- Author Rachel Wainwright [email protected].
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Gonorrhea in men
The content of the article:
- Causes and risk factors
- Forms
- Symptoms of gonorrhea in men
- Diagnostics
- Treatment of gonorrhea in men
- Forecast
- Complications and possible consequences
- Prevention
Gonorrhea in men is a common venereal disease of an infectious and inflammatory nature that affects the cylindrical epithelium of the mucous membranes of the urethra and paraurethral glands. Less commonly, there is a lesion of the pharynx, soft palate, tonsils, rectum and conjunctiva of the eyes.
Causes and risk factors
The disease is caused by gonococci - gram-negative diplococci of the species Neisseria gonorrhoeae, which are localized on the surface of epithelial cells, erythrocytes and sperm, in the intercellular and subepithelial space. Also, bacteria can be located inside leukocytes, epithelial cells and other microorganisms, especially Trichomonas.
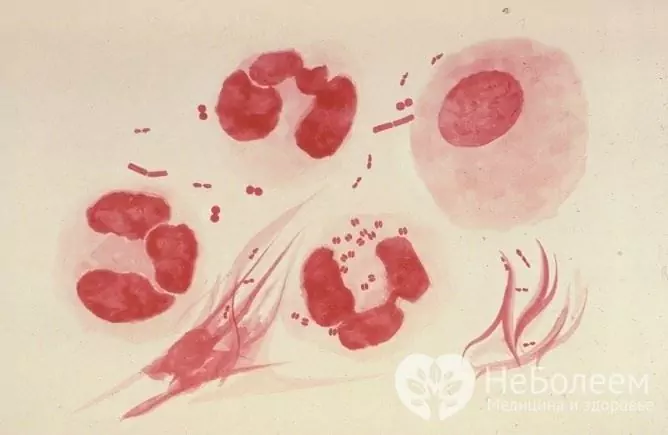
Source: wikizero.com
Infection with gonorrhea in men occurs mainly through sexual contact; the probability of infection with a single contact with a sick woman is 25-50%. Susceptibility to gonococcal infection increases with prolonged intercourse, ejaculation and during menstruation in a partner. Contact transmission of gonorrhea is not typical for men.
The peak incidence occurs at the age of maximum sexual activity - from 20 to 30 years. After infection, the body produces antibodies to gonococci, but immunity to gonorrhea does not develop.
Forms
Gonococcal infection is characterized by a wide variety of manifestations. Depending on the localization, several forms of gonorrhea are distinguished:
- gonorrheal urethritis (gonococcal infection of the lower genitourinary system) with and without complications;
- ascending gonorrhea - gonorrheal pelviperitonitis and damage to the upper urinary tract (it is extremely rare in men);
- gonococcal infection of the anorectal region (gonorrheal proctitis);
- gonococcal pharyngitis, tonsillitis and stomatitis;
- gonococcal infection of the musculoskeletal system (gonarthritis);
- gonococcal eye infection (blenorrhea); etc.
Most often, gonorrhea in men occurs in the form of urethritis. The infection spreads along the entire length of the genitourinary tract, capturing the seminal vesicles, prostate, testicles and epididymis; in severe cases, the peritoneum is affected.
Gonorrheal pharyngitis, stomatitis and tonsillitis result from infection during genital-oral contact; gonorrheal proctitis is more common in people of non-traditional sexual orientation. Extragenital foci appear due to the generalization of the infectious process. The joints are the first to be affected, less often gonorrheal meningitis or endocarditis develops.
Depending on the duration of the course, fresh and chronic gonorrhea are distinguished. Fresh gonorrhea in men is diagnosed with the manifestation of the disease for less than two months, the chronic form - with the persistence of symptoms or alternating exacerbations with remissions for two months or more, as well as with an unknown duration of the disease.
Fresh gonorrhea, in turn, is subdivided into acute, subacute and torpid, that is, erased or asymptomatic. In the chronic form of the disease, gonococci often form L-forms, which have partially lost their antigenic properties and therefore are not sensitive to treatment. When infected with strains of gonococcus that produce β-lactamase, atypical forms of gonorrhea that are resistant to antibiotics of the beta-lactam series develop. There are also known cases of gonococcal carriage, when the ability to spread infection is not accompanied by the development of pathological processes in the host's body.
