- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Impetigo
Brief description of the disease
Impetigo is a skin disease caused by streptococci and staphylococci. It is most often found in children's groups, since the body of any child does not resist infections as effectively as the body of an adult. In addition, children are more actively communicating with each other and exchanging various things, which also contributes to the rapid spread of the disease. When a diagnosis of impetigo is made, treatment should be prescribed as soon as possible, since the infection gives complications to the internal organs, causes diseases of the kidneys and the cardiovascular system.
Causes of the disease
The main provoking factors include microtrauma, maceration of the skin, ingestion of pathogenic strains of cocci. Depending on the cause, impetigo in children is divided into primary and secondary. In the latter case, the infection is a consequence of a complication of dermatoses, scabies, eczema, or head lice.
Impetigo - symptoms and clinical picture of the disease

Currently, doctors isolate streptococcal, staphylococcal and mixed forms of infection.
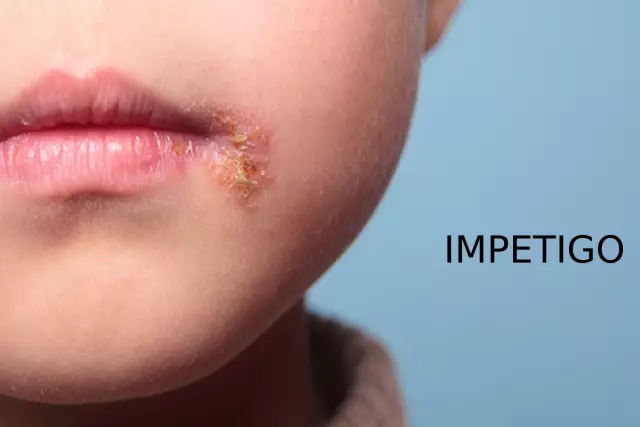
Streptococcal impetigo - the disease begins with the formation of bubbles (flikten), which slightly rise above the surface of the skin, measure from 2 to 10 mm and are surrounded by a narrow red rim. Rashes can be both scattered and crowded into separate groups. In the early stages, the contents of the bubbles are transparent, but later on it becomes cloudy and after a while dries up, forming light yellow crusts. After they fall off, only small, unpigmented spots remain. There are several types of streptococcal impetigo. In children, the most common so-called seizures. The main symptom of this form is the presence of a bubble in the corner of the mouth. Its contents quickly form a crust, which, when removed, reveals a bleeding surface. Seizures rarely cause severe pain. The only exceptions are cases when impetigo affects the oral mucosa.
Staphylococcal impetigo (foliliculitis) - with this form, the inflammatory process affects the hair follicles. A characteristic symptom of stephilococcal impetigo is the formation of many pustules on the hairy areas of the skin. They are surrounded by a pinkish border and grow up to 5 mm. in diameter. In milder forms of infection, the contents of the pustules dries out quickly, leaving behind a yellow crust that disappears after a few days. If deep staphylococcal impetigo is diagnosed in children, treatment should be immediate, since the pustules cause pain to the child, and after their opening and healing, noticeable scars remain.
Mixed (vulgar) impetigo - occurs when both streptococcal and staphylococcal infections are present in the body. With this form, the contents of the vesicles (flikten) are both transparent and purulent, and the ones formed after opening the crust are more massive than with pure types of infection. Vulgar impetigo in children and adults is usually located on the face, but often the pathological process also affects the skin of other parts of the body. As a rule, children and young women get sick. Sources of infection are both strains and underwear or any other personal items. If a patient has mixed impetigo, treatment is necessary, since more and more conflicts appear on the body, and the infection process can easily spread to a very large area of the skin.
Impetigo - treatment of the disease in children and adults
In most cases, the infection proceeds without complications and is quite amenable to outpatient treatment. The main tactic in this case is the refusal to wash the damaged skin areas and the use of various medicinal ointments and disinfectant solutions (salicylic or camphor alcohol). New bubbles are opened immediately after they appear. Then they are treated with brilliant green and ointments, which include antibiotics. This procedure must be repeated for 7-10 days 3-4 times a day until the conflict disappears completely. No bandage is applied to the skin. After the end of the course of treatment, the damaged areas are regularly treated with alcohol to prevent recurrence of the disease.
In severe forms of impetigo in children, treatment is carried out using antibiotics, which are taken by mouth or through intramuscular injections.
For the entire period of treatment, the child's communication with peers should be limited and the rules of personal hygiene should be observed (but you should not wash the damaged areas). With a responsible, correct approach, the prognosis is usually favorable. Untreated impetigo leads to the formation of new conflicts and the development of complications (nephritis, myocarditis and some other diseases).
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!