- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
First aid for a tick bite

The danger of ticks is that these blood-sucking insects are carriers of many infections, both bacterial and viral, among which the most dangerous are hemorrhagic fevers, encephalitis and borreliosis.
The traditional habitat of ticks is woodland, the greatest activity is observed in the warm season, from about mid-spring to mid-summer. During this period, you need to be especially careful when visiting the forest - it is best to wear closed clothes.
If, nevertheless, trouble did occur, you should know how to properly provide first aid in order to minimize the possible danger. It should be remembered that severe infectious diseases that are transmitted by ticks appear some time after the bite, and this time can vary significantly - from several days to several weeks. Only when no unpleasant symptoms appeared within two months after the tick bite, it can be argued that the danger has passed.
First aid measures for a tick bite
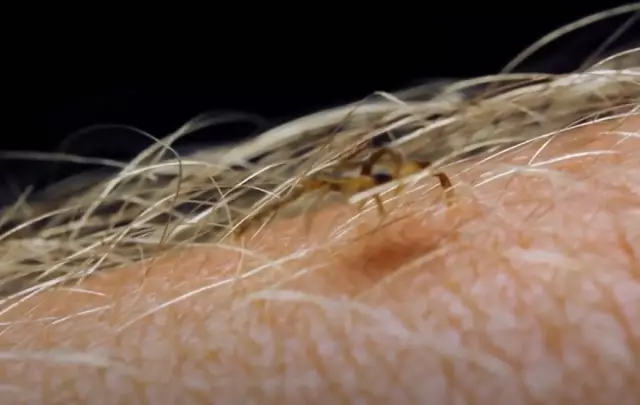
The tick bite is insidious in that it is often not detected immediately, since by itself it does not cause any sensations, all the troubles begin later. As a rule, a person discovers a sucked tick on himself - the bite can last from 15 minutes to several hours.

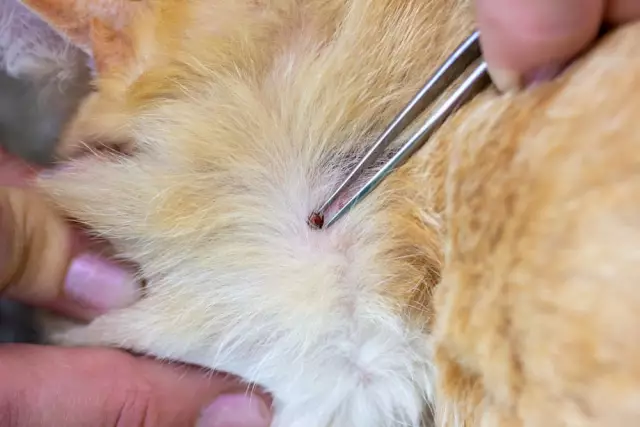
The first thing to do is remove the tick. This should be done very carefully, trying not to crush the insect, since in this case the risk of infection increases many times over. To remove the tick, you can use medical tweezers, a special device sold in pharmacies, or a loop made yourself from thread. It is necessary to try to grab the insect closer to the head, remove it slowly, pull it perpendicular to the skin, while making swinging or slightly rotating (unscrewing) movements. The removed tick must be placed in a small glass container with water, equipped with a tight-fitting lid.
After the insect has been completely removed, the wound is washed with soap and water, then treated with an antiseptic. If the proboscis of the tick breaks off and remains in the skin, it should not be picked out; after a while - usually it takes several days - it will come out on its own. The bite site is treated in the same way.
Attention! Contrary to the often described so-called folk methods, you cannot drip oil, alcohol or any other liquid onto the tick, and also cauterize it so that its breathing becomes impaired and it falls off on its own. In this case, the risk of infection is extremely high, since when breathing is disturbed, the insect secretes saliva into the wound, which, quite possibly, contains a huge number of pathogens.
A tick bite, in addition to a wide variety of diseases, can cause a fairly strong allergic reaction. It manifests itself in edema at the site of the bite, reddening of the skin, the appearance of itching and / or rash. Symptoms range from mild to very severe, up to life-threatening Quincke's edema (swelling of the upper respiratory tract that leads to respiratory failure). Therefore, at the first signs of an allergic reaction, as a first aid measure, it is necessary to give the victim an antihistamine (Loratadin, Suprastin, Diazolin, Tavegil, etc.).
First aid provided, what to do next?
If the region in which such a case occurred is classified as unfavorable in terms of the epidemiological situation in relation to ticks, for example, cases of tick-borne encephalitis or other infectious diseases transmitted by them are known, then immediately after first aid is provided, it is necessary to take the extracted insect to the laboratory for analysis. The addresses of laboratories in Russia can be found in Rospotrebnadzor. Usually, the results of the study are ready on the same day or the next, and depending on them, a decision is made on further actions.
It should be borne in mind that only slightly more than 10% of ticks are carriers of viruses and / or bacteria, so the chances that the insect will turn out to be sterile, and first aid measures can be limited, are quite high. If it is found that the tick contains pathogens of any disease, and even more so several, it will be necessary to seek medical help and get vaccinated.
If there is no possibility of attributing the tick to the analysis, then the health of the victim should be monitored. In the event that the signs of inflammation at the site of the bite have disappeared within 1-2 days, the likelihood of developing any pathology is considered minimal. However, if in 2 days redness and swelling remain at the site of the bite, and even more so if they increase, it is necessary to consult a doctor immediately.
Body temperature should be measured and recorded for 10 days after the bite. An increase in temperature during this period may indicate the onset of an infectious disease, in which case it is also necessary to seek medical help.
Some diseases, which are carried by ticks, can appear long after the bite - for example, borreliosis develops after 2-3 weeks, so during this time it is necessary to be vigilant. If any abnormalities in health appear (weakness, fever, spots on the skin, stiff neck muscles, headache, etc.), you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.