Symptoms of gonorrhea in men
The clinical picture of primary gonococcal infection depends on the site of entry of the pathogen. With gonorrheal urethritis, patients complain of frequent urge to urinate, dysuric phenomena (pain, stinging and burning when urinating), clouding of urine and profuse purulent or purulent-serous leucorrhoea. With a torpid course of gonorrheal urethritis, dysuric and exudative phenomena are weak and pass without treatment after a few days, but they can return under the influence of provoking factors - the use of alcohol and sexual activity.
Gonorrheal pharyngitis is characterized by a sore throat, difficulty swallowing, swelling and redness of the mucous membranes of the soft palate and tonsils. Gonorrheal proctitis is most often asymptomatic, occasionally itching or burning in the anorectal region, purulent discharge from the anus, tenesmus and painful bowel movements can be felt. As a rule, the incubation period of gonorrhea in men with a primary infection lasts from 3 to 15 days, with mixed infections - about a month or more.
Chronic gonorrhea in men usually takes on a protracted nature with periodic exacerbations. Patients are worried about the frequent urge to urinate at night, scanty mucous discharge from the urethra in the morning; in the first portion of urine, threads of exudate secreted from the excretory ducts of the glandular lobules are found. Spattering of urine and reduced jet range indicate adhesions in the urethra. At the same time, sexual disorders are observed: premature ejaculation, erectile dysfunction, anorgasmia and decreased libido. When the inflammatory process spreads to the seminal vesicles, prostate and Cooper's glands, patients are pursued by pain along the urethra and in the head of the penis, in the perineum, pubis and sacrum; paresthesias, discomfort while sitting and a foreign body sensation in the rectum appear.
Diagnostics
Gonorrhea in men is diagnosed by a venereologist or urologist on the basis of clinical examination, ureteroscopy, medical history and laboratory results. For a fresh gonococcal infection of the lower genitourinary system, a picture of acute anterior urethritis is characteristic: hyperemia and edema of the sponges of the urethra, edema of the mucous membrane, thickening and smoothing of folds. Torpid forms are manifested by both anterior and total urethritis with a general smoothing of the symptoms of the inflammatory process and moderate exudation. In chronic gonorrhea in men, during urethroscopy, congestive hyperemia and infiltration of the urethral sponges are found.
Currently, gonorrhea occurs mainly as a mixed infection. As a result, pronounced signs of gonorrhea in men are rare. To confirm the diagnosis, laboratory tests are required - bacterioscopy and bacterial culture of scrapings and swabs from the urethra and rectum. At the same time, diagnostics of other sexually transmitted diseases is carried out: syphilis, HIV, hepatitis B and C, trichomoniasis, chlamydia, etc.
The bacterioscopic method is most effective for fresh gonorrhea. After drying and fixation, biological products are stained with methylene blue and Gram, however, due to the high variability, it is not always possible to detect the pathogen by bacterioscopy.
Erased and asymptomatic forms of gonorrhea are diagnosed by bacterial culture on artificial media. To obtain reliable results, the purity of the material and strict adherence to the biomaterial selection technique are important. In case of contamination of biological samples with urethral microflora, selective media with antibiotics are used.
Sometimes gonorrhea is diagnosed using polymerase chain reaction, sometimes they turn to enzyme immunoassay and immunofluorescence methods.
If fresh gonorrhea is found in a man, an examination of all his sexual partners is shown, intimate contacts with whom were carried out for 14 days before the onset of symptoms of the disease. In the case of an erased or asymptomatic course of gonorrhea, women and men who have had intimate relationships with the patient for two months preceding the onset of symptoms are examined. If the patient lives with female children, they are examined to exclude the transmission of the disease by contact and everyday life.
Treatment of gonorrhea in men
The treatment strategy for gonorrhea in men depends on the form and duration of the disease. With a fresh uncomplicated gonococcal infection of the lower urinary tract, a single intramuscular or oral administration of an antibiotic is sufficient.
