Diseases
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Dizziness is an unpleasant sensation of objects moving around
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
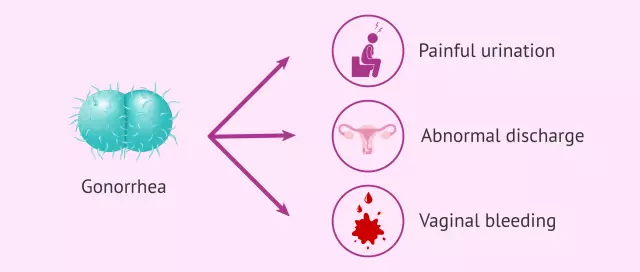
Gonorrhea is an infectious disease in which the pathogen is transmitted sexually. The main treatment for gonorrhea in women is antibiotic therapy. The latest generation antibiotics are used
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Gonorrhea, which is common in both men and women, is caused by streptococci. With a timely diagnosis and adequate treatment, the disease does not pose a serious danger
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Purulent otitis media is an infectious and inflammatory disease in which the structures of the middle ear are affected. With inadequate therapy, the risk of complications is high
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Altitude sickness is a type of altitude sickness, a painful condition that develops when climbing to great heights
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
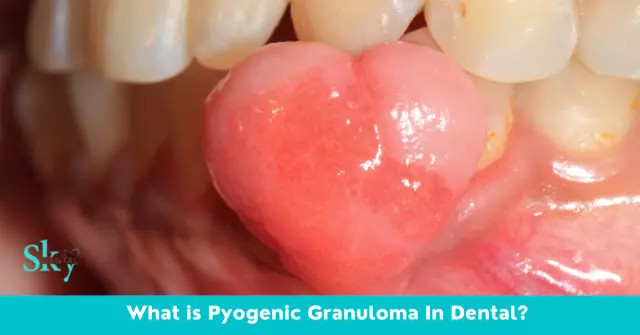
A tooth granuloma is a localized area of inflamed tissue of small size or a small (about 0.5 cm in diameter) nodule in the root area
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
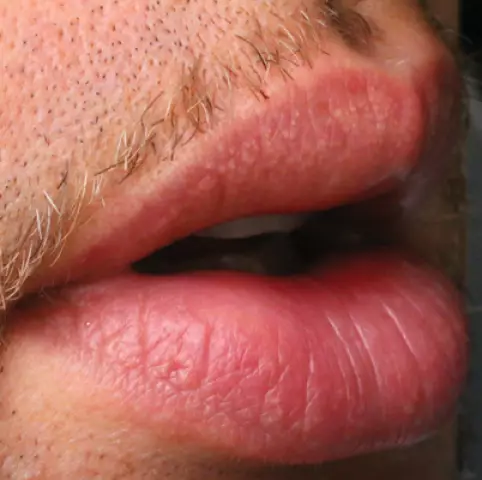
Fordyce granules appear on the skin as light pimples in the genitals, nipples, groin, mucous membrane of the mouth and lips. Fordyce granules are not transmitted either sexually or with any other type of contact and are considered the norm
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Gonorrhea is a common sexually transmitted disease that often leads to chronic prostatitis and male infertility
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
A granuloma is a focal spread of inflammation in the cells of young connective tissue. It looks like a small knot
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Granular pharyngitis is one of the varieties of the inflammatory process in the pharynx, which can develop both independently and against the background of other diseases
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
The disease of angina pectoris is not as dangerous as other heart diseases, but if adverse factors coincide, it can lead to serious complications and even death of a person
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Nail fungus is one of the most common sites for fungal infections. The nail plates of the lower extremities are more often affected
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Foot fungus is a group of highly contagious infectious diseases of smooth skin of the feet, often complicated by nail damage caused by dermatophyte fungi
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Chest osteochondrosis is a chronic disease of the spine. Its symptoms are similar to a number of medical conditions
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
A hernia of the white line of the abdomen is a pathological condition in which the abdominal organs protrude through the cracks of the aponeurosis along the midline of the abdomen
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
A hernia of the esophagus is a gastroenterological disease characterized by displacement of anatomical structures from the abdominal cavity into the chest cavity
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
A hernia of the stomach is a pathological condition in which there is a protrusion of the esophagus and stomach from the abdominal cavity to the chest cavity
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Schmorl's hernia is a partial prolapse (indentation) of the cartilaginous substance of the intervertebral disc into the spongy part of the body of the adjacent vertebra. The hernial protrusion does not compress the substance of the spinal cord, blood vessels or nerve roots - this is how Schmorl's hernia differs from a true intervertebral hernia
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
A hernia of the lumbar spine is a protrusion of the nucleus pulposus outside the vertebrae with a high risk of damage to the structures of the spinal canal
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Pathological processes in the body, in which there is an intracavitary protrusion and infringement of any organs, are collectively called "hernia". In most cases, the treatment of a hernia consists of a surgical excision
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
