- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Tooth granuloma

Tooth granuloma is an inflammation of the tissues in the area of the tooth root, which is a small purulent node with a diameter of 5-8 mm. This focus of infection, despite its small size, can cause complications that go beyond dentistry:
- Tooth cyst;
- Formation of a sinus tract;
- Inflammation of the gums;
- Phlegmon;
- Sinusitis;
- Jaw osteomyelitis;
- Pyelonephritis;
- Infectious myocarditis;
- Disruption of the kidneys, heart and other vital organs;
- General blood poisoning.
Such consequences can occur if the treatment of tooth granulomas was not carried out in the initial stage of the disease, and the gum tissue has grown deep into the purulent sac.
Causes and symptoms of tooth granuloma
The appearance and development of tooth granulomas can be caused by a number of reasons:
- Injuries - damage to the jaw and soft tissues;
- Dental diseases - periodontitis, pericoronitis, pulpitis;
- Negligence of doctors - incorrect treatment or removal of nerves, the use of non-sterile instruments.
The following adverse factors can provoke acute clinical manifestations of tooth root granulomas:
- Decreased immunity;
- Hypothermia;
- Cold;
- A sharp change in climatic conditions;
- Excessive physical activity;
- Mental stress;
- Psycho-emotional shock.
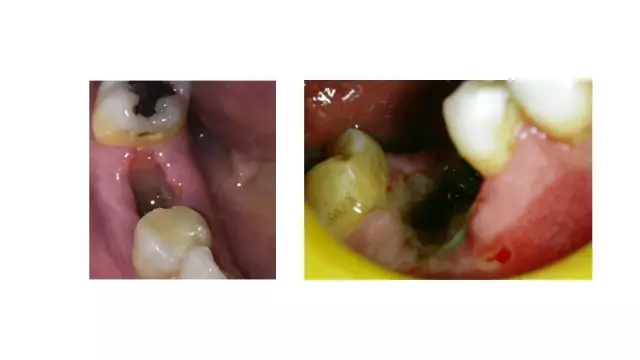
Tooth granuloma is a localized inflammatory formation with thin walls. Granulation tissue grows intensively because it replaces cells that die during the inflammatory process. The existence of a granuloma can go unnoticed until it reaches a significant size.
Sometimes the disease is detected only with the help of an orthopantomogram or X-ray of the tooth when visiting the dentist for other reasons, since signs of tooth root granuloma may be absent. This is dangerous because the chronic asymptomatic course of the disease can lead to a jaw cyst. In this case, necrotic masses and dead bacteria accumulate inside a dense capsule, which is formed when the tooth granuloma is delimited from the surrounding tissues.

In the initial stage of inflammation, minor manifestations are likely in the form of swelling and redness of the gums, darkening of the tooth and pain. Subsequently, with the growth of the nodule, the body temperature rises and the toothache increases. Pus begins to stand out from the infectious focus. Suppuration is usually accompanied by odontogenic periostitis (gumboil).
Prevention and treatment of tooth granulomas
Depending on the size of the inflamed node, the condition of the surrounding tissues and the presence of complications, the tooth granuloma is treated with various methods:
- Conservative. The granuloma cavity is filled with filling material, which is introduced through the root canal. The infection is cleared up with antibiotics;
- Surgical. Root apex resection, tooth hemisection or extraction are performed. If a concomitant peri-maxillary abscess develops, then it is opened and drained.
Preservation of a tooth is impossible if the granuloma is accompanied by such complications as a vertical crack and multiple root perforations, root canal obstruction, as well as severe tooth decay, in which it cannot be restored.
Preventive measures consist primarily of maintaining oral hygiene and regular visits to the dental office. It is necessary to consult a doctor at the first symptoms of a tooth granuloma or other diseases of the dentoalveolar system that can cause it.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!