- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Nail fungus
The content of the article:
- Causes of nail fungus and risk factors
- Forms of the disease
- Symptoms of nail fungus
- Diagnostics
- Nail fungus treatment
- Possible complications and consequences
- Forecast
- Prevention
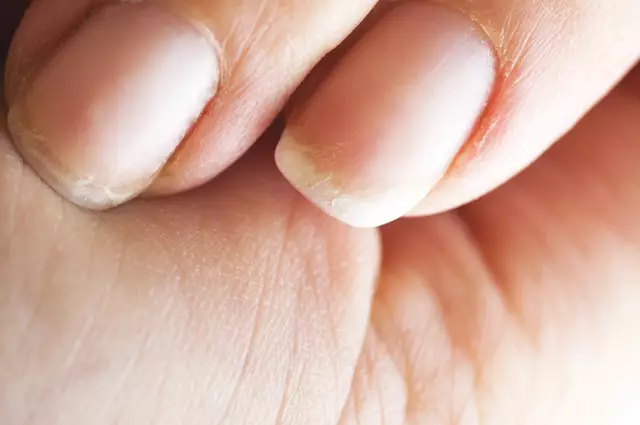
Nail fungus (nail mycosis, onychomycosis) is an infectious lesion of the nails on the hands and feet caused by pathogenic and opportunistic microscopic fungi, which leads to a change in the nail plate. The pathological process can affect both one and several nails on the upper or lower extremities, mixed variants of the lesion are also possible. Nail fungus is diagnosed in all age categories, regardless of gender. The prevalence of pathology depends on climatic conditions (the disease is more common in those climatic zones where there is a need to wear tight warm closed shoes for a long time). According to various sources, nail fungus is recorded in 10-20% of the population, and in the age group over 60 it occurs in about 30% of people. Fungus of the nails can accompany the fungus of the skin of the feet or hands.

Symptoms of nail fungus
Causes of nail fungus and risk factors
An infectious agent in nail fungus is pathogenic or opportunistic fungi. Most often, the causative agents of the disease are yeast-like and mold fungi, dermatophytes. The transmission of the pathogen can be carried out through a handshake, upon contact with objects contaminated with an infectious agent (most often when using personal hygiene items, shoes of an infected person), as well as in swimming pools, baths, showers, and other public places with high humidity. Microscopic fungi can be inactive on the surface of the skin and nail plates for a long time until favorable conditions for their development are created.

The causative agents of the disease are yeast-like, molds, dermatophytes
Risk factors contributing to the onset of the disease include:
- elderly age;
- phlebeurysm;
- flat feet;
- disorders of the functions of the endocrine and immune systems;
- limb vascular pathology;
- increased sweating;
- long-term use of drugs (hormonal, antibacterial, cytostatic);
- constant stressful situations;
- injury to nails and / or cuticles;
- wearing shoes that are too tight and / or of poor quality (impermeable to air, causing increased sweating);
- non-compliance with the rules of personal hygiene;
- nail extension;
- occupational hazards (military service, chemical, metallurgical, mining).
In addition, the lymphogenous spread of the infection in the body can become the cause of nail fungus.
Recurrences of the disease can be caused by the choice of inappropriate treatment for nail fungus, a violation of the therapy procedure, neglect of the doctor's recommendations, etc.
Forms of the disease
Nail fungus is classified according to several characteristics.
Depending on the morphological changes in the nail plates, the following forms of the disease are distinguished:
- normotrophic (the shape and size of the nail remain unchanged, but the color of the nail plate changes - spots and lines of white or yellowish color appear in the lateral parts of the nail);
- hyperkeratotic (the nail plate grows dull, there is a thickening of the nails and a change in their structure - the nail plate becomes compacted or loose, brittle nails are observed);
- atrophic (the nail plate becomes brown, the nail exfoliates from the nail bed, its dystrophy is noted);
- mixed.

The development of nail fungus
Depending on the localization of the lesion, the following forms of nail fungus are distinguished:
- superficial (the nail plate is practically unchanged, the spots on the nail visually resemble scattered powder);
- lateral (the pathological process affects one or two lateral surfaces of the nail);
- distal (the lesion begins at the free edge of the nail plate);
- distal-lateral (damage to the nail plate, subungual space and periungual space);
- proximal (damage to the nail plate at the base of the socket);
- total (the pathological process extends to the entire nail surface).
Also, nail fungus is subdivided into forms depending on the type of pathogen:
- dermatophytic;
- moldy;
- candidiasis.
Symptoms of nail fungus
The symptoms of nail fungus depend on the shape and severity of the disease. Fungus of toenails is observed more often (about 80% of cases), the nails on the hands are less often affected, in some cases, there is a combined lesion of the nails on the upper and lower extremities. The pathological process on the lower extremities usually begins with the first and / or fifth toes. Fungal lesions of the nail plates can be accompanied by an inflammatory process in the periungual space, the addition of a secondary infection, itching and hyperemia of the skin near the affected nail.
With the normotrophic form of the disease, stripes and spots of white or yellowish color appear on the nail plate, the nail shines, acquires a yellowish color at the distal edge, its thickness does not change.