A hernia of the cervical spine is a disease in which degeneration and protrusion of the cervical intervertebral disc occurs beyond its anatomical limits
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Schmorl's hernia - pushing the own tissue of the intervertebral disc into the spongy bone of the vertebral body (intraspongy protrusion) through the border hyaline plate separating the base of the vertebra from the body of the disc
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
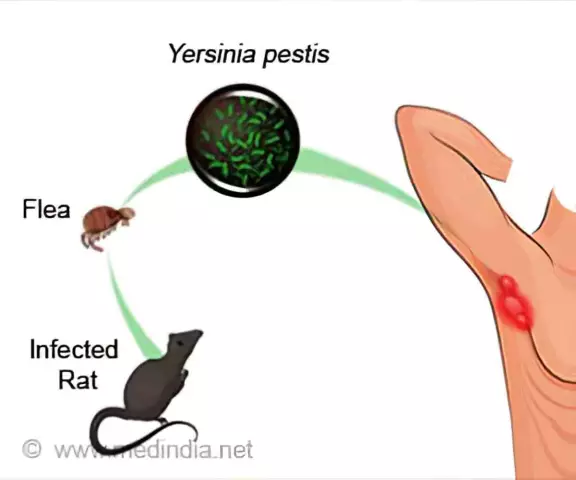
Yersiniosis is an infectious disease characterized by a predominant lesion of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as generalized damage to the skin, joints, other systems and organs
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Excess iron is a pathology in which an increased iron content is noted in the human body
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
An excess of iodine is a disease no less dangerous than its lack. More common in people employed in iodine production
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Excess zinc - poisoning with zinc derivatives, the acute form of which is treated in a hospital with unithiol
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Excess copper usually results from eating foods with an increased concentration of this element. Treatment consists in the use of drugs that remove copper from the body
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Idiocy (idiocy) is the most severe degree of mental retardation (oligophrenia), which can be caused by both congenital and acquired factors. The incidence is approximately the same among men and women. Idiocy is characterized by a mental defect that is present from birth or early childhood
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Hiccups - a human condition characterized by a violation of the function of external respiration
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Heartburn can occur for a variety of reasons, therefore, if it bothers you constantly, you need to find out the cause and undergo etiotropic treatment
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
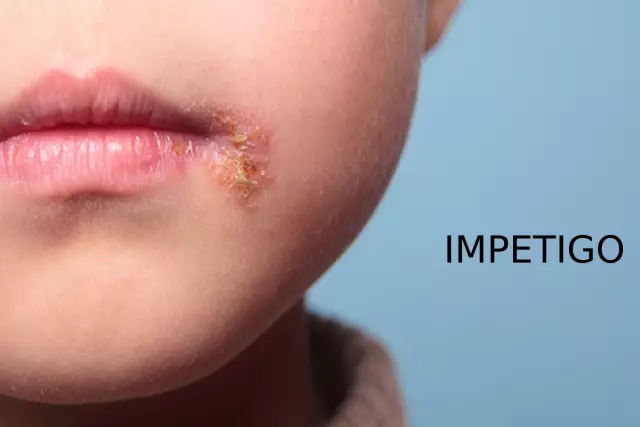
Impetigo is a skin disorder that mainly occurs in children and can be transmitted through household items, toys, and other objects. Untreated impetigo leads to serious complications - nephritis, myocarditis and other diseases
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Ileitis is an inflammatory disease that affects the ileum and can be acute or chronic. The main importance in treatment is given to proper nutrition
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Intussusception of the intestine (intussusception intestinal obstruction) is one of the types of intestinal obstruction, in which one part of the intestine is inserted into the lumen of another. It occurs predominantly in infants and is one of the most common causes of intestinal obstruction in this age group, but also affects adults
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
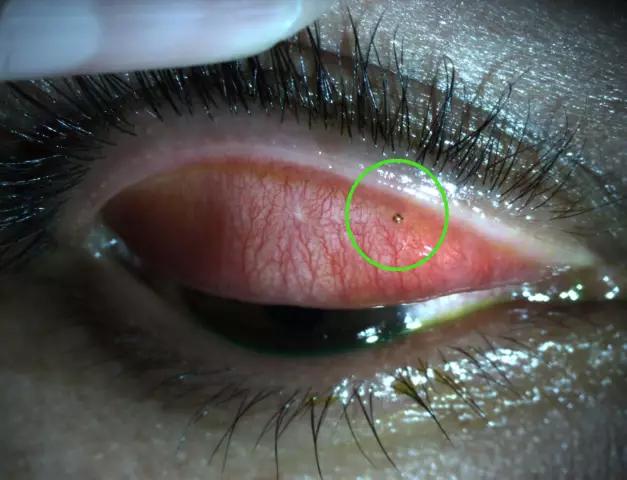
A foreign body in the eye is one of the most common causes of damage to its structures (cornea, sclera, conjunctiva)
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Imbecility (from Latin imbecillus - "weak", "insignificant") is the average severity of mental underdevelopment (mental retardation, dementia or oligophrenia), which is a consequence of the biological insufficiency of the structures of the brain, in which there is a delay in mental development and the formation of intelligence suffers, emotional and volitional spheres, behavioral reactions, speech
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Insulinoma is an insulin-producing tumor that causes the development of hypoglycemic syndrome
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Interstitial nephritis is a disease resulting in acute or chronic inflammatory lesions of the kidney tubules
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Kidney infarction is a rare disease in which necrosis of organ tissues occurs against the background of local circulatory disorders, followed by a decrease in its function
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Insulin resistance is a condition in which cells in the body become immune to the action of insulin
Last modified: 2025-11-02 20:11
Infectious erythema is a viral respiratory disease characterized by the appearance of a rash on the body