Complicated gonorrhea requires longer treatment. In this case, antibiotics are administered intravenously or intramuscularly every day, every 12 hours or every 8 hours, depending on the drug, for a week. Etiotropic treatment of gonorrhea in men in acute cases must be continued for at least 48 hours after the disappearance of symptoms. For mixed infections, another antibiotic or antiprotozoal drug is added to the scheme. At the time of antibiotic therapy, the patient should completely exclude alcohol and refrain from sexual intercourse. In order to increase the effectiveness of antibiotic therapy, it is recommended to use a bacteriological method to control the sensitivity of the pathogen to the prescribed drugs.
In case of subacute, torpid and chronic gonorrhea in men, in addition to general antibacterial therapy, local remedies are prescribed - instillation of antiseptics into the urethra, and in case of rectal damage - microclysters with antiseptic solutions and anti-inflammatory suppositories. In the absence of an exacerbation, physiotherapeutic methods can be used:
- laser therapy;
- inductothermy;
- magnetotherapy;
- UHF;
- ultraviolet irradiation;
- electrophoresis and phonophoresis.
In some cases, specific and non-specific immunotherapy is carried out: patients are injected with a gonococcal vaccine, immunomodulators are prescribed, and sometimes autohemotherapy is performed. Immunotherapeutic treatment begins either after the acute inflammatory process has subsided, or before a course of antibiotics for subacute, torpid and chronic course of the disease.
To control the effectiveness of therapeutic measures, bacteriological and bacterioscopic studies are repeated 7-10 days after the start of treatment; serological - after 3, 6 and 9 months. The decision to use provocative methods of monitoring the effectiveness of treatment is made on an individual basis. The provocation effect is achieved in the following ways:
- lubrication of the urethra with 1-2% silver nitrate solution;
- exposure to high-frequency electromagnetic field;
- eating spicy and salty food or alcohol before taking biomaterial;
- the introduction of a gonococcal vaccine;
- combined provocation - a combination of several of the above methods.
Forecast
With timely initiation of treatment and adequate therapeutic measures, fresh gonorrhea in men is cured without consequences for health and reproductive function. The transition of the disease into a chronic form, the addition of other infections, the appearance of complications, attempts at self-medication and, in particular, the unauthorized intake of antibiotics increase the likelihood of developing infertility. In the case of generalization of the infectious process, the prognosis is cautious.
Complications and possible consequences
A fresh gonococcal infection, neglected, spreads along the entire length of the urethra, provoking inflammatory diseases of the urogenital tract. Typical complications of acute gonorrhea include:
- epididymitis and deffenditis - inflammation of the epididymis and vas deferens;
- funiculitis - the spread of the inflammatory process to the entire vas deferens;
- periorchitis - an infectious and inflammatory lesion of the testis membrane, externally manifested by a sharp increase in the scrotum, smoothing the boundaries between the testicle and the epididymis;
- prostatitis - inflammation of the prostate gland;
- cooperite - an inflammatory lesion of the cooper's gland with the formation of a dense painful pea-shaped node;
- spermatocystitis, or vesiculitis - inflammation of the seminal vesicles;
- paraurethritis - exudative inflammation of the paraurethral glands. In patients, there is a narrowing of the lumen of the urethra and the appearance of false abscesses due to clogging of the paraurethral passages with purulent exudate;
- cavernitis - the formation of an inflammatory node in the corpus cavernosum, causing a curvature of the penis in a state of erection.
Acute inflammatory processes in the organs of the male reproductive system are often accompanied by an increase in body temperature and general intoxication of the body. The appearance of a twitching pain may indicate the development of an abscess; in such cases, you should immediately seek medical attention.
With chronic gonorrhea, men develop chronic inflammatory diseases of the vas deferens. Chronic vesiculitis is manifested by a dull pain along the urethra and painful sensations during the ejaculation process, radiating to the sacrum and lower back. Chronic cooperitis provokes severe soreness of the rectum, discomfort when sitting on hard stools, and difficulty in defecation. For men planning paternity, chronic prostatitis is especially dangerous, which causes spermatogenesis disorders, which lead to a decrease in mobility and, as a result, the fertilizing ability of sperm.
Prevention
Personal prevention of gonorrhea in men involves adherence to sexual hygiene: it is necessary to avoid unprotected contacts and casual relationships.

Source: likar.info
To avoid the spread of infection, laboratory diagnostics of gonorrhea is included in the program of routine medical examinations for food industry workers, medical personnel and employees of child care facilities.
YouTube video related to the article:

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!