- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Intestinal intussusception
The content of the article:
- Causes and risk factors
- Forms of the disease
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Possible complications and consequences
- Forecast
- Prevention
Intestinal intussusception (intussusception intestinal obstruction) is one of the types of intestinal obstruction, in which one part of the intestine is inserted into the lumen of another. The disease occurs predominantly in infants and is one of the most common causes of intestinal obstruction in this age group, but also affects adults.
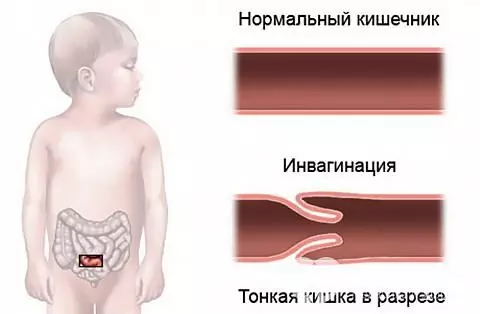
Schematic representation of intestinal intussusception
Causes and risk factors
The most common causes of intestinal intussusception in adults are neoplasms, polyps, cicatricial narrowing of the intestines, and infectious diseases.
The causes of the disease in children in the first years of life are not fully understood. Risk factors include:
- cystic fibrosis;
- complementary foods containing fruit or vegetable components;
- changes in diet;
- food that is rough or too thick;
- inflammatory processes in the mucous membrane of the stomach and (or) intestines.
Forms of the disease
Depending on the localization of the pathological process, intestinal intussusception is of the following forms:
- small bowel;
- colonic;
- small intestinal;
- thin cecum;
- thin-thick-cecal.
On the etiological basis, there are primary and secondary forms of the disease. In addition, depending on the direction of the pathological process, intestinal intussusception is divided into isoperistaltic (descending) and antiperistaltic (ascending), and by the number of invaginates - into single and multiple.
Symptoms
Intestinal intussusception in children of the first year of life often manifests itself as cramping abdominal pains that occur every 10-20 minutes. At a later age, the pain is permanent. Due to hemorrhages in the mucous membrane, blood is found in the stool. Sometimes the stool takes on the appearance of "raspberry jelly". Palpation reveals a movable painful formation, which changes its shape and localization depending on the timing of the disease. Body temperature, as a rule, remains within the normal range. In severe cases, pronounced signs of intoxication appear.

In children of the first year of life, intussusception of the intestine is manifested by cramping pain in the abdomen
In addition, intussusception may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- vomiting;
- sinking of the abdomen;
- defecation disorders;
- prolapse of the invaginate through the anus;
- relaxation of the sphincter of the anus.
Diagnostics
To diagnose intussusception, anamnesis, physical examination, and instrumental examinations such as ultrasound, computed tomography and radiography of the abdominal organs are performed. To accurately determine the site of intussusception, a radiopaque study with barium is performed.
Treatment
Treatment of intussusception should be started immediately after the first clinical manifestations of the disease. The choice of the method of therapy depends on the form of the disease, as well as on the individual characteristics of the patient's body.
With intussusception of the intestine in children, an effective method of conservative treatment is cleansing enemas with saline, barium or air. This method is not used for inflammatory processes, perforation, sepsis. In adult patients, conservative therapy rarely has a positive effect.

With intussusception of the intestine in children, cleansing enemas with air, barium, saline are effective
The indications for surgical intervention for intestinal intussusception in children may be:
- lack of a positive effect from conservative treatment;
- damage to the intestinal wall, ingestion of feces into the abdominal cavity;
- serious condition of the patient;
- intestinal necrosis; and etc.
Surgical intervention is performed by the method of laparotomy followed by manual disinvagination. If disinvagination is not feasible or is not indicated, resection is performed within healthy tissues with the imposition of an interintestinal anastomosis. When a large section of the intestine is removed or when an infectious process is attached, an ileostomy is indicated. After the operation, it is necessary to maintain hygiene in the suture area in order to prevent infection of the postoperative wound. In some cases, intestinal intussusception may recur, then the operation is repeated.
Possible complications and consequences
In severe cases of the disease, peritonitis, internal hernias and adhesions develop, which can lead to life-threatening conditions. If untreated, there is a risk of intestinal obstruction and generalization of infection, which in some cases leads to death.
Forecast
With timely diagnosis and adequate treatment, the prognosis is favorable.
Prevention
In order to prevent intestinal intussusception, it is recommended:
- timely treatment of helminthic invasions;
- regular medical examination of the child;
- adequate nutritious food;
- timely treatment of intestinal infections.
YouTube video related to the article:

Anna Aksenova Medical journalist About the author
Education: 2004-2007 "First Kiev Medical College" specialty "Laboratory Diagnostics".
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!






