- Author Rachel Wainwright wainwright@abchealthonline.com.
- Public 2023-12-15 07:39.
- Last modified 2025-11-02 20:14.
Gonorrhea in women
Gonorrhea is an infectious disease in which the pathogen is transmitted sexually (STIs - sexually transmitted infections). Gonorrhea in women has certain characteristics of the course associated with the characteristics of the female reproductive system. Gonorrhea in women is dangerous because, if untreated and the process becomes chronic, it can lead to infertility.
The cause of gonorrhea in women
The cause of gonorrhea in women is in the overwhelming majority of cases unprotected sexual contact with a carrier of the infection. In rare cases, it is possible for a woman to become infected with gonorrhea in a household way, usually when using towels or washcloths shared with the carrier of the pathogen. Younger girls (2-6 years old) are most often infected with gonorrhea in the household, and in the vast majority of cases, the source of infection is an infected mother.
The causative agent of gonorrhea is gonococcus. Gonococci are a type of bacteria that are sensitive to drying, antiseptics, high temperature processing (death occurs at temperatures exceeding 55 ° C), as well as under the influence of direct sunlight. Gonococcus is a highly contagious microorganism. This means that the chances of a woman contracting gonorrhea through direct contact with the pathogen are very high, the probability is about 70%.
Symptoms of gonorrhea in women
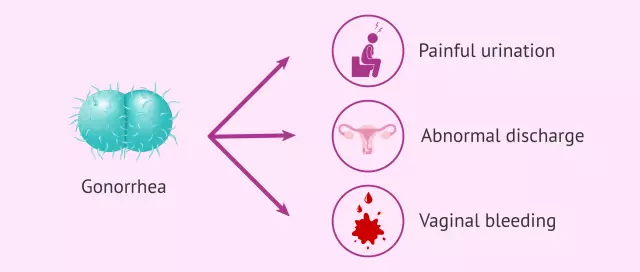
The insidiousness of this disease is that the early symptoms of gonorrhea in women are usually absent. This is the main difference between gonorrhea in women and gonorrhea in men, since due to the erased clinical picture, gonorrhea in women often spreads to the internal organs of the genitourinary system and acquires a chronic course.
Signs of gonorrhea in women in the initial stage of the acute form, with damage to the lower genital tract (labia, vagina, cervical canal, urethra), are not expressed. You may feel a slight burning sensation when urinating, itching in the vagina, and a white thick discharge. If treatment is not undertaken at this stage, the gonococci along the genitourinary tract spread further and affect the upper part of the genitourinary system, usually these are the fallopian tubes and paraurethral glands. In this case, the symptoms of gonorrhea in women are more pronounced. These are lower abdominal pain, fever, a sharp deterioration in general condition, frequent painful urination, and menstrual irregularities.
With the transition of the inflammatory process into a chronic one, the signs of gonorrhea in women are again erased. In this case, the leading symptoms of gonorrhea in women are menstrual irregularities and infertility.
In addition, in some cases, any signs of gonorrhea in women may be absent, and the disease will proceed in a latent form until it is detected either by building a chain from an infected partner, or by examination for another reason.
It should be noted that the gonococcus affects the epithelium mainly at the site of infection. Therefore, if sexual contact with the carrier of the infection was carried out by the oral or anal method, then the signs of gonorrhea in women will appear in the form of gonorrheal stomatitis, tonsillitis, pharyngitis, or gonorrheal paraproctitis.
Diagnosis of gonorrhea in women
Gonorrhea in women is detected by bacteriological examination of the contents of the vagina. The diagnostic sign is the detection of a gonococcus in a smear. Doctors note that in recent years, isolated gonococcus almost never occurs, but polyinfection occurs when other STIs are present along with gonococcus.
Treatment of gonorrhea in women

Treatment of gonorrhea in women, however, like gonorrhea in men, should be started immediately after the diagnosis is confirmed. The later treatment of gonorrhea in women is started, the more likely it is to develop irreversible changes in the uterine appendages as a result of a chronic inflammatory process.
The main treatment for gonorrhea in women is antibiotic therapy. The latest generation antibiotics are used that can affect the gram-negative flora, which includes the gonococcus. It must be borne in mind that gonococcus can be resistant to antibiotics, and also that the treatment of gonorrhea in women at different stages requires different dosages, so self-medication is unacceptable.
The use of antibiotics leads to dysbiosis, both of the intestine and the vagina, therefore, the treatment of gonorrhea in women is completed with the intake of drugs that help restore microflora. An important condition for the treatment of gonorrhea in women is the rejection of alcohol and sexual intercourse. The therapy is carried out under bacteriological control. Gonorrhea in a woman is considered cured only when a control bacteriological study shows the absence of gonococci in smears or scrapings.
Consequences of gonorrhea in women
As already mentioned, chronic gonorrhea in women can cause adhesions in the uterine appendages, which is the reason for their obstruction, and subsequently infertility. Since the uterus is also involved in the process, even with the onset of pregnancy, the risk of miscarriage is very high. In most cases, pregnancies in women with gonorrhea end in miscarriage or premature birth. A child, passing through the birth canal of a woman with gonorrhea, is in direct contact with the pathogen, which results in gonorrheal blepharitis and conjunctivitis of newborns.
YouTube video related to the article:
The information is generalized and provided for informational purposes only. At the first sign of illness, see your doctor. Self-medication is hazardous to health!