- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Causes of blood in feces in an adult
The content of the article:
-
Bleeding in different parts of the gastrointestinal tract
Ulcer perforation
-
Scarlet blood in feces
- Ulcerative colitis
- Intestinal diverticulosis
- Hemorrhoids
- Anal fissure
- Crohn's disease
- Colorectal cancer
- What to do if blood is found in the stool
The causes of blood in the stool in an adult can be different. Bloody stool, or hemocolitis, is a symptom of many diseases that affect different parts of the gastrointestinal tract and occur with a violation of the integrity of the mucous membrane. The systematic appearance of blood in the feces usually serves as a sign of serious pathology, therefore, at the very first such symptoms, a comprehensive examination is necessary.
Bleeding in different parts of the gastrointestinal tract
By the appearance of the feces, it can be assumed in which part of the digestive tract bleeding occurred. For this, the color of the blood is assessed: the higher the lesion is, the darker the blood. Feces containing dark blood (tarry feces, melena) signal diseases in the upper gastrointestinal tract - the stomach, small intestine or the initial sections of the colon.
Attention! Photo of shocking content.
Click on the link to view.
Ulcer perforation
If the dark blood in the stool is accompanied by intense abdominal pain, a perforated stomach or intestinal ulcer may be suspected. In this state, the stool will be significantly thinned, saturated dark color. Ulcer perforation is a serious complication of peptic ulcer disease, which leads to the development of peritonitis - an acute inflammation of the peritoneum. This is the most common cause of dark blood in the stool.
Ulcer perforation requires urgent medical attention, so you need to know its signs. There are three periods:
- Painful shock - occurs at the moment of perforation of the ulcer. Suddenly there is a sharp, sharp pain in the abdomen, aggravated by movement. Initially, it is localized in the upper abdomen, then spreads down, recoil is possible in the right shoulder, supraclavicular region and right scapula. The patient in this period cannot get up in bed and takes a forced position - lying on his side with his legs pulled up to his stomach. The abdomen is pulled in, the abdominal muscles are sharply tense and stop participating in breathing. The body temperature rises, cold sweat appears on the forehead, blood pressure drops, and the pulse slows down.
- Imaginary well - being - pulse, pressure and temperature equalize. Acute pain subsides, although soreness persists when feeling the abdomen.
- Purulent diffuse peritonitis - begins 10-12 hours after the attack in the absence of treatment. The first symptom is vomiting. The skin and mucous membranes become dry, the body temperature rises, and breathing becomes more frequent. In this period, medical assistance may already be too late.
At the first sign of ulcer perforation, an ambulance must be called.
Scarlet blood in feces
Bright scarlet blood in the feces indicates the development of pathologies of the lower gastrointestinal tract: ulcerative colitis, intestinal diverticulosis, infectious inflammation, benign or malignant tumors, Crohn's disease.
Ulcerative colitis
Ulcerative colitis is an inflammatory disease that affects the mucous membrane of the large intestine and manifests itself as a destructive ulcerative process. Ulcerative colitis always proceeds in a chronic form, so patients may not notice its symptoms for a long time or do not attach importance to them. It is the appearance of blood in the feces that often becomes the symptom of ulcerative colitis with which patients go to the doctor. Bleeding in ulcerative colitis occurs in 90% of patients, but the amount of blood can vary - from barely noticeable marks on toilet paper or streaks of blood in the stool to large blood loss.
In addition to bleeding, ulcerative colitis is characterized by:
- mucus and pus in the stool;
- diarrhea several times a day;
- constipation - occurs less often than diarrhea, their appearance indicates an inflammatory process in the rectum and / or sigmoid colon;
- false urge to empty the intestines, in which, instead of defecation, blood comes out of the intestines with pus or mucus;
- nighttime bowel movements that interfere with sleep;
- fecal incontinence;
- bloating;
- pain in the left side of the abdomen, moderate or low intensity;
- signs of general intoxication - fever, vomiting, heart palpitations, weight loss, dehydration.
Intestinal diverticulosis
Intestinal diverticulosis is a disease in which bag-like protrusions form in the wall of the colon. This disease is typical for older people, since with age, the elasticity of the intestinal wall decreases, and the pressure on it associated with flatulence or constipation leads to the formation of diverticula.
Diverticulosis can proceed without pain, unnoticed by the patient, less often there is moderate pain in the left abdomen. Stool disturbances in the form of constipation or diarrhea, as well as bloating, may appear.
Hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids are an extremely common disease associated with venous congestion in the lower intestines. With hemorrhoids, the vessel walls lose their elasticity, which leads to the formation of hemorrhoids. The disease is often asymptomatic for a long time, but with an increase in the nodes, pain and bleeding from the anus appear. There are external and internal forms of hemorrhoids - depending on which vessels are affected. The development of hemorrhoids is promoted by sedentary work, improper diets that contribute to constipation, alcohol abuse, smoking, and pregnancy and childbirth.
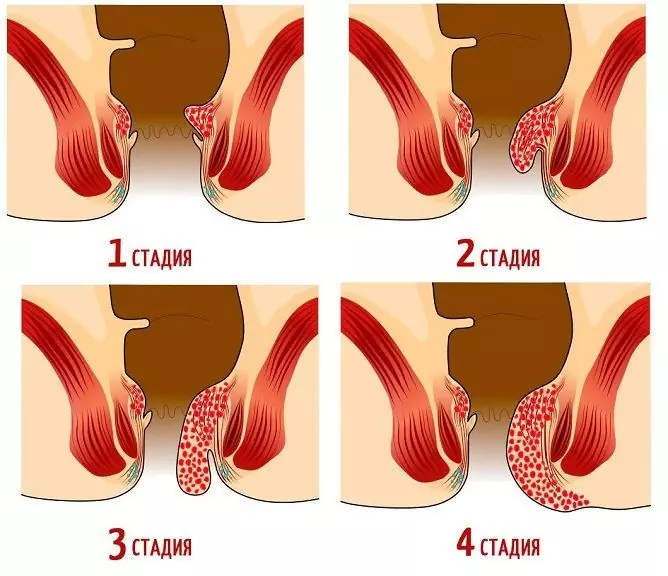
There are 4 stages of the course of hemorrhoids:
- It is characterized by an increase in hemorrhoids, itching, bloody discharge during bowel movements - from time to time there is blood in the stool or on toilet paper.
- The prolapse of hemorrhoids joins during bowel emptying or physical exertion. Bleeding from the anus is moderate, the prolapsed hemorrhoids are reduced spontaneously or with a finger.
- Hemorrhoids fall out even with slight physical exertion, do not spontaneously adjust, only manually. Bloody discharge becomes more noticeable and frequent, the patient feels heaviness, swelling of the anus.
- Hemorrhoids are constantly falling out, cannot be repositioned, frequent and profuse bleeding, pain, inflammation of the tissues around the anus. Anemia develops due to constant bleeding.
The choice of treatment method depends on the stage of hemorrhoids. In the early stages, non-surgical methods of treatment are used - ligation of hemorrhoids with latex rings, infrared photocoagulation, sclerotherapy, vascular ligation. To relieve the symptoms of hemorrhoids, local anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed in the form of ointments and rectal suppositories, which help stop bleeding and avoid pain during bowel movements. It is recommended to change your lifestyle, including diet, and also give up bad habits. Strong physical activity is contraindicated.

