- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2024-01-15 19:51.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Warts on hands
The content of the article:
- What it is
- Causes of the appearance of warts on the hands
-
Varieties
- Ordinary (vulgar)
- Flat (youth)
- Diagnostic methods
- What should the patient do
-
Treating warts on the hands
- Cryodestruction
- Electrotherapy
- Laser therapy
- Cantharidin
- Bleomycin
- Surgical removal
- Antiviral therapy
- Folk remedies: help or not
- Prognosis and complications
- Video
Warts are small growths that are localized in different areas of the skin. This is a widespread pathology, according to various sources, about every 3rd adult and every 2nd child are sick. The cause of their appearance is a viral infection (human papillomavirus). Warts on the hands are one of the most common localizations. Not all formations can be removed; in some cases, the growths pass on their own. To get rid of pathology, minimally invasive methods of treatment are used.

Vulgar warts are dense nodules protruding above the skin.
What it is
Warts are benign neoplasms that are not prone to malignancy. They can appear on any part of the skin: face, palms, fingers, soles, genitals. Two types of neoplasms appear on the hands - ordinary and flat.
Warts on the hands can be single or multiple. They are characterized by the following signs:
- the color can be flesh, brown, or grayish;
- size varies from 3 mm to 1.5 cm;
- usually look like a small nodule (seen in the photo).
Normally, their appearance is not accompanied by any symptoms. The formation is painless, sometimes itching of the skin may appear.
Causes of the appearance of warts on the hands
The cause of the pathology on the hands is infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV). There are several ways the infection can spread:
- direct contact when shaking hands, touching;
- indirect infection through common items: door handles, handrails, buttons in the elevator;
- household contamination, when several people use one towel or other personal hygiene item.
It usually takes several months from infection to the first manifestations of pathology, during which time the wart grows to 0.5-1 cm.
Not all people who come into contact with the source of infection develop warts. In many ways, the likelihood of infection depends on the state of immunity. Predisposing factors include:
- any somatic diseases that affect the state of the immune system;
- diabetes;
- dermatological diseases;
- very dry skin of the hands;
- increased sweating of the palms.
The onset of pathology is also facilitated by the frequent trauma to the skin of the hands: the habit of biting nails, biting fingers, and tearing off burrs. Non-compliance with personal hygiene rules plays an important role.
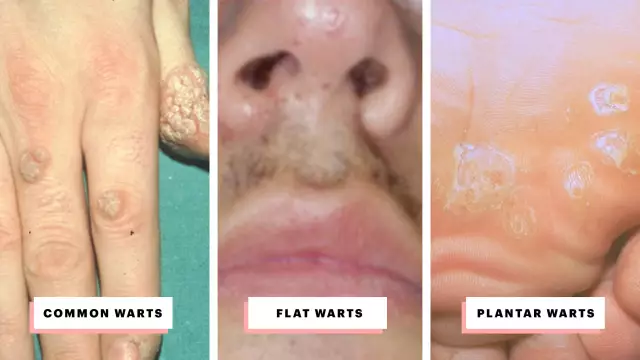
Varieties
2 types of neoplasms appear on the hands: ordinary (vulgar) and flat. The differences lie in location, shape, size and treatment approach.
Ordinary (vulgar)
Common warts are the most common form of the disease. They are found mainly in adults, but children can also get sick. Localized on the fingers, the back of the hand, in the interdigital spaces.
What they look like:
- size 0.5-1.5 cm;
- rise above the skin;
- more often single;
- have an uneven, rough surface.
Flat (youth)
This is a relatively rare form of the disease, occurring in 4-5% of cases. Flat warts occur mainly at a young age, hence their other name - youthful. They are localized on the dorsum of the hands. Formations are usually multiple, appear in groups. They are small nodules up to 0.5 cm in size, which almost do not rise above the surface of the skin.

