- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Granular pharyngitis
The content of the article:
- Causes and risk factors
- Forms of the disease
- Granular pharyngitis symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment of granular pharyngitis
- Possible complications and consequences
- Forecast
- Prevention
Pharyngitis is an inflammation of the pharyngeal mucosa, usually of infectious origin. In this case, tissues of the soft palate and lymph nodes can also be involved in the pathological process. Often combined with tonsillitis - inflammation of the tonsils.
Granular pharyngitis is a form of chronic hypertrophic pharyngitis, which is characterized by the formation of small nodules (granules) on the back of the pharynx, consisting of lymphoid tissue, dead cells, and leukocytes.

Granular pharyngitis is a form of chronic hypertrophic pharyngitis
Causes and risk factors
Granular pharyngitis is a variant of the course of chronic pharyngitis, which develops in the absence of adequate treatment for the acute form. An important role in the occurrence of this disease is played by a genetic predisposition: granulosa pharyngitis is often diagnosed in members of the same family. This disease is a polyetiological one - for its development it is necessary to combine several causal factors at once, one of which is a hereditary predisposition, and the other (others) - endogenous (for example, diseases) or exogenous (for example, work in a hazardous production) traumatic factors.
Risk factors for developing pharyngitis are:
- chronic infectious processes in the upper respiratory tract, especially chronic rhinitis;
- Difficulty nasal breathing (with polyps, adenoids, mouth breathing, etc.);
- constant irritation of the pharyngeal mucosa (including antihypertensive drugs, food irritants, alcoholic beverages, tobacco smoke);
- injuries to the nasal septum;
- dental caries;
- throwing the contents of the stomach into the pharynx through the esophagus (with gastroesophageal reflux disease, hiatal hernia);
- diseases of the internal organs;
- metabolic disorders;
- decreased immunity;
- tendency to allergic reactions;
- industrial hazards;
- exposure to negative environmental factors (too dry and / or polluted, dusty air).
Forms of the disease
Pharyngitis is divided into acute and chronic. In acute pharyngitis, the inflammatory process is usually observed in all parts of the pharynx. In the case of chronic pharyngitis, there is a clearer localization of lesions - in the lower, middle or upper part of the pharynx.
Depending on the etiological factor, acute pharyngitis is subdivided into infectious (bacterial, viral, mycotic), traumatic, allergic, and acute pharyngitis caused by exposure to irritating factors.

Symptoms of acute pharyngitis
Chronic pharyngitis is catarrhal (simple), atrophic (when the affected tissues atrophy, that is, decrease) and hypertrophic (when the affected tissues are hypertrophied, that is, increase). Granular pharyngitis is a variant of a hypertrophic inflammatory process in the pharynx.
Granular pharyngitis symptoms
Symptoms of granular pharyngitis:
- persistent or frequent feeling of perspiration, soreness, tickling, dry throat;
- a feeling of a foreign body in the throat or a lump in the throat (does not interfere with food intake, but makes you want to cough up and / or make frequent swallowing movements);
- slight pain when swallowing, especially solid food;
- dry cough, often in the form of obsessive coughing, constant need to cough up;
- rapid fatigue of the voice.
On examination, patients have a thickening and swelling of the uvula and soft palate. The back wall of the pharynx is edematous, the blood and lymphatic vessels are dilated, creating a specific branched pattern, the mucous membrane is hyperemic, and red lymphoid formations (granules) are visible on it. A large amount of viscous mucous or mucopurulent secretion accumulates in the pharynx. Due to the need to constantly cough up or swallow accumulated mucus, patients become irritable, among other things, it disrupts sleep and can lead to persistent headaches, a decrease in overall well-being. Coughing up copious mucous secretions can cause nausea and sometimes vomiting.