The greater the stage of hemorrhoids, the more significant and more frequent the bleeding
If in the early stages hemorrhoids were not diagnosed, and also if the treatment for one reason or another did not have the desired effect, the disease gradually becomes more complicated and becomes chronic. In the later stages, they resort to surgical intervention.
Anal fissure
Symptoms similar to hemorrhoids have another lesion of the lower part of the intestine - a crack in the anus. It can be a consequence of trauma to the intestinal mucosa with hard feces in chronic constipation, infectious diseases (syphilis, gonorrhea, AIDS), leukemia and other pathologies leading to a deterioration in the blood supply to the rectal mucosa. The development of anal fissures is also promoted by unhealthy diet, leading to constipation, alcohol and tobacco abuse, anal sex, and a sedentary lifestyle. This disease is more common in women.
Anal fissures are acute and chronic. Acute anal fissure usually results from trauma to the rectum. It does not require any special treatment and heals within a few weeks.
Chronic anal fissure tends to progress.
In the absence of adequate treatment, its depth is constantly increasing. Her symptoms:
- severe pain during and after the act of defecation;
- swelling of the anus;
- spasm of the anal sphincter associated with inflammatory damage to the nervous tissue.
Crohn's disease
Crohn's disease is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by damage to all layers of the digestive tube, the formation of ulcers and scars of the mucous membrane, and inflammation of the regional lymph nodes. Perforation of ulcers is possible, which leads to the formation of fistulas and abscesses.
Crohn's disease can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract, including the oral cavity, but its most common localization is the end of the small intestine, the ileum. This disease develops in both children and adults. The symptoms of Crohn's disease are similar to those of ulcerative colitis, which complicates the diagnosis. It is characterized by:
- stomach ache;
- persistent or nocturnal stool disorder;
- bloating, rumbling of the abdomen;
- streaks of scarlet blood and mucus in the stool;
- false urge to defecate;
- vomiting that leads to dehydration;
- signs of general intoxication - fever, sudden weight loss, lack of appetite, general weakness and apathy;
- anemia;
- inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eyes and mouth;
- inflammation in the perianal region;
- joint pain;
- enlargement and soreness of the lymph nodes.
The admixture of blood in the feces can be latent; to detect it, an occult blood test is prescribed.
Colorectal cancer
Colorectal cancer can be asymptomatic for a long time, in such cases, the tumor is detected by chance during a dispensary examination. A screening study that allows diagnosing bowel cancer at a relatively early stage is the analysis of feces for occult blood - it is the appearance of an admixture of blood in the feces that often serves as the first manifestation of the disease.
As the tumor progresses, the blood in the stool becomes more and more, it becomes visible in the stool in the form of veins, painful sensations during defecation join. In the future, bleeding increases, intestinal functions are disturbed, and pain appears. It is important to diagnose cancer at an early stage, therefore all patients at risk (people with a family history of colorectal cancer, as well as all people over 50) are recommended to have a fecal occult blood test once a year.
What to do if blood is found in the stool
With repeated appearance of blood in the feces, you need to consult a doctor - a therapist, proctologist or gastroenterologist. If necessary, a gastroenterological examination will be prescribed, a consultation with an oncologist, infectious disease specialist or surgeon.

In case of significant discharge of blood with feces, as well as if the blood in the feces is accompanied by a rapid deterioration in the general condition, an ambulance should be called.
You should immediately seek medical help if the appearance of blood in the stool is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- an increase in body temperature to febrile values;
- intense abdominal pain, regardless of the department;
- other bleeding, such as from the nose;
- subcutaneous hemorrhages, hematomas;
- general deterioration of health, impaired consciousness, weakness;
- nausea, vomiting, blood in the vomit.
Also, urgent medical attention is needed when the bleeding does not stop for a long time and there is a threat of large blood loss.
When blood appears in the feces of an adult or a child, one should not self-medicate - this will not lead to recovery, it will only increase the risk of developing severe complications.
YouTube video related to the article:

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.