Most often, the fungus affects the toenails
The hypertrophic form is characterized by a thickening of the nail plate, the nail crumbles, deforms. Initially, the nail acquires a yellowish color, then becomes a dirty gray color with transverse striation, loosened at the free edge. Over time, continuing to thicken, the nail can completely lose its flexibility, injure the finger. Also, nails often take on a beak-like shape. With the development of a hypertrophic form of nail fungus of the lower extremities, pain is often observed when walking. The pressure of the thickened nail on the nail bed also causes pain.
In the event of an atrophic form of nail fungus, the nail plate fades, becomes thinner, acquires a yellowish or gray color, spots and / or white stripes appear on it. The nail bed is partially exposed, covered with layers of crumbling horny masses.
In some cases, patients are diagnosed with a mixed form of nail fungus. Deformation of the nail plates, especially their thickening, creates difficulties in hygienic nail care.
In addition, the clinical picture of the disease has its own characteristics, depending on the type of infectious agent that caused the development of the pathological process.
In the case of the dermatophytic form of foot nail fungus, the disease debuts with the appearance of longitudinal stripes or yellow spots on the lateral edges of the nail plates. With nail fungus on the hands, spots and stripes are characterized by a lighter color (whitish or gray), they appear in the center of the nail plate. In some cases, the nail at the free edge may thicken, the nail plate is deformed.
In the candidal form of the disease, the pathological process begins with the posterior or lateral nail ridges, usually on the nails of the hands. The nail folds thicken, there is edema, hyperemia in the affected area. The nail plates become uneven, covered with transverse grooves, the nail collapses in the proximal part, becomes thinner from the lateral edges or in the distal part. Affected nail folds are usually painful on palpation, sometimes pus is released. In some cases, the nail plate is affected without the involvement of the nail fold in the pathological process.
In the case of the development of a moldy form of nail fungus, the color of the affected nail plate depends on the type of pathogen and can be yellow, blue, green, brown or black.
With a prolonged course of the disease, partial or complete destruction of the nail plate occurs.
Diagnostics
Primary diagnosis consists in collecting complaints and anamnesis. To confirm the diagnosis of nail fungus, a luminescent study is carried out (examination of the affected nails in the ultraviolet light of a Wood lamp), confocal laser scanning microscopy of scrapings from the affected areas, sowing of biological material on nutrient media. In case of suspicion of the presence of an oncological process in the subungual and / or periungual space, microbiological and histological laboratory studies are indicated.

To diagnose nail fungus, scraping is taken from the affected areas, sowing the biomaterial on nutrient media
Differential diagnosis is required with lichen planus, psoriasis, eczema, inflammation of the periungual ridge (paronychia), onychodystrophy, keratoderma, vegetative keratosis, photoonycholysis, as well as congenital pachyonychia and injuries.
Nail fungus treatment
The choice of a treatment regimen for nail fungus depends on the form of the disease and the degree of neglect of the pathological process.
For superficial damage to the nail plate, local treatment is usually sufficient. Patients are prescribed antimycotic, keratolytic creams, gels, sprays or varnishes, as well as patches based on antifungal drugs.
With deeper lesions of the nail with its partial detachment, systemic or combination therapy is indicated. Local treatment of nails is supplemented by oral administration of antimycotic drugs, drugs that improve blood microcirculation, in addition, if necessary, treatment of concomitant diseases is carried out.

With confirmed nail fungus, the patient is prescribed antimycotics
In case of complete nail damage, minimally invasive (for example, using a keratolytic plaster) or radical removal of the nail plate, followed by sanitation of the nail bed, antifungal and antiseptic dressings, as well as restorative treatment with vitamin complexes and gelatin solutions, is necessary.
In the course of further treatment, such physiotherapeutic procedures as diathermy, amplipulse therapy, UHF therapy can be used.
The criterion for the cure of nail fungus is the absence of clinical manifestations of the disease, as well as diagnostic confirmation of the absence of an infectious agent two and four months after the end of the course of therapy.
Patients are shown dispensary observation throughout the year with a frequency of examinations 1 time in 3 months.
Possible complications and consequences
The lack of the necessary treatment for nail fungus can lead to the further spread of the infectious process, a decrease in immunity, which, in turn, can cause an exacerbation of existing chronic diseases. Also, untreated nail fungus contributes to the development of eczema, dermatitis, urticaria, conjunctivitis, rhinitis, asthmatic bronchitis and bronchial asthma.
Forecast
With timely diagnosis of nail fungus and adequate treatment, the prognosis is favorable.
Treatment of advanced nail fungus is long-term. Relapses are observed in 40-70% of cases. In patients with concomitant chronic diseases, the prognosis of nail fungus in relation to recovery worsens.
Prevention
There are primary and secondary prevention of nail fungus. Primary prevention involves preventing the onset of nail fungus in healthy individuals. Secondary prevention is aimed at preventing the development of relapses of the disease.
For primary prevention, it is recommended:
- compliance with the rules of personal hygiene;
- refusal to put on someone else's shoes, walking barefoot in public places, trying on shoes on bare feet in stores;
- using only personal manicure and pedicure supplies;
- avoiding injury to the nails, in case of injuries to the nail plate, the damaged surface should be treated with an iodine solution, which will prevent the penetration of the fungus;
- timely access to a doctor if you suspect the appearance of a pathology;
To prevent recurrence of nail fungus, it is recommended:
- strictly follow all the doctor's orders;
- disinfect individual tools for manicure and pedicure;
- dispose of shoes, socks and / or gloves that have come into contact with affected nails and cannot be disinfected; other footwear should be disinfected (40% formalin solution is used for this), ventilated and washed with laundry soap.
YouTube video related to the article:

Anna Aksenova Medical journalist About the author
Education: 2004-2007 "First Kiev Medical College" specialty "Laboratory Diagnostics".
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!