Pharyngitis granulosa is characterized by slight tenderness when swallowing
Body temperature usually remains within normal limits. In some cases, patients complain of ear popping, which is noted during swallowing and disappears after several swallowing movements.
Diagnostics
For the diagnosis of pharyngitis granulosa, complaints and anamnesis are collected, an objective examination of the patient, and pharyngoscopic examination. To clarify the diagnosis, it may be necessary to conduct a bacteriological or virological laboratory study of a throat swab.
Differential diagnosis with acute tonsillitis is required.
Treatment of granular pharyngitis
Treatment of granular pharyngitis is aimed, first of all, at eliminating the factors that caused the development of the disease, as well as relieving inflammation, getting rid of granules and preventing further tissue proliferation.
In order to fight the infection, local (more often) and / or systemic (the need for them arises much less often) anti-infectious drugs are used, the choice of which depends on the type of infectious agent (antibacterial, antiviral, antimycotic drugs). Fortifying agents, immunomodulators, vitamin complexes (especially vitamins A, E, group B) are prescribed.
The granules are removed by cauterization. For this purpose, solutions of chemicals are used (iodine-containing drugs, trichloroacetic acid, silver nitrate). In the presence of large granules, liquid nitrogen is used (cryocoagulation method), as well as the minimally invasive method of laser coblation and radio wave suppression of the posterior pharyngeal wall.

As part of the complex treatment of granular pharyngitis, fortifying agents and vitamin complexes are used
To relieve puffiness, local astringents are prescribed (they are lubricated or irrigated with the back wall of the pharynx). Moisturizers are applied to the affected areas of the mucous membrane to relieve soreness.
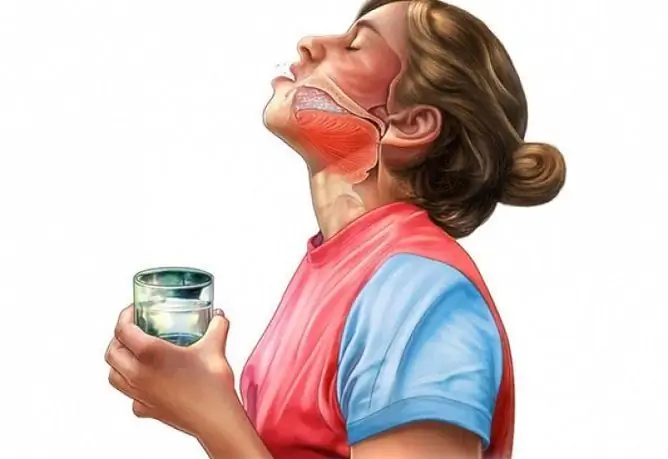
Gargling with warm solutions of sodium chloride, antiseptic drugs is prescribed, which helps to cleanse the mucous membrane of pathogenic microorganisms and secretions accumulated on the mucous membrane. It is effective to use medicinal herbs (chamomile, sage, linden, calendula), essential oils (lavender, eucalyptus, thuja oil), honey, propolis for this purpose. Inhalations with mucolytic agents that soften the mucous membrane, as well as drugs with an anti-inflammatory effect, mineral water, essential oils, and herbal infusions are recommended.
Physiotherapeutic procedures are effective - electrophoresis, laser therapy.
One of the conditions for the effectiveness of treatment is diet. You should avoid eating too hot or cold, fried, spicy, salty foods, carbonated and sour drinks, alcohol, foods that irritate the mucous membrane of the pharynx. Smoking cessation is also necessary. To liquefy and remove mucus from the pharynx, an abundant drinking regimen is indicated.
Possible complications and consequences
Granules formed with granular pharyngitis, if untreated, can grow significantly, causing constant accumulation of mucus, difficulty eating, voice changes and other manifestations that reduce the quality of life.
Forecast
With timely and adequate treatment, the prognosis is favorable.
Prevention
To prevent the development of granular pharyngitis, it is recommended:
- timely treatment of pathologies that contribute to the onset of the disease;
- hardening;
- regular walks in the fresh air;
- regular physical activity;
- correction of the microclimate in rooms where a lot of time is spent (in particular, the humidity indicator);
- rejection of bad habits;
- rational nutrition, and other measures to strengthen the body.
YouTube video related to the article:

Anna Aksenova Medical journalist About the author
Education: 2004-2007 "First Kiev Medical College" specialty "Laboratory Diagnostics".
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!