also, in some cases of hydronephrosis, an endoscopic examination can be applied - urethrocystoscopy or ureteroscopy. All these methods are aimed at visualizing the internal structure of the kidney, ureters and vessels supplying them.
Since hydronephrosis contributes to the addition of infection, urine culture is performed. Functional urine tests (Zimnitsky test, Nechiporenko test) are carried out to study kidney function.
Hydronephrosis treatment
Hydronephrosis is treated only surgically. Conservative treatment of hydronephrosis is used only to eliminate inflammation if a secondary infection has occurred, or as a therapy to relieve the symptoms of hydronephrosis before surgery.
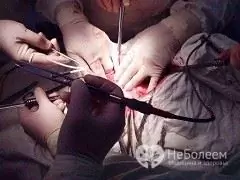
Surgery to treat hydronephrosis consists in removing an obstacle that interferes with the normal flow of urine. In each case, an individual approach is required, so the choice of a surgical method for treating hydronephrosis remains with the surgeon. Currently, the surgical treatment of hydronephrosis is performed endoscopically, which does not require a large and traumatic incision to access the operating field.
The endoscope is inserted into the abdominal cavity through two small punctures, all manipulations are performed with a thin surgical instrument under the control of what is happening on the monitor. This method of treating hydronephrosis can significantly reduce the invasiveness of the operation, the risk of postoperative complications and is practically bloodless.
Hydronephrosis in young children in a minor stage may not require medical attention. In such cases, follow-up with ultrasound examination is recommended two to four times a year. Hydronephrosis in children of the first and even second degree sometimes goes away on its own during the first year of life; surgical treatment of hydronephrosis is not required. However, the disease in the third degree, as well as the increase in the symptoms of hydronephrosis in children, require urgent surgical intervention.
With hydronephrosis in the terminal stage, in case of kidney death, it is removed. Usually, such an operation is performed in elderly people, when the regenerative functions of the body are significantly reduced.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!