Flat warts are also called juvenile
Diagnostic methods
Clinical data are usually sufficient for diagnosis. The shape and size of the formation, as well as the absence of unpleasant sensations in the affected area, are taken into account. The doctor may order additional tests to rule out malignant tumors and other dermatological diseases. What studies can be assigned:
| Diagnostic method | Indications for the study, explanation |
| Dermatoscopy | Allows you to examine the skin formation under 10x magnification. With the help of dermatoscopy, it is possible to assess the edges of the neoplasm, symmetry or asymmetry, color, surface and other parameters. The study is carried out for all patients to determine whether it is necessary to remove the formation or not. |
| Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) | For determining HPV infection. With the help of a study, you can not only confirm or deny the presence of infection, but also determine the type of HPV (carcinogenic, non-carcinogenic). |
| Histological examination | The main diagnostic method. Postoperative histological examination allows a diagnosis to be made with a probability of 100%. |
What should the patient do
Not all warts can be removed. In children, such formations in most cases pass on their own, without requiring medication. They are also rarely dangerous in adults.
In what cases surgery may be required:
- education begins to grow rapidly;
- the number is increasing;
- frequent trauma occurs;
- soreness;
- there are signs of malignancy (asymmetry, rapid growth, etc.).
In any case, the decision on removal should be made by the doctor after a complete examination of the patient.
Treating warts on the hands
There are many ways to get rid of pathology. The choice depends on several factors: the general condition of the body, the number of formations, their size and variety. The essence of the treatment is to remove the wart using special drugs, laser, liquid nitrogen, electric current. Given the viral nature of the disease, antiviral treatment is additionally prescribed, which is aimed at preventing relapse.
Cryodestruction
Cryodestruction is a method of treatment based on exposure to liquid nitrogen. Exposure to low temperatures leads to freezing and tissue death.
Freezing is carried out using a special applicator. How is the treatment going:
- the wart is treated with an antiseptic solution;
- an applicator is applied perpendicularly to its surface with slight pressure;
- the exposure time depends on the size of the formation and is 5-30 seconds.
The formation under the action of liquid nitrogen turns pale, becomes more dense. After 1-2 minutes, the freezing zone becomes red and swollen, then a small bubble appears, which lasts up to 1 week, gradually decreasing. A crust appears in its place, which is rejected after 1-2 weeks, leaving no noticeable scarring of the skin.
Cryodestruction for the treatment of warts is used most often, which is associated with a number of advantages of this method:
- ease of use and availability;
- painlessness;
- no postoperative scar.
The disadvantages of cryodestruction include the need to repeat the procedure, since complete destruction of the formation is rarely achieved in 1 session.

Cryodestruction is a minimally invasive and therefore popular method for removing warts
Electrotherapy
Electrocoagulation is a treatment that uses a surgical coagulator to remove the mass. Electrocoagulation is based on the action of an electric current. This treatment is used to remove vulgar warts.
How is the treatment going:
- local anesthesia is performed;
- with the help of a metal loop, to which a high-frequency current is supplied, the wart is removed;
- remote education is sent for histological examination.
The advantages of coagulation include a low risk of postoperative complications, since heating the tissues stops bleeding and the spread of infection.
Whether a scar remains after such treatment depends on the depth of the lesion.
Laser therapy
Removing warts with a laser is one of the most modern methods of treatment. Depending on the type of laser, this treatment is based on coagulation or evaporation.
Treatment is performed under local anesthesia. The wart is removed with a laser layer by layer, the duration of the procedure is 2-3 minutes.
Postoperative complications are extremely rare; a small depression remains at the site of removal of the formation.
Cantharidin
For treatment, you can use medications that have a cauterizing effect. Cantharidin can help get rid of warts on the hands. The substance, if in contact with the skin, causes burns and blisters. Cantharidin is applied directly to the dried wart for 24 hours.
Bleomycin
Another medication that can be used to treat pathology is Bleomycin. Bleomycin belongs to antineoplastic drugs. The substance is injected directly into the wart, which leads to its death.
Such treatment is effective, but it is not often used, which is associated with a high risk of complications.

Bleomycin is used to treat warts, but it has a high risk of complications, so only an experienced doctor should treat it
Surgical removal
The traditional method of getting rid of the disease is surgical excision of the formation. Treatment consists of a small operation under local anesthesia. Surgical excision is usually prescribed for large lesions when other methods are ineffective.
A scalpel or other surgical instruments may be used to remove the wart. After excision of the formation, cosmetic sutures are applied to the skin, which are removed on the 5-7th day. After removing the stitches, a small scar remains on the skin.
Antiviral therapy
Unfortunately, there are no specific drugs that would get rid of human papillomavirus infection. You can use local preparations in the form of creams and ointments: Aldara, Isoprinosine.
Folk remedies: help or not
For home treatment, folk remedies are often used: celandine juice, flaxseed oil, onions, rowan, thuja. Folk recipes are based on the treatment of affected areas with herbal remedies that have a cauterizing or destructive effect.
Treatment with folk remedies does not lead to a complete cure. Even if it comes out to cauterize the wart, after a while it will grow back. This treatment often leads to complications.
Prognosis and complications
The forecast is almost always favorable. In some cases, the warts go away on their own, more often they persist for a long time, but do not bring significant discomfort. An unfavorable prognosis is usually associated with the development of complications:
- ulceration;
- attachment of bacterial flora;
- damage to surrounding tissues;
- overgrowth.
Complications are relatively rare, usually associated with frequent trauma or improper treatment of the disease.
The biggest problem in the treatment of pathology is frequent relapses. Given the viral nature of the disease, surgical removal of the formations also does not guarantee a complete cure.
Video
We offer for viewing a video on the topic of the article.

Anna Kozlova Medical journalist About